textbook sections 27-1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
textbook sections 27-1
Description:
Physics 1161: Lecture 19 Lenses and your EYE textbook sections 27-1 27-3 Ciliary Muscles – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:85
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: textbook sections 27-1
1
Physics 1161 Lecture 19 Lenses and your EYE
- textbook sections 27-1 27-3
2
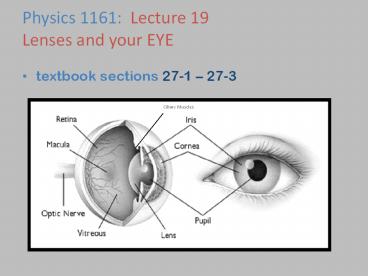
Parts of the Eye
3
Review of LensesPreflight 18.8
Focal point determined by geometry and Snells
Law n1 sin(q1) n2 sin(q2)
n1ltn2
P.A.
Fat in middle Converging Thin in middle
Diverging Larger n2/n1 more bending, shorter
focal length. n1 n2 gt No Bending, f infinity
Lens in water has _________ focal length!
4
Review of LensesPreflight 18.8
Focal point determined by geometry and Snells
Law n1 sin(q1) n2 sin(q2)
n1ltn2
P.A.
Fat in middle Converging Thin in middle
Diverging Larger n2/n1 more bending, shorter
focal length. n1 n2 gt No Bending, f infinity
Lens in water has larger focal length!
5
Preflight 19.1
A converging lens is used to project a real image
onto a screen. A piece of black tape is then
placed over the upper half of the lens.
1. Only the lower half will show on screen 2.
Only the upper half will show on screen 3. The
whole object will still show on screen
48
40
12
How much of the image appears on the screen?
6
Preflight 19.1
A converging lens is used to project a real image
onto a screen. A piece of black tape is then
placed over the upper half of the lens.
7
Preflight 19.1
Still see entire image (but dimmer)!
8
Two very thin converging lenses each with a focal
length of 20 cm are are placed in contact. What
is the focal length of this compound lens?
- 10 cm
- 20 cm
- 40 cm
9
Two very thin converging lenses each with a focal
length of 20 cm are are placed in contact. What
is the focal length of this compound lens?
- 10 cm
- 20 cm
- 40 cm
10
Amazing Eye
- One of first organs to develop.
- 100 million Receptors
- 200,000 /mm2
- Sensitive to single photons!
- http//hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/vision/
retina.htmlc2
11
Which part of the eye does most of the light
bending?
Cornea n 1.38 Lens n 1.4 Vitreous n 1.33
- Lens
- Cornea
- Retina
- Cones
12
Which part of the eye does most of the light
bending?
Cornea n 1.38 Lens n 1.4 Vitreous n 1.33
- Lens
- Cornea
- Retina
- Cones
Laser eye surgery changes Cornea
Lens and cornea have similar shape, and index of
refraction. Cornea has air/cornea interface
1.38/1, 70 of bending. Lens has Lens/Vitreous
interface 1.4/1.33. Lens is important because it
can change shape.
13
Preflight 19.3
1) 13 cm 2) 26 cm 3) 52 cm
32
56
12
14
Preflight 19.3
1) 13 cm 2) 26 cm 3) 52 cm
Image from mirror becomes object for eye!
15
Multiple Lenses
Image from lens 1 becomes object for lens 2
1
2
Example
f1
f2
Complete the Rays to locate the final image.
16
Multiple Lenses
Image from lens 1 becomes object for lens 2
1
2
Example
f1
f2
17
Multiple Lenses Magnification
1
2
do 15 cm
L 42 cm
di 8.6 cm
f1
f2
f1 10 cm
f2 5 cm
Example
di 30 cm
do12 cm
18
Near Point, Far Point
- Eyes lens changes shape (changes f )
- Object at any do can have image be at retina (di
approx. 25 mm) - Can only change shape so much
- Near Point
- Closest do where image can be at retina
- Normally, 25 cm (if far-sighted then further)
- Far Point
- Furthest do where image can be at retina
- Normally, infinity (if near-sighted then closer)
19
Preflight 19.4
- Two people who wear glasses are camping. One of
them is nearsighted and the other is farsighted.
Which persons glasses will be useful in starting
a fire with the suns rays?
Farsighted 68 Nearsighted 32
20
Preflight 19.4
- Two people who wear glasses are camping. One of
them is nearsighted and the other is farsighted.
Which persons glasses will be useful in starting
a fire with the suns rays?
21
Angular SizePreflight 19.6, 19.7
Both are same size, but nearer one looks bigger.
- Angular size tells you how large the image is on
your retina, and how big it appears to be.
22
The focal length of the lens of a simple camera
is 40 mm. In what direction must the lens be
moved to change the focus of the camera from a
person 25 m away to a person 4.0 m away? i.e.
does the image distance increase or decrease?
- Away from the film
- Towards the film
23
The focal length of the lens of a simple camera
is 40 mm. In what direction must the lens be
moved to change the focus of the camera from a
person 25 m away to a person 4.0 m away? ? i.e.
does the image distance increase or decrease?
- Away from the film
- Towards the film
24
Unaided Eye
How big the object looks with unaided eye.
- Bring object as close as possible (to near point
N)
If q is small and expressed in radians.
25
Magnifying Glass
Magnifying glass produces virtual image behind
object, allowing you to bring object to a closer
do and larger q
Ratio of the two angles is the angular
magnification M




![[PDF] Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology Full PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10102439.th0.jpg?_=20240820077)

![[PDF] Oxford Textbook of Palliative Medicine Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10084267.th0.jpg?_=20240724121)





![[PDF] Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 6th Edition Full PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10102440.th0.jpg?_=20240820078)

![[PDF] The Complete Textbook of Veterinary Nursing 2nd Edition Ipad PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10105971.th0.jpg?_=202408230511)





![[PDF]❤️Download ⚡️ Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 6th Edition PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10128490.th0.jpg?_=20240910112)






![[PDF] Oxford Textbook of Headache Syndromes (Oxford Textbooks in Clinical Neurology) Kindle PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10084266.th0.jpg?_=20240724121)


