Protein Synthesis PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Protein Synthesis
1
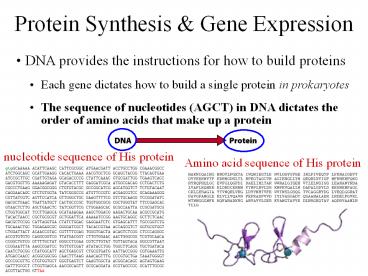
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- DNA provides the instructions for how to build
proteins - Each gene dictates how to build a single protein
in prokaryotes - The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA
dictates the order of amino acids that make up a
protein
nucleotide sequence of His protein
2
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
3
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- The process in which the instructions encoded by
a gene are used to build a protein
4
(No Transcript)
5
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Transcription
- RNA polymerase makes an mRNA (messenger RNA)
copy of a gene - occurs in cytoplasm of prokaryotes, nucleus of
eukaryotes - Enables cell to make many copies of a gene so
that a lotof protein can be made at onetime - Enables eukaryotic cells tokeep DNA protected in
the nucleus, only mRNA copiesof genes leave the
nucleus
6
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Transcription Initiation
- RNA polymerase binds to a region on DNA known as
the promoter, which signals the start of a gene - Promoters are specific to genes
- RNA polymerase does not need a primer
- Transcription factors assemble at the promoter
forming a transcription initiation complex
activator proteins help stabilize the complex
- Gene expression can be regulated (turned on/off
or up/down) by controlling the amount of each
transcription factor
HONORS
7
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Transcription Elongation
- RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA and breaks the
H-bonds between the bases of the two strands,
separating them from one another - Base pairing occurs between incoming RNA
nucleotides and the DNA nucleotides of the gene
(template) - recall RNA uses uracil instead of thymine
AGTCAT
UCA
GUA
HONORS
8
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Transcription Elongation
The gene occurs on only one of the DNA strands
each strand possesses a separate set of genes
RNA polymerase slides down the template strand
connecting together RNA nucleotides
9
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Transcription Termination
- A region on DNA known as the terminator signals
the stop of a gene - RNA polymerase separates from the mRNA and the DNA
HONORS
10
(No Transcript)
11
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
HONORS
- Exons are coding regions provide
instructionsfor one or more proteins) - Introns are removed
- different combinations of exons form different
mRNA resulting in multiple proteins from the same
gene - Humans have 30,000 genes but are capable of
producing 100,000 proteins
- Alternative Splicing (eukaryotes only)
12
Web Resources
- Transcription
- http//www.biostudio.com/d_20Transcription.htm
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vWsofH466lqk
- http//www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranscriptionBas
ic_withFX.html
- Alternative Splicing
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vFVuAwBGw_pQfeature
related
13
(No Transcript)
14
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Translation
- mRNA is used by ribosome to build polypeptides
(Ribosomes attach to the mRNA and use its
sequence of nucleotides to determine the order of
amino acids in the polypeptide) - occurs in cytoplasm of prokaryotes and eukaryotes
- some polypeptides feed directly into rough ER in
eukaryotes where they are modified and folded
into the final protein
15
Protein Synthesis
- TranslationInitiation
- Start codon signals where the gene begins (at 5
end of mRNA)
5
3
AUGGACAUUGAACCG
start codon
16
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- TranslationInitiation
- Start codon signals where the gene begins (at 5
end of mRNA) - Ribosome binding site on the mRNA binds to a
small ribosomal subunit - Then this complex binds to a large ribosomal
subunit forming the complete ribosome
17
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- TranslationScanning
- The ribosome moves in 5 to 3 direction
reading the mRNA and assembling amino acids
into the correct polypeptide
18
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- TranslationScanning
- Every three mRNA nucleotides (codon) specify an
amino acid
19
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- TranslationScanning
- Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid
- tRNA have an anticodon region that specifically
binds to its codon
anticodon
20
Protein Synthesis
- TranslationTermination
- Ribosome disengages from the mRNA when it
encounters a stop codon
21
Web Resources
- Translation
- Eukaryotic http//www.youtube.com/watch?v5bLEDd
-PSTQfeaturerelated - Prokaryotic http//www.biostudio.com/d_20Protei
n20Synthesis20Prokaryotic.htm - http//www.biostudio.com/d_20Peptide20Bond20For
mation.htm - http//www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html
- http//www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationBasic
_withFX0.html - http//www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationAdvan
ced.html
22
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Post-Translational Modifications
- Polypeptide is modified in the rough ER this
might include cutting out sections and/or cut a
section from one part of the polypeptide and
moving it to another part - Chaperone proteins help to fold the polypeptide
into its final tertiary shape. Now it is called a
protein.
23
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Folded membrane that forms compartments where
newly synthesized proteins are processed (cut,
joined, folded into their final shape) - Ribosomes bind to rough ER when they start to
synthesize proteins that are intended to be
exported from the cell the proteins enter the
ER directly from the ribosome
24
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
Golgi Apparatus
- Folded membranes form compartments that each
contain different enzymes which selectively
modify the contents depending on where they are
destined to end up - Processes and packages macromolecules produced
by the cell (e.g. proteins and lipids) sent
out as excretory vesicles labeled for their
destination
25
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
Translation
- Multiple RNA polymerases can engage a gene at one
time - Multiple ribosomes can engage a single mRNA at
one time
Transcription
26
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Eukaryotes transcription occurs in the nucleus
and translation occurs in the cytoplasm - Prokaryotes Transcription and translation occur
simultaneously in the cytoplasm
27
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- There are three main types of RNA
- mRNA (messenger RNA) - RNA copy of a gene used
as a template for protein synthesis - rRNA (ribosomal RNA) - part of structure of
ribosomes - tRNA (transfer RNA)- amino acid carrier that
matches to mRNA codon
28
Practice Question
Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACG
CACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC
29
Practice Question
Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACG
CACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC
Serine Tyrosine Histidine Threonine
Histidine Proline Serine Serine Serine -
Serine
30
Practice Question
Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACG
CACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC
Serine Tyrosine Histidine Threonine
Histidine Proline Serine Serine Serine -
Serine
Ser Tyr His Thr His Pro Ser Ser
Ser - Ser
31
Practice Question
Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACG
CACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC
Serine Tyrosine Histidine Threonine
Histidine Proline Serine Serine Serine -
Serine
Ser Tyr His Thr His Pro Ser Ser
Ser - Ser
S Y H T H P S S S - S
32
Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Protein Synthesis Gene Expression
- Process in which a gene is used to build a
protein resulting in the presence of a particular
phenotype (physical characteristic) - Phenotypic variation among organisms is due to
genotypic variation
(differences in the sequence of their DNA
bases) - Differences exist between species and within a
species - Different genes (genomes) ? different proteins
(proteomes) - Different versions of the same gene alleles
- Differences in gene expression epigenetics
33
Web Resources
Insulin Example of Protein Synthesis http//www.bi
otopics.co.uk/as/insulinproteinstructure.html
Hemoglobin Example of Protein Synthesis http//www
.biotopics.co.uk/as/insulinproteinstructure.html
Collagen Example of Protein Synthesis http//www.b
iotopics.co.uk/JmolApplet/collagen.html