Animal Reproduction PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
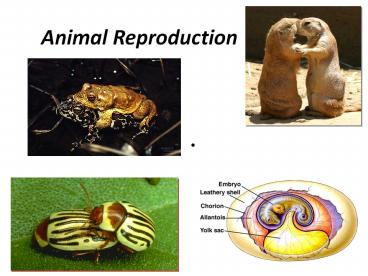
Title: Animal Reproduction
1
Animal Reproduction
2
Overview
- Asexual (one parent) no variation
- fission (parent separation)
- budding (corals)
- gemmules (porifera)
- fragmentation regeneration (inverts)
- Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) variation
- gametes (sex cells)
- zygote (fertilized egg)
- ovum (unfertilized egg)
- spermatozoon (male gamete)
3
Mechanisms of sexual reproduction
- Fertilization (union of sperm and
egg) external (usually aquatic
animals) internal (usually terrestrial animals)
4
Mammalian Reproduction, I
The Human Male A Bladder urine storage B -
Vas deferens tube through which sperm is
carried C Penis semen delivery D Testes
male gonads E Scrotum spermatogenesis,
needs to occur outside of the human body at a
cooler temperature F Epididymis sperm
reservoir sperm development G - Urethra tube
through which semen urine are carried J -
Prostrate gland anticoagulant nutrients fluid
added to semen K - Seminal vesicle secretes
mucous which forms semen
5
Mammalian reproduction, II
- The Human Female
- A - Oviduct (fallopian tube)
- fertilization
- B - Ovary
- female gonads
- C - Uterus
- womb/lining
- D - Bladder
- urine storage
- F - Cervix
- allow flow of menstrual blood from
- the uterus into the vagina, and direct
- the sperms into the uterus
- H - Vagina
- sperm receptacle
6
Spermatogenesis
- Epididymous location
- Spermatogonium (2N) sperm precursor
- Repeated mitosis into.
- Primary spermatocyte (2N)
- 1st meiotic division
- Secondary spermatocyte (1N)
- 2nd meiotic division
- Spermatids (1N)
- Sperm cells (1N)
7
Oogenesis
- As embryo until menopause...
- Ovaries
- Oogonium (2N)
- Primary oocyte (2N)
- Between birth puberty prophase I of meiosis
- Puberty FSH completes meiosis I
- Secondary oocyte (1N) polar body
- Meiosis II stimulated by fertilization
- Ovum (1N) 2nd polar body
8
FERTILIZATION
Begins with 46 pair of chromosomes, splits off to
23 then combine for a unique new 46 pair. Occurs
in outer 1/3 of fallopian tube Mucous strands in
cervix guide sperm into uterus Ovum attracts
sperm with special peptides
9
Embryonic fetal development
A - Amniotic sac B - Amniotic fluid X -
Placenta Y - Fetus Z - Umbilical cord
10
Amniotic Fluid
- Protects Fetus
- Encased in and amniotic sac
- Controls Temperature
- Supports Symmetrical Growth Prevents Adherence to
amnion - Allows Movement
- Source of oral fluid
- Acts as a excretion-collection
- repository
11
Umbilical Cord
- Connecting link between fetus and placenta.
- Transports oxygen and nutrients to fetus
- from the placenta and returns waste products from
the fetus to the placenta. - Contains 2 arteries and 1 vein
- supported by mucoid material (whartons jelly) to
prevent kinking and knotting. - Contains NO pain receptors.
12
Placenta
- primary role - ensure that oxygen is moved into
babys blood stream and carbon dioxide is carried
away from baby - also cleaning out other waste which is produced
by baby - -it also plays a role in ensuring that some
nutrients are received.
- Sieve/filter allows smaller particles through
and holds back larger molecules. Passage of
materials in either direction is effected by - ?Diffusion gases, water, electrolytes
- ?Facilitated transfer glucose, amino acids,
minerals. - ?Pinocytosis movement of minute particle
- Mother transmits immunoglobulin G (IgG) to fetus
providing limited passive immunity. - Leakage caused by membrane
- defect may allow maternal and fetal blood mixing.
13
Embryonic fetal development
Gestation pregnancy -3 trimesters approx. 266
days (38-40 WEEKS)
Trimesters 1st weeks 1-13 2nd weeks 14
26 3rd weeks 27 and on
14
First Trimester
weeks 1-13
Month 1
At the end of the first month Baby is 1/4
inch in length Heart, digestive system,
backbone and spinal cord begin to form
Placenta (sometimes called "afterbirth") begins
to develop The single fertilized egg is now
10,000 times larger than size at conception
15
Month 2
At the end of 8 weeks Baby is 1-1/8 ? Heart
is functioning ? Eyes, nose, lips, tongue,
inches long ears and teeth are forming Baby
is moving, although the mother can not yet feel
movement
16
Month 3
First Trimester At the end of 12 weeks Baby is
2 ½ to 3 inches long Weight is about ½ to 1
ounce Baby develops recognizable form Nails
start to develop and earlobes are formed Arms,
hands, fingers, legs, feet and toes are fully
formed Eyes are almost fully developed Baby has
developed most of his/ her organs and tissues
Baby's heart rate can be heard at10 weeks with a
special instrument called a Doppler
17
Human fetal development
4 weeks
7 weeks
12 weeks
18
Second Trimester
weeks 14 26
Month 4 Baby is 6 ½ to 7 inches long Weight is
about 6 to 7 ounces Baby is developing reflexes,
such as sucking and swallowing and may begin
sucking his/her thumb Tooth buds are developing
Sweat glands are forming on palms and soles
Fingers and toes are well defined Sex is
identifiable Skin is bright pink, transparent
and covered with soft, downy hair Although
recognizably human in appearance, the baby would
not be able to survive outside the mother's body
19
Month 5
Baby is 8 to 10 inches long Weight is about 1
pound Hair begins to grow on babys head Soft
woolly hair called lanugo will cover its body.
Some remains until a week after birth, when it is
shed Mother begins to feel fetal
movement Internal organs are maturing Eyebrows,
eyelids and eyelashes appear
20
Human fetal development
- The fetus just spends much of the 2nd 3rd
trimesters just growing - and doing various flip-turns kicks inside
amniotic fluid
Week 20
21
- 6 months - 24 weeks
Baby is 11-14 inches long Weight is about 1 ¾ to
2 pounds Eyelids begin to part and eyes open
sometimes for short periods of time Skin is
covered by a waxy coating called vernix Baby is
able to hiccup
22
Third Trimester
- weeks 27 and on
Fetus grows rapidly and is very
active. Terminates with parturition ( BIRTH)
30 weeks (7.5 months)
23
Getting crowded in there!!
- 32 weeks (8 months)
The fetus sleeps 90-95 of the day sometimes
experiences REM sleep, an indication of dreaming