The Policy Cycle PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title: The Policy Cycle
1
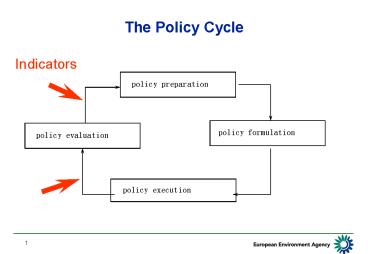
The Policy Cycle
Indicators
2
The link of Indicators to the policy process
3
Why indicators? Accountability!
relevant policy questions
indicators
distance to target analysis
accountability of policy makers/ environmental
managers
4
Why indicators? Peer pressure!
relevant policy questions
indicators
country comparison
peer pressure to do better (naming and shaming)
5
Why indicators? Benchmarking!
relevant policy questions
Transport CO2 emissions change 1990-1999
indicators
country comparison
benchmarking
dissemination of best experiences
6
Why indicators? Support target setting!
relevant policy questions
indicators
selection "convergence criteria"
target setting
7
Why indicators? From Chaos
The Public and Decision-Makers
The Public and Decision-Makers
EuroStat
EC
EEA
OECD
UNEP
EuroStat
EC
EEA
OECD
UNEP
DG
DG
ETC
ETC
DG
DG
National Institutions
8
to order
The Public and Decision-Makers
EuroStat
EC
EEA
OECD
UNEP
DG
ETC
DG
EIONET
National Institutions
9
Steps in indicator based reporting
1. Agree on a story 2. List (most important)
policy questions 3.Select indicators that come
close to answering these (ideal and actual) 4.
Data compilation 5. Assessment 6. Conclusion
(and modify, adapt, update and iterate)
10
TERM the story
- Growing greenhouse gas emissions from the
transport sector - jeopardise the achievement of the EU's emission
reduction target - under the Kyoto Protocol
- Impacts on air quality, noise nuisance and the
increasing - fragmentation of the EU's territory, are equally
worrying - Transport growth - which remains closely linked
to - economic growth - and the shift towards road and
aviation are - the main drivers behind this development.
- Technology and fuel improvements prove to be only
partly - effective to reduce impacts
- They need to be complemented with measures to
restrain - the growth in transport and to redress the modal
balance.
11
TERM main questions
- Is the environmental performance of the transport
sector improving? - Are we getting better at managing transport
demand and at improving the modal split? - Are spatial and transport planning becoming
better coordinated so as to match transport
demand to the needs of access? - Are we optimising the use of existing transport
infrastructure capacity and moving towards a
better-balanced intermodal transport system? - 5. Are we moving towards a fairer and more
efficient pricing system, which ensures that
external costs are internalised? - 6. How rapidly are improved technologies
being implemented and how efficiently are
vehicles being used? - 7. How effectively are environmental
management and monitoring tools being used to
support policy and decision-making?
12
(No Transcript)
13
A Performance Indicator
14
An Eco-efficiency Indicator
The energy supply sector
15
A Policy Effectiveness Indicator
Reference emission
Measures taken
Actual emission
16
TERM 2001 Indicators tracking transport and
environment integration in the European Union
17
The 'three corridors model' to follow progress in
sustainable development
Strategy for Sustainable Development (Gothenburg
Summit June 2001 to RIO10 June 2002)
Structural Indicators
Sectoral integration ind.
Issues indicators
Lisbon agenda (socio-economic policies)
Sectoral strategies
6th Environmental action plan (and specific
thematic plans)
Headline indicators
Headline indicators
Headline indicators
Sectoral reporting Environmental
issues reporting Integrated Monitoring and
reporting Synthesis report with an annex of 35
Indicators
18
Indicator architecture
env. issue indicators
sectoral indicators
env. issue headline indicators
sectoral headline indicators
structural indicators
Spring council indicators
19
EEA indicator products
sector/environment indicators TERM, EERM, AERM
(IRENA) environmental issues air pollution in
Europe, trends in greenhouse gas
emissions issue and sector indicators
Environmental signals Headline/structural
indicators input to DG Environment