Unit 9 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 45
Title: Unit 9
1
Unit 9 The Heart
- Cardiovascular System
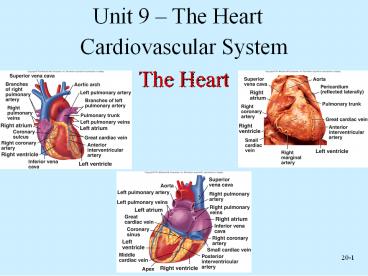
- The Heart
2
Functions of the Heart
- Generating blood pressure
- Routing blood
- Heart separates pulmonary and systemic
circulations - Ensuring one-way blood flow
- Heart valves ensure one-way flow
- Regulating blood supply
- Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
delivery to changing metabolic needs
3
The Closed Circulatory System
- Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical
of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to
vessels and is distinct from the interstitial
fluid. - The heart pumps blood into large vessels that
branch into smaller ones leading into the organs. - Materials are exchanged by diffusion between the
blood and the interstitial fluid bathing the
cells.
4
The Cardiovascular System
Three Major Elements Heart, Blood Vessels,
Blood
5
Size, Shape, Location of the Heart
- Size of a closed fist
- Shape
- Apex Blunt rounded point of cone
- Base Flat part at opposite of end of cone
- Located in thoracic cavity in mediastinum
6
Heart Cross Section
7
Pericardium
8
Heart Wall
- Three layers of tissue
- Epicardium This serous membrane of smooth outer
surface of heart - Myocardium Middle layer composed of cardiac
muscle cell and responsibility for heart
contracting - Endocardium Smooth inner surface of heart
chambers
9
Heart Wall
10
External Anatomy
- Four chambers
- 2 atria
- 2 ventricles
- Auricles
- Major veins
- Superior vena cava
- Pulmonary veins
- Major arteries
- Aorta
- Pulmonary trunk
11
External Anatomy
12
Coronary Circulation
13
Heart Valves
- Atrioventricular
- Tricuspid
- Bicuspid or mitral
- Semilunar
- Aortic
- Pulmonary
- Prevent blood from flowing back
14
Heart Valves
15
Function of the Heart Valves
16
Lets Practice.
17
Did you get them all correct?
18
Blood Flow Through Heart
19
(No Transcript)
20
Systemic and PulmonaryCirculation
Pulmonary circuit The blood pathway between the
right side of the heart, to the lungs, and back
to the left side of the heart. Systemic
circuit The pathway between the left and right
sides of the heart.
21
Heart Skeleton
- Consists of plate of fibrous connective tissue
between atria and ventricles - Fibrous rings around valves to support
- Serves as electrical insulation between atria and
ventricles - Provides site for muscle attachment
22
The Circulatory System
- Blood Vessels -A network of tubes
- Arteries?arterioles move away from the heart
- Elastic Fibers
- Circular Smooth Muscle
- Capillaries where gas exchange takes place.
- One cell thick
- Serves the Respiratory System
- Veins?Venules moves towards the heart
- Skeletal Muscles contract to force blood back
from legs - One way values
- When they break - varicose veins form
23
(No Transcript)
24
Cardiac Muscle
- Elongated, branching cells containing 1-2
centrally located nuclei - Contains actin and myosin myofilaments
- Intercalated disks Specialized cell-cell
contacts - Desmosomes hold cells together and gap junctions
allow action potentials - Electrically, cardiac muscle behaves as single
unit
25
Conducting System of Heart
26
Electrical Properties
- Resting membrane potential (RMP) present
- Action potentials
- Rapid depolarization followed by rapid, partial
early repolarization. Prolonged period of slow
repolarization which is plateau phase and a rapid
final repolarization phase - Voltage-gated channels
27
Action Potentials inSkeletal and Cardiac Muscle
28
SA Node Action Potential
29
Refractory Period
- Absolute Cardiac muscle cell completely
insensitive to further stimulation - Relative Cell exhibits reduced sensitivity to
additional stimulation - Long refractory period prevents tetanic
contractions
30
Electrocardiogram
- Action potentials through myocardium during
cardiac cycle produces electric currents than can
be measured - Pattern
- P wave
- Atria depolarization
- QRS complex
- Ventricle depolarization
- Atria repolarization
- T wave
- Ventricle repolarization
31
Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Tachycardia Heart rate in excess of 100bpm
- Bradycardia Heart rate less than 60 bpm
- Sinus arrhythmia Heart rate varies 5 during
respiratory cycle and up to 30 during deep
respiration - Premature atrial contractions Occasional
shortened intervals between one contraction and
succeeding, frequently occurs in healthy people
32
Alterations in Electrocardiogram
33
Cardiac Cycle
- Heart is two pumps that work together, right and
left half - Repetitive contraction (systole) and relaxation
(diastole) of heart chambers - Blood moves through circulatory system from areas
of higher to lower pressure. - Contraction of heart produces the pressure
34
Cardiac Cycle
35
Events during Cardiac Cycle
36
Heart Sounds
- First heart sound or lubb
- Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid
vibrations as valves close at beginning of
ventricular systole - Second heart sound or dupp
- Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary
semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular
diastole, lasts longer - Third heart sound (occasional)
- Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles
and detected near end of first one-third of
diastole
37
Location of Heart Valves
38
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
- Average blood pressure in aorta
- MAPCO x PR
- CO is amount of blood pumped by heart per minute
- COSV x HR
- SV Stroke volume of blood pumped during each
heart beat - HR Heart rate or number of times heart beats per
minute - Cardiac reserve Difference between CO at rest
and maximum CO - PR is total resistance against which blood must
be pumped
39
Factors Affecting MAP
40
Regulation of the Heart
- Intrinsic regulation Results from normal
functional characteristics, not on neural or
hormonal regulation - Starlings law of the heart
- Extrinsic regulation Involves neural and
hormonal control - Parasympathetic stimulation
- Supplied by vagus nerve, decreases heart rate,
acetylcholine secreted - Sympathetic stimulation
- Supplied by cardiac nerves, increases heart rate
and force of contraction, epinephrine and
norepinephrine released
41
Heart Homeostasis
- Effect of blood pressure
- Baroreceptors monitor blood pressure
- Effect of pH, carbon dioxide, oxygen
- Chemoreceptors monitor
- Effect of extracellular ion concentration
- Increase or decrease in extracellular K
decreases heart rate - Effect of body temperature
- Heart rate increases when body temperature
increases, heart rate decreases when body
temperature decreases
42
Baroreceptor and ChemoreceptorReflexes
43
Baroreceptor Reflex
44
Chemoreceptor Reflex-pH
45
Effects of Aging on the Heart
- Gradual changes in heart function, minor under
resting condition, more significant during
exercise - Hypertrophy of left ventricle
- Maximum heart rate decreases
- Increased tendency for valves to function
abnormally and arrhythmias to occur - Increased oxygen consumption required to pump
same amount of blood