Cell%20Cycle - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Cell%20Cycle
Description:
Cell Cycle Cells are the basic unit of life. Just like you and me, as they get older they grow bigger. This triggers the cell to divide. First, let s talk about the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:185
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell%20Cycle
1
Cell Cycle
2
- Cells are the basic unit of life.
- Just like you and me, as they get older they grow
bigger. This triggers the cell to divide. - First, lets talk about the stages of the cell
cycle
3
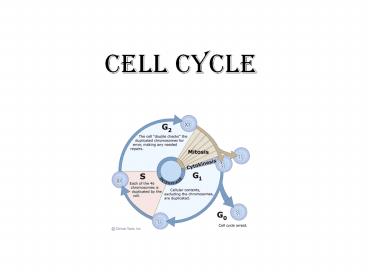
G1 Phase
- Or the Growth 1 Phase is the first event in the
life cycle of a cell.
4
G1 Phase
- During this phase
- the cell is metabolically active with chemical
reactions mostly in the cytoplasm - Cellular respiration (makes ATP)
- Produces protein
- At the end organelles are duplicated
5
S Phase
- Or the Synthesis phase.
- Synthesisto put parts together to equal a whole.
- During this phase
- DNA is replicated in the nucleus
6
G2 Phase
- Or Growth 2 Phase is a second period of growth
after the DNA has been replicated. - (SO the cell has TWICE the amount of genetic
material it needs) - During this phase
- Cell resumes making proteins and other molecules
7
Interphase
- Interphase G1,S,G2
- Cells spend most of their life in interphase
- During Interphase
- The cell appears normal
- Nucleus is visible
- DNA is loosely organized (bowl of spaghetti)
- This is called Chromatin
8
M phase
- Or Mitosis Phase
- During Mitosis
- The nucleus divides in a series of steps to form
two nuclei - The nuclei, duplicated organelles and cytoplasm
are separated in cytokinesis.
9
Stages of Mitosis
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
10
Prophase
- The FIRST step in Mitosis.
- During Prophase
- DNA condenses to form chromosomes
- To make a chromosome the DNA is wrapped around
proteins called histones - Chromosome looks like a X
11
Prophase
- Chromosomes
- Each half of the X is called a chromatid.
- These chromatids are held together in the center
of the X in a region called the centromere.
12
Prophase
- Microfiliments in the cytoskeleton begin to break
down - In animals, Centrioles move to the opposite sides
of the cell and form spindle fibers toward the
center of the cell - In plants, spindle fibers form at the opposite
ends of the cell in regions called asters
13
Prophase
- By the end of prophase, the nuclear membrane has
been broken down and the nucleolus disappears. - This is the longest phase of Mitosis
14
Metaphase
- The second phase of mitosis
- During Metaphase
- Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres on each
chromosome - Chromosomes are lined up down the middle of cell.
15
Anaphase
- The third phase of mitosis
- During Anaphase
- The chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere
by spindle fibers - Spindle fibers pull the chromatids to opposite
sides of the cell
16
Telophase
- The last phase in mitosis
- During Telophase
- Chromatids arrive at the opposite poles of the
cell - The nuclear membrane forms around each new set of
chromosomes - DNA uncoils and the nucleoli reappear
17
Telophase
- Once the nuclear membrane completely forms, the
new nuclei appear - Each nuclei contains a complete set of
chromosomes identical to the parent cell - Microfiliments reform the cytoskelton and move
the duplicated organelles to opposite sides
18
Just Remember
- ProphaseMetaphaseAnaphaseTelophase
19
Cytokinesis
- The division of the cytoplasm
- In animals, the cytoplasm pinches in from the top
form the cleavage furrow - The cleavage furrow continues to constrict
towards the center until pinching off the two
cells.
20
Cytokinesis
- In plants, a cell plate forms in the middle of
the cell which turns into the new cell wall.
21
Controlled Cell Growth
- Cell growth and division is controlled by
internal and external factors - These can tell a cell to divide or to continue to
grow - Example Human growth hormone which tells bone
cells to grow and divide
22
Uncontrolled Cell Growth
- If uncontrolled by internal or external factors
cells will divide continuously. - Example Cancer
- Causes cells to form masses called tumors
- Malignancy is when a cancer cell breaks away and
forms a new mass
23
Uncontrolled Cell Growth
- Cancer cells use up nutrients and oxygen and do
not provide any function for the organism - The tumor can add stress to surrounding cells
24
Causes of Cancer
- A carcinogen is something that causes cancer.
- Causes a mutation in the genetic material (DNA)
which can prevent the cell from responding to
external and internal signals. - Examples smoking, exposure to excessive
radiation from the Sun, pollution, and some
viruses.