Ecology - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Ecology
Description:
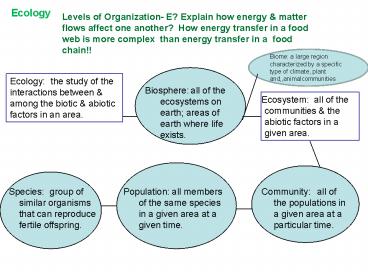
Ecology Levels of Organization- E? Explain how energy & matter flows affect one another? How energy transfer in a food web is more complex than energy transfer in a ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:56
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ecology
1
Ecology
- Levels of Organization- E? Explain how energy
matter flows affect one another? How energy
transfer in a food web is more complex than
energy transfer in a food chain!!
Biome a large region characterized by a specific
type of climate, plant and,,animalcommunities
the study of the interactions
between among the biotic abiotic factors in
an area.
Ecology
all of the ecosystems on earth areas
of earth where life exists.
Biosphere
all of the communities the abiotic
factors in a given area.
Ecosystem
all of the populations in a
given area at a particular time.
all members of the same species in a
given area at a given time.
group of similar organisms that can
reproduce fertile offspring.
Species
Population
Community
2
Energy Flow
producers(autotrophs)
consumers(heterotrophs)
energy
- Organisms that can produce their own
- food .
Autotrophs
Solar energy
6CO2
6H2O
6O2
C6H12O6
Heterotrophs
Organisms that must get their food by consuming
other organisms.
3
the level(s) at which an organism feeds
withinits ecosystem
E? Explain why an energy pyramid is a
representation of trophic levels.
Tophic Level
Tertiary consumers
Heterotrophs
Secondary consumers
Primary Consumers
Autotrophs
Producers
Ecological pyramid
4
Principles of Ecology
Chapter 2
2.2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem
Models of Energy Flow
- Food chains and food webs model the energy flow
through an ecosystem.
- Each step in a food chain or food web is called a
trophic level.
Model Ecosystems
5
Principles of Ecology
Chapter 2
2.2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem
Food Chains
- A food chain is a simple model that shows how
energy flows through an ecosystem.
6
Principles of Ecology
Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem
Food Webs
- A food web is a model representing the many
interconnected food chains and pathways in which
energy flows through a group of organisms.
7
Compare and Contrast the different types of
consumers
Carnivores- Energy source is other Consumers.
EX Lions, hawks, snakes
Omnivores- Energy source is both producers and
consumers. EX Bears, Pigs, cockroaches, humans
Herbivores-Energy source is producers. EX cows,
sheep, deer, grasshopper
Detrivores- Heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by
consuming decomposing organic matter. EX
Earthworm
Decomposer- Breaks down dead organisms in an
ecosystem and returns nutrients to the soil,
water, air. EX Fungi and Bacteria
- The cycle of matter is important because
necessary substances and building materials can
be used over and over so that the cycle of life
can continue.
8
The Biogeochemical Cycle
- What is it?
- The cycle in which nitrogen, carbon, and other
inorganic elements of the soil, atmosphere, etc.
of a region are converted into the organic
substances of animals and plants of the region
and released back into the environment.
9
The Water Cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic
cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous
movement of water on, above and below the surface
of the Earth.
10
Role of organisms in the Water Cycle
- Living organisms, mainly plants and animals,
contribute to this last step of the cycle through
processes, such as respiration, perspiration and
transpiration.
11
The Carbon Cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the
atmosphere into organisms and back again.
12
Role of organisms in the Carbon Cycle
- Plants, animals, and soil interact to make up the
basic cycles of nature. - In the carbon cycle, plants absorb carbon dioxide
from the atmosphere and use it, combined with
water they get from the soil, to make the
substances they need for growth. - Animals, such as a rabbit, eat the plants and use
the carbon to build their own tissues. - Animals return carbon dioxide into the air when
they breathe, and when they die, since the carbon
is returned to the soil during decomposition.
13
The Nitrogen Cycle
14
The Role of Organisms in the Nitrogen Cycle
- Producers Legumes act as natural "fertilizer
factories," and they pump large amounts of
nitrogen back into the soil. - Consumers When animals eat these plants, some of
the nitrogen in them is used by the animals to
synthesize, or make, their own tissues. - Decomposers Decaying tissues from plants,
animals or other organisms free, or release, the
nitrogen atoms they contain. The next generation
of organisms can then use these freed nitrogen
atoms to make their own tissues.