Quantum Control PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Quantum Control
1
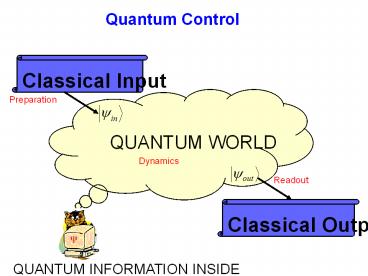
Quantum Control
Classical Input
Preparation
Dynamics
Readout
Classical Output
QUANTUM INFORMATION INSIDE
2
Q.C. Paradigms
Hilbert Space
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
We dont live in Hilbert space
6
Hilbert space and physical resources
Hilbert-space dimension is a physical quantity
that costs physical resources.
Single degree of freedom
7
qudits
8
Hilbert space and physical resources
Many degrees of freedom
9
Quantum computing in a single atom
Characteristic scales are set by atomic units
10
Quantum computing in a single atom
Characteristic scales are set by atomic units
5 times the diameter of the Sun
11
(No Transcript)
12
Physical resources classical vs. quantum
A classical bit involves many degrees of
freedom. Our scaling analysis applies, but with
a basic phase-space scale of arbitrarily small.
Limit set by noise, not fundamental physics.
The scale of irreducible resource requirements
is always set by Plancks constant.
13
Why Atomic Qubits?
State Manipulation
Potentials/Traps Control Fields Particle
Interactions
Laser cooling
Quantum Optics NMR
State Readout
Quantum Jumps State Tomography Process
Tomography
Fluorescence
14
Optical Lattices
15
Designing Optical Lattices
16
Lin-q-Lin Lattice
17
Multiparticle Control
Controlled Collisions
18
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Resonant dipole-dipole interaction
19
Cooperative level shift
20
Two Gaussian-Localized Atoms
21
Three-Level Atoms
22
Molecular Hyperfine
Atomic Spectrum
0.8 GHz
5P1/2
F2
F1
F2
6.8 GHz
5S1/2
F1
87Rb
23
Controlled-Phase Gate Fidelity
24
Controlled-Phase Gate Fidelity
25
Leakage Spin-Dipolar Interaction
Noncentral force
26
Suppressing Leakage Through Trap
Energy and momentum conservation suppress spin
flip for localized and separated atoms.
27
Dimer Control
Lattice probes dimer dynamics
Localization fixes internuclear coordinate
28
Separated-Atom Cold-Collision
Short range interaction potential, well
characterized by a hard-sphere scattering with
an effective scattering length.
29
Energy Spectrum
30
Shape Resonance
Molecular bound state, near dissociation, plays
the role of an auxiliary level for controlled
phase-shift.
31
Dreams for the Future
Qudit logic Improved fault-tolerant
thresholds?
Topological lattice - Planar codes?
32
http//info.phys.unm.edu/deutschgroup
I.H. Deutsch, Dept. Of Physics and
Astronomy University of New Mexico
- Collaborators
- Physical Resource Requirements for Scalable Q.C.
Carl Caves (UNM), Robin Blume-Kohout (LANL)
- Quantum Logic via Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Gavin Brennen (UNM/NIST), Poul Jessen (UA), Carl
Williams (NIST)
- Quantum Logic via Ground-State Collisions
René Stock (UNM), Eric Bolda (NIST)