Modifying Theorem 2 PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Modifying Theorem 2
1
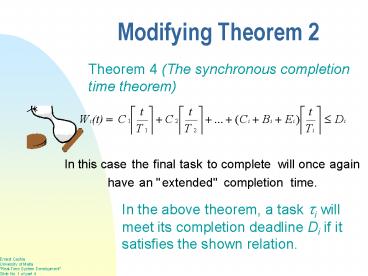
Modifying Theorem 2
Theorem 4 (The synchronous completion time
theorem)
In the above theorem, a task ?i will meet its
completion deadline Di if it satisfies the shown
relation.
2
One Final Example(Taken from Software
Engineering Fundamentals by A. Behforooz)
- Consider the following 3 dependent and periodic
tasks - Task 1 C30 T100 D100 E0 B0
- Task 2 C70 T200 D200 E0 B30
- Task 3 C30 T200 D150 E50 B6
- Using theorem 3 ?1 30/100 0.3 ? schedulable
- ?1,?2 (30/100)(7030)/200 0.8 ? schedulable
- ?1,?2,?3 (30/100)(70/200)(30506)/200 1.08
? NOT schedulable - Using theorem 4 W3(t)t03070306 136 ms
- N1,1 1?(136-100)/100? 2
- ? t1 136(2-1)30 166 ms (beyond ?3 deadline)
- Changing task priority from (1-2-3) to (1-3-2)
results in - W3(t)t030307030 166 ms
3
Priority Inversion
- Meaning A lower priority task executing before
one with a higher priority
4
Timeline of previous slide
5
Expanded Portion of Previous Timeline
6
Modified and Augmented Portion from Previous Slide
?1 queued
?1 queued
7
A Solution to Priority Inversion
- Use of Priority Ceiling Protocol (PCP) which is
made up of 3 rules - Pre-emption rule
- Regular priority pre-emption
- Inheritance rule
- If a lower priority task blocks a higher
priority one, the lower inherits the priority of
the higher priority task - Priority ceiling rule
- A task cannot get at a shared resource if its
priority is less than any of the ceilings of the
shared resources currently locked by other tasks
8
Bad PCP usage Example
Assume tasks A, B, C, and D have priorities as A
highest and D lowest. The tasks use 2 server
tasks as follows S1 used by A and C S2 used by
tasks B and D.
9
McCabes R-T System Analysis
- Uses a modified interpretation of standard DFDs
- Transform ? Markov process state (a probabilistic
queuing model) - Data flow ? Transitions
- Therefore the following reasoning may be
applied - 0 lt pij 1.0
- (p transitional probability)
- True for each flow path
10
Example of McCabes R-T System Analysis
- Due to the lengthiness of this example it was
thought better to hand it out as an MS-Word97
document. Therefore, it is available online and
in hard-copy form separately. Please refer to it
while it is explained during lecture sessions.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.