The Urinary System PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title: The Urinary System
1
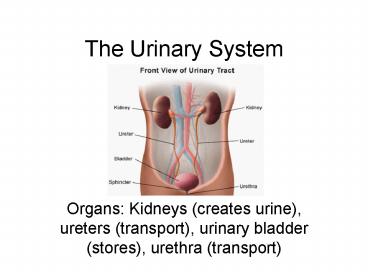
The Urinary System
- Organs Kidneys (creates urine), ureters
(transport), urinary bladder (stores), urethra
(transport)
2
Kidney Function
- Filter fluids from bloodstream and maintain
homeostasis in body - Rids body of wastes, excess ions, toxins, and
drugs in urine - Regulate blood volume, pH, salt content
- Secretes renin regulates blood pressure
- Secretes erythropoietin increases rbc
production
3
Kidney Anatomy
- 5 long, 2.5 wide
- Renal capsule
- encloses kidney
- Renal cortex
- outer region
- Renal medulla
- deep to cortex w/ medullary pyramids separated by
renal columns - Renal hilus
- medial indentation
- Rich Blood Supply
- Renal artery ? segmental arteries ? lobar
arteries ? interlobar artery ? afferent arteriole
? glomerulus capillaries ? efferent arteriole ?
peritubular capillaries ? interlobular vein ?
arcuate vein ? interlobar vein ? renal vein
4
Nephrons
- Nephrons form urine
- Glomerulus knot of capillaries
- Renal tubule w/ enlarged bowmans capsule at end
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting ducts receive urine from many
nephrons deliver urine to renal pelvis
5
Urine Formation
- Filtration
- Water and solutes smaller than proteins are
forced thru capillary walls and pores of
glomerular capsule into the renal tubule - Tubular reabsorption
- Water, glucose, amino acids, and needed ions are
transported out of the filtrate into the tubule
cells and then enter the capillary blood - Tubular Secretion
- Urea, H, K, creatinine, and drugs are removed
from the peritubular blood and secreted by the
tubule cells into the filtrate - Urine 1-2 L produced every 24 hrs
6
Ureters
- 10-12 long tubes
- Carry urine from kidneys to bladder
- Peristalsis propels urine transport
- Valve-like folds prevent back flow from bladder
7
Urinary Bladder
- Smooth, collapsible muscular sac
- Temporarily stores urine
- Empty 2-3 long
- Full 5long and stores 1-2 pints urine
8
Urethra
- Thin walled tube
- Carries urine (by peristalsis) from bladder to
outside the body - Females 3-4 long, opening is anterior to
vaginal opening - Males 8 long, opening at tip of penis
- Double function passageway for sperm ejaculation
- internal urethral sphincter
- Involuntary smooth muscle, keeps closed when
urine is not being passed - External urethral sphincter
- Voluntary skeletal muscle through pelvic floor
- Micturition emptying the bladder
- 200mL urine collects and activates stretch
receptors and cause bladder to contract to force
open internal urtheral sphincterfeel urge to
void
9
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
- 2/3 water in intracellular fluid (ICF)
- 1/3 water in extracellular fluid (ECF)
- Electrolytes charged ions that conduct
electrical current, alters blood volume and blood
pressure - Ex. sodium, potassium, calcium ions
- Electrolyte balance maintained by hormones
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- Aldosterone
10
Acid-Base Balance
- Proper function, blood pH between 7.35-7.45
- Alkalosis rise in blood pH above 7.45
- Acidosis drop in pH below 7.35
- Blood Buffers
- Respiratory System
- Renal Mechanisms
- Excreting bicarbonate ions
- Reabsorbing or generating new bicarbonate ions