Let PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title: Let
1
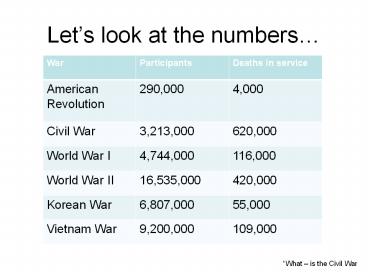
Lets look at the numbers
War Participants Deaths in service
American Revolution 290,000 4,000
Civil War 3,213,000 620,000
World War I 4,744,000 116,000
World War II 16,535,000 420,000
Korean War 6,807,000 55,000
Vietnam War 9,200,000 109,000
What is the Civil War
2
What is a civil war?
- a war between opposing groups of citizens in
the same country
Confederate names for the war
Union names for the war
- The War for States Rights
- The War for Southern Independence
- The Yankee Invasion
- The Civil War
- The Southern Rebellion
- The War of Abolition
- The War Against Slavery
3
Civil War Basics
- April 12, 1861 - April 9, 1865(Ft. Sumter,
SC) (Appomattox Court House, VA) - Two sides Union (United States of America)
(North) Confederacy (Confederate States of
America) (South) - Fought on two fronts East (coast) and West
(Mississippi River) - Winner Union
4
Civil War Basics
- Why?
- Keep the Union together (Lincoln)
- States Rights (strong state govt. weaker
federal govt. limit the ability to end slavery
throughout the country) - Turning Point Gettysburg, PA (East/NE) Vicks
burg, MS (West) Ft. Wagner, SC (East/SE) - Strategy North Scotts Great Snake South
Defensive War
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
Recruiting an Army
- Lincoln called for 75,000 volunteers to serve as
soldiers in a campaign to squash the Southern
rebellion. By the end of 1861, 527,000 volunteers
had joined the Union Army. - Despite preparing for a defensive war, Davis too,
made a call for troops. We seek no conquest, all
we ask is to be let alone. By the end of 1861,
258,000 men had joined the Confederate Army.
8
Volunteer Armies
- Northerners believed they needed to fight to save
the Union (united is better/stronger, stick
together, end slavery, safe from capture, North
economically benefited from the South, etc.). - Southerners believed they were fighting a war of
independence (states rights, for slavery, for
foreign trade without tariffs, etc.) similar to
the American Revolution. - Men on both sides were eager to enlist
9
The sides
- Blue- North
- Union Army United States of America, Federal
Army, Yankee Army, Northern Army, or Army - of the river (Potomac, Cumberland, Tennessee)
- Gray- South
- Confederate Army Confederate States of America,
The Confederates, Rebel Army, or Army of the
land mass (Northern Virginia, Tennessee)
10
North
- We shall crush out this rebellion as an elephant
would trample on a mouse.
Both sides believed the war would end quickly.
South
Just throw three or four bomb shells among
those blue-bellied Yankees and theyll scatter
like sheep.
11
As the war dragged on
- Public support dwindled and so did the number of
volunteers - By the spring of 1862 the Confederacy passed its
first conscription act and by 1863 the Union was
forced into doing the same. This required all
able bodied men between 18 and 35 to serve if
called (later draft ages 17-50).
12
Leaders
- North- President Lincoln had very little military
or national political experience, but proved to
be a good leader - South- President Davis was thought to be a
stronger president because he went to West Point
and was a former Secretary of War
13
Finding a General
- Following the quick attack and defeat at Fort
Sumter, Lincoln asked Robert E. Lee to lead the
Union Army. When Virginia seceded (spring 1861),
Lees loyalty remained with his home state not
the Union. He declined the offer and later
became commander of the Confederate Army. - Lee commands the South in all major battles in
the Northern Virginia Area and could arguably be
the best General of the entire war. - In the end, Lee will eventually surrender to
General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox
Courthouse, VA to end the war.After the war,
Lee is stripped of US citizenship which was
restored to in 1975 (105 years after his death).
Ironically his homestead property in Virginia has
been made into the countys most prestigious
military cemeteries.Arlington National
Cemetery.
14
Lincoln had trouble finding a good General
- Winfield Scott
- George B. McClellan
- Henry W. Halleck
- Ulysses S. Grant
15
- The Civil War consisted of nearly 10,500 battles,
engagements, and other military actions including
nearly 50 major battles and about 100 others that
had major significance.
16
Plans
- The Souths plan was simple.defense, defense,
defense! - The Norths planthe Anaconda Plan (Scotts Great
Snake)wrap around the south and suffocate it
like a snake! - Seal off the coast with a naval blockade
- Protect the Union Capitol Washington,
D.C.Capture Confederate Capitol Richmond,
Virginia - Conquer the Mississippi River
- Squeeze/Suffocate the South to submission
17
(No Transcript)