THIOPHENES PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: THIOPHENES
1
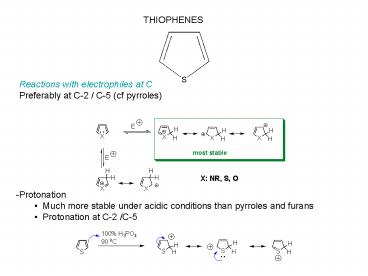
THIOPHENES
Reactions with electrophiles at C Preferably at
C-2 / C-5 (cf pyrroles)
- -Protonation
- Much more stable under acidic conditions than
pyrroles and furans - Protonation at C-2 /C-5
2
Reactions with electrophiles at C
- -Nitration
- Not complete selectivity
- Not HNO3 (explotions)
3
Reactions with electrophiles at C
-Halogenation ca 108 times more reactive than PhH
Chlorination
Bromination
Iodination
4
Reactions with electrophiles at C
-Acylation (FC alkylation not good react)
(strong Lewis acid, AlCl3, polym.)
-Condensation with carbonyl comps
c.f.
5
Reactions with electrophiles at C
-Condensation with carbonyl comps, cont.
-Condensation with imines / iminium ions
Mannich react.
in case of pyrrol, Mannich reag. generated in
situ
Thiophene (and furan) Preformed reagent
generally required
6
Reactions with electrophiles at Sulfur
- Possible for thiophene S in 3rd row
- Not possible for furan / pyrrole O and N in 2nd
row - Probably sp3 S. tetrahedral
- Works best for electron rich thiophenes
7
Reactions with electrophiles at Sulfur
React. with carbenes
8
Reactions with electrophiles at Sulfur
React. with carbenes
9
Reactions with electrophiles at Sulfur
Reactions with nucleophiles NB! Electron rich Aryl
10
Reactions with nucleophiles
11
C-metallation and further reactions
12
Pd cat. couplings
Reat with radicals Seldom synthetically usefull
Cycloadditions
Easier with furan
13
Oxythiophenes
c.f.
Aminothiophenes
c.f. Aminopyrroles
-Amino (not iminoform) - unstable
14
Synthesis of Thiophenes
Carbonyl condensations
Strategy a
15
Strategy a, cont.
Strategy b
Strategy c
16
Strategy d
Hinsberg synth.
17
Miscellaneous carbonyl reactions
18
Cycloadditions
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.