Sense Organs - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Sense Organs
Description:
Sense Organs ... Sense Organs – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:332
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Sense Organs
1
Sense Organs
2
Chemoreceptors
- Taste and smell sensory receptors
- Most primitive sense, all animals have it
- Important in finding food, locating a mate and
detecting chemicals - Location varies by animal
- Jacobsens organ - snakes
3
Taste
- 4 primary types of taste
- Sweet, sour, salty, bitter,
- umami? Cheeses, broth, seafood, Asian foods
- Microvilli of taste cell has receptor proteins
for food molecules
4
Smell
- 10 20 million olfactory cells!! (modified
neurons) - Declines with age
- Located on roof of nasal cavity
- Olfactory bulb (extension of brain) has direct
connection with limbic system (emotions and
memory) - Smell and taste work together in cerebral cortex
- Sometime molecules from smell travel to mouth and
you taste it
5
Vision
- Photoreceptors sensitive to light
- Some animals have eye spots, some have image
forming eyes - Insects have color vision, shorter spectrum but
includes ultraviolet light - Some fish, all reptiles, most birds
- monkeys, apes and humans only mammals
- Stereoscopic vision (binocular in front)
- Panoramic vision eyes on side, prey
6
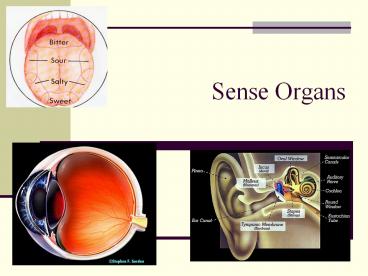
Human Eye
7
Human eye
- 3 layers
- Sclera clear outer layer
- Cornea refracts light rays
- Conjunctive moistens
- Pupil light enters
- Choroid middle, includes blood vessels
- iris color of eye, regulates light entrance
- Ciliary muscle holds lens in place
- Retina inner layer, metallic
- Rods sensitive to light, black and white, night
vision - Cones color vision
- Fovea centralis acute vision
8
Eye
- Lens
- Refracts and focuses light, can be replaced
- Aqueous humor
- Water solution, anterior of eye, behind lens
- Glaucoma pressure builds up
- Vitreous humor
- Gel material in posterior of eye
- Stabilizes the shape of eye, support retina
- Optic nerve sends info to brain
- Blind spot optic nerve exits the retina, no
rods or cones
9
Disorders of eye
- Presbyopia old-sightedness
- lens loses its ability to accommodate near
objects - Nearsighted (myopia)
- Elongated eyeball, image in focus in front of
retina - Farsighted (hyperopia)
- Shortened eyeball, image focused behind the
retina - Astigmatism
- Cornea or lens is uneven, image is fuzzy
- Cataract aging, exposure to sun, lens is milky
and cannot transmit light rays
10
Hearing and balance The Ear
- Mechanoreceptors
- sensitive to pressure, sound waves and gravity
- Outer ear pinna flap, auditory canal
- Middle ear tympanic membrane (ear drum)
- Ossicles stapes (stirrup), incus (anvil),
malleus (hammer) - Eustachian tube equalization of pressure
- Inner ear contains fluid
- Semicircular canals, vestibule equilibrium
- Cochlea - hearing
11
Sound
- Auditory canal? tympanic membrane? malleus?
incus? stapes? oval window ? endolymph in cochlea
? hair cells of cochlea ? synapse with nerve
fibers of auditory nerve ?basilar membrane organ
of corti? nerve impulse travels to brain stem ?
auditory area of cerebral cortex sound!!
12
Sense of Balance
- Semicircular canals mechanoreceptors
- Rotational equilibrium head rotation
- Gravitational equilibrium straight line
movement
13
Sensory receptors in animals
- Lateral line fish
- Detects water currents and pressure waves
- Collection of hair cells with cilia
- Statocysts gravitational equilibrium
- Cnidarians, molluscs, crustaceans
- Give information only about the head