Cell Membranes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
Cell Membranes
Description:
... in both directions volume of cell doesn t change balanced Division Ave High School Ms. Foglia Regents Biology Regents Biology Regents Biology ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:192
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Membranes
1
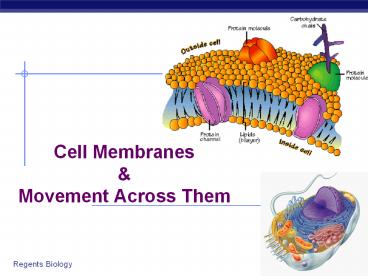
Cell Membranes Movement Across Them
2
Cell (plasma) membrane
- separate cell from its environment
- cell membrane is the boundary
IN food sugars proteins fats salts O2 H2O
OUT waste ammonia salts CO2 H2O products
cell needs materials in products or waste out
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
Building a membrane
- How do you build a barrier that keeps the watery
contents of the cell separate from the watery
environment?
What substance do you know that doesnt mix with
water?
- ? FATS ?
- ? LIPIDS ?
- oil water dont mix!!
7
Lipids of cell membrane
- Membrane is made of phospholipids
- phospholipid bilayer
phosphate
attracted to water
lipid
repelled by water
8
Semi-permeable membrane
- Need to allow passage through the membrane
- But need to control what gets in or out
- membrane needs to be semi-permeable
So what needs to get across the membrane?
aa
H2O
sugar
lipid
salt
NH3
So how do you build a semi-permeable membrane?
9
Phospholipid bilayer
- What molecules can get through directly?
- small molecules
fats other lipids can slip directly through the
phospholipid cell membrane, but what about
other stuff?
lipid
salt
waste
aa
H2O
sugar
10
Permeable cell membrane
- Need to allow more material through
- membrane needs to be permeable to
- all materials a cell needs to bring in
- all waste a cell needs excrete out
- all products a cell needs to export out
inside cell
lipid
sugar
aa
H2O
holes, or channels, in cell membrane allow
material in out
salt
waste
outside cell
11
Semi-permeable cell membrane
- But the cell still needs control
- membrane needs to be semi-permeable
- specific channels allow specific material in
out
inside cell
sugar
aa
H2O
salt
waste
outside cell
12
How do you build a semi-permeable cell membrane?
- channels are made of proteins
- proteins both like water like lipids
bi-lipid membrane
protein channelsin bi-lipid membrane
13
Protein channels
- Proteins act as doors in the membrane
- channels to move specific molecules through cell
membrane
14
- Most cell membranes are composed principally of
- DNA and ATP
- proteins and lipids
- chitin and starch
- nucleotides and amino acids
15
- Most cell membranes are composed principally of
- DNA and ATP
- proteins and lipids
- chitin and starch
- nucleotides and amino acids
16
Movement through the channel
- Why do molecules move through membrane if you
give them a channel?
?
?
17
Molecules move from high to low
- Diffusion
- move from HIGH to LOW concentration
18
Diffusion
- Move from HIGH to LOW concentration
- passive transport
- no energy needed
19
(No Transcript)
20
Simple Diffusion
- Move from HIGH to LOW
fat
fat
fat
Which way will fat move?
inside cell
fat
fat
fat
fat
outside cell
fat
fat
fat
fat
fat
fat
fat
21
(No Transcript)
22
Diffusion through a channel
- Move from HIGH to LOW
sugar
sugar
sugar
sugar
inside cell
sugar
sugar
low
Which way will sugar move?
?
high
outside cell
sugar
sugar
sugar
sugar
sugar
sugar
sugar
23
Diffusion
- Move from HIGH to LOW concentration
- through membrane
- simple diffusion
- no energy needed
- through a protein channel
- facilitated diffusion (with help)
- no energy needed
high
low
24
(No Transcript)
25
Active transport
- Cells may need molecules to move against
concentration difference - need to pump uphill
- from LOW to HIGH using ATP
- protein pump
- requires energy
- ATP
ATP
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
Transport summary
diffusion
facilitateddiffusion
ATP
activetransport
29
OsmosisMovement of Water Across Cell Membrane
30
Osmosis
- Osmosis
- diffusion of water from HIGH concentration of
water to LOW concentration of water - across a semi-permeable membrane
31
- Normally, in the process of osmosis, the net flow
of water molecules into or out of the cell
depends upon differences in the - 1. concentration of water molecules inside and
outside the cell - 2. concentration of enzymes on either side of the
cell membrane - 3. rate of molecular motion on either side of the
cell membrane - 4. rate of movement of insoluble molecules inside
the cell
32
Keeping water balance
- Cell survival depends on balancing water uptake
water loss
33
Managing water balance
- Balanced conditions
- no difference between cell environment
- example blood
- problem none
- water flows across membrane equally, in both
directions - volume of cell doesnt change
balanced
34
Managing water balance
- Freshwater
- a cell in fresh water
- example Paramecium
- problem gains water, swells can burst
- water continually enters Paramecium cell
- solution contractile vacuole
- pumps water out of cell
freshwater
35
Controlling water
- Contractile vacuole in Paramecium
36
Managing water balance
- Saltwater
- a cell in salt water
- example shellfish
- problem lose water
- plasmolysis in plants
- shrinking cell
- solution take up water
saltwater
37
(No Transcript)