Nature of Light PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title: Nature of Light
1
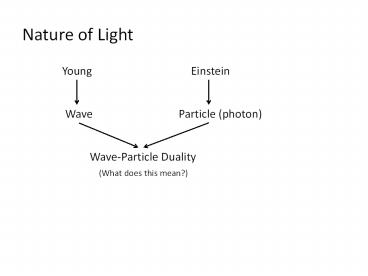
Nature of Light
Young
Einstein
Particle (photon)
Wave
Wave-Particle Duality
(What does this mean?)
2
Rutherfords Gold Foil Experiment
Ernest Rutherford (1871 1937)
One day Geiger came to and said, Dont you think
that young Marsden, whom I am training in
radioactive methods, ought to begin a small
research? Now I had thought that too, so I
said, Why not let him see if any alpha particles
can be scattered through a large angle? I
may tell you in confidence that I did not believe
that there would be, since we knew the alpha
particle was a very fast massive particle, with a
great deal of energy, and you could show that if
the scattering was due to the accumulated effect
of a number of small scatterings the chance of an
alpha particle being scattered backward was very
small.
3
Then I remember two or three days later Geiger
coming to me in great excitement and saying, We
have been able to get some of the alpha particles
coming backwards It was quite the
most incredible event that has ever happened to
me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if
you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue
paper and it cam back and hit you.
http//waowen.screaming.net/revision/nuclear/rsani
m.htm
4
Atomic Spectra
Hydrogen
Helium
Neon
Mercury
5
The Hydrogen Spectrum
Johann Jakob Balmer (1825 - 1898)
6
Johannes Rydberg (1854 1919)
WalterRitz (1878 1909)
Ritz Combination Principle
The sum of the frequencies of two spectral lines
equals the frequency of a third.
7
The Complete Hydrogen Spectrum
Lyman Lines
Balmer Lines
Paschen Lines
8
Energy Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom
9
Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
Neils Bohr (1885 1962)
10
Matter Waves
Louis de Broglie (1892 1987)
l h/p
11
Electron Diffraction Observed in 1927
Crystalline Nickel as an Electron Target
L. H. Germer
C. J. Davisson
studying electron scattering from a nickel
target at Bell Laboratories. After heating the
target to remove an oxide coating that had
accumulated during an accidental break in the
vacuum system, they found that the
scattered-electron intensity as a function of
the scattering angle showed maxima and minima.
Their target had crystallized, and by accident
they had observed electron diffraction.
Physics by Paul A. Tipler
12
Electron as Orbiting Wave
Constructive Interference
Destructive Interference
(Standing Wave)
http//www.youtube.com/watch?v_S7-PDF6Vzc
13
Quantized Orbits Due To Standing Wave Req.
14
Now What?
The wave function contains all possible informatio
n about a system, so instead of speaking of the
state described by the wave function Y, we
simply say the state Y.
Quantum Chemistry by Ira N. Levine
Erwin Schrodinger (1887 1961)
15
What is the Wave Function?
Quantum mechanics does not say that an electron
is distributed over a large region of space as a
wave is distributed. Rather, it is the
probability patterns (wave functions) used to
describe the electrons motion that behave like
waves and satisfy a wave equation.
Quantum Chemistry by Ira N. Levine
Max Born (1882 1970)