Electric Current - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Electric Current
Description:
The Four Energy Systems Mechanical Fluid Electrical Thermal The Prime Movers of the Four Energy Systems Mechanical - Force Fluid- Pressure Electrical- Voltage Thermal ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:50
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Electric Current
1
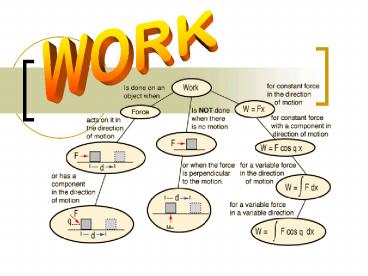
WORK
2
The Four Energy Systems
- Mechanical
- Fluid
- Electrical
- Thermal
3
The Prime Movers of the Four Energy Systems
- Mechanical - Force
- Fluid- Pressure
- Electrical- Voltage
- Thermal- Temperature
4
Work in a Mechanical Energy System
- Mechanical work happens when forces or torques
cause objects to move. - Work Force X Distance
- Work Torque X Angle
5
Work in a Fluid Energy System
- In Fluid systems, work is done when a pressure
difference causes liquids or gases to move. - Work Pressure X Volume
6
Work in a Fluid Energy System
- Work occurs in a fluid system when fluid pressure
p causes a given volume (?v) of liquids or gases
to move. - W p X (?v)
7
Work in a Fluid Energy System
- Work occurs in a fluid system when a fixed volume
of fluid v moves through a pressure difference
(?p). - W (?p) X v
8
What is Mechanical Work?
- Work in a mechanical system involves two parts.
- An applied force must act on an object.
- The object must move while the force is applied.
9
What is Energy?
- ENERGY is the ability to do WORK
- To cause something to MOVE!
- ENERGY is the ability to cause Change
- Living things cannot work without Energy, and
machines cannot work without Energy.
10
What is Energy?
- You cannot get no more Work out of a Machine then
the ENERGY you put into it.
- Due to FRICTION, the WORK produced is usually
less than the Energy used.
11
What is Energy?
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
- Forms of ENERGY can be transferred from one form
to another. - The use of Energy and the lost of Energy usually
ends up as HEAT.
12
How do you define the amount of work being done?
- The force applied in the direction of the motion
of the object times the distance the object moves
while the force is acting.
13
Name Six Simple Machines?
- Lever
- Pulley
- Wheel Axle
- Inclined Plane
- Wedge
- Screw
14
Lever
15
Every Lever has three (3) parts A.
Resistance Force or Load, What you are
trying to move or lift. B. Effort Force
- The Work done on the Lever. C. Fulcrum
A fixed pivot point.
16
Three Types of Levers
The position of the fulcrum in relation to the
applied force determines the lever class
17
Three Types of Levers
18
Pulley
19
Pulley Mechanical Advantage
A fixed pulley has no mechanical advantage. It
only changes direction.
20
Pulley Mechanical Advantage
A movable pulley has mechanical advantage based
upon how many supporting strands.
21
Wheel Axle
22
(No Transcript)
23
Incline Plane
24
Inclined Plane
25
Wedge
26
Wedge
27
Screw
28
Screw
29
Open Systems
In open systems, matter may flow in and out of
the system boundaries. The first law of
thermodynamics for open systems states the
increase in the internal energy of a system is
equal to the amount of energy added to the system
by matter flowing in and by heating, minus the
amount lost by matter flowing out and in the form
of work done by the system.
30
Open Systems
This type of system uses wells or a body of water
as the source of heat exchange fluid that
circulates directly through a heat exchanger in
the building. Once it has circulated through the
heat exchanger, the water returns to the ground
through the recharge well or the body of water.
31
Closed Systems
A closed systems can exchange heat and work, but
not matter, with its surroundings.
32
Closed Systems
Closed/Pond Loop System Since water transfers
heat much better than soil, closed loop systems
are often located in lakes or ponds by submerging
GeoExchange loop coils in the water.
33
Information can be found on the class web site.
34
Information can be found on the class web site.
35
Information can be found on the class web site.