MODULE C5: CHEMICALS OF THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: MODULE C5: CHEMICALS OF THE NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
1
MODULE C5 CHEMICALS OF THE NATURALENVIRONMENT
2
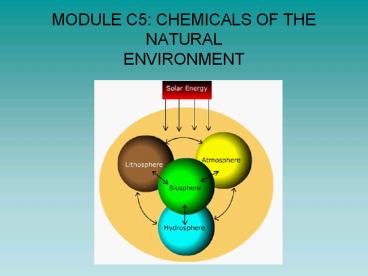
Atmosphere
- Molecular elements (e.g. oxygen, nitrogen, ozone)
and compounds (e.g.carbon dioxide, water) - Monoatomic elements (e.g. argon)
- hydrosphere
- Mainly water plus
- Solution of ionic compounds (e.g. sodium chloride)
Q. Give the chemical symbols and state symbols
for all the chemicals above.
3
Properties
Molecular compounds Ionic compounds
Made from Two or more non-metal atoms bonded Metal ions with non metal ions
Electrical properties Insulators (no ions!) Conduct only when molten or dissolved in water
Forces holding them together Strong covalent bonds within the molecule but weak forces between molecules Strong attractions between oppositely charged ions
Melting and boiling points Low found as gases at room temperature High found as solids or in solution
4
Formulae of salts
The group number of the atom can tell us which
ion it will form..
- Metal ions () combine with non-metal ions (-) to
form neutral compounds. - The formula of magnesium oxide is MgO
- The formula of sodium oxide is Na2O
group ion
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 None
5 3-
6 2-
7 1-
0 None
Mg 2
Mg 2
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
Mg 2
Mg 2
Mg 2
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
Mg 2
Mg 2
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
O 2-
Na
O 2-
Na
O 2-
Find the formula of aluminium with fluorine,
calcium with chlorine, sulphur with potassium
5
Lithosphere
- Made of the crust and upper mantle
- Composed of minerals e.g. quartz containing
silicon dioxide found in granite and sandstone - Rich in the atoms of silicon, oxygen and aluminium
Treasures of the Earth Gemstones for beauty,
hardness, rarity
6
Chemical Brothers
- Carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are both
covalently bonded compounds but with very
different physical properties
Carbon dioxide Silicon dioxide
Molecular structure (limited covalent bonding) Giant structure (more extensive covalent bonding)
Low melting point High melting point
insulator Semi-conductor
gas Hard solid
Soluble in water Insoluble in water
negatively charged electrons are attracted to the
positively charged nuclei to form strong covalent
bonds
7
Biosphere
- the total sum of living organisms
- Contains large molecules such as fats,
carbohydrates, proteins, DNA - Mostly carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
- Minor contributions from phosphorus and sulphur
Whats the formula of the glucose molecule above?
8
Cycling of nutrients
- Many elements are cycled in nature including
carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. - Identify in the cycle opposite where carbon can
be found as (i) simple molecular compounds, (ii)
large molecules and (iii) as the element
9
Extracting metals
- For zinc, iron and copper (fairly un-reactive
metals) the ore (often an oxide) is mined,
concentrated then the metal is extracted by
heating with carbon - Copper oxide carbon copper
carbon dioxide - lost oxygen gained oxygen
- When oxygen is lost REDUCTION
- When oxygen is gained OXIDATION
- Overall the process is REDOX
- Re-write the equation above using symbols
(chemical and state symbols!) - Write out the equivalent equation for iron (III)
oxide (where iron has a 3 charge)
10
Extracting reactive metals
- The oxides of the more reactive metals are very
stable so they require large amounts of energy
supplied by electricity in order to extract the
metal. The electricity decomposes the compound
into simpler substances.
Electrolyte aluminium oxide (bauxite) with
cryolite added
11
in more detail
cathode
Al 3
anode
oxygen gas released
- The cryolite makes the aluminium oxide (bauxite)
easier to melt so the ions in it are free to move
to each electrode to become neutral atoms
O 2-
Al 3
Al 3
O 2-
O 2-
Molten aluminium metal drops to the bottom
Use an ionic equation to show what happens at
each electrode
12
Metals
- The typical properties of high melting/ boiling
points, high strength, malleable and conduction
of heat/ electricity can all be explained by
their structure
Giant structure held together by ionic bonding
M
M
M
Metal ions in a lattice
M
M
M
Sea of electrons (free to move)
M
M
M
13
Environmental issues
- The (i) mining, (ii) extraction, (iii) transport,
(iv) maintenance and (v) disposal of metals all
have an impact on the environment. - For each stage above suggest how it may affect
the surroundings