Hopper Design Process PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title: Hopper Design Process
1
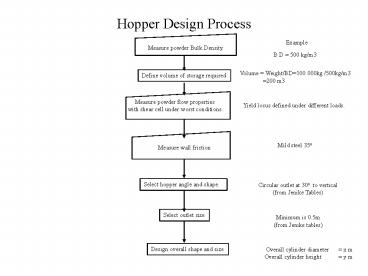
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
Yield locus defined under different loads.
Mild steel 35o
Measure wall friction
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
2
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
How?
Weigh a fixed volume of powder poured into a box
from above.
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
Yield locus defined under different loads.
1 litre
Mild steel 35o
Measure wall friction
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
500 gm
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
3
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
How?
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
Yield locus defined under different loads.
Calculate the weight of powder to be stored, e.g
100 tonnes. Then divide the weight by the bulk
density. This gives the volume of powder
required e.g 200 m3. Add a peaking allowance
of 20 to allow for variations in supply or
demand.
Mild steel 35o
Measure wall friction
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
4
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
How?
Yield locus defined under different loads.
Measure shear stress required for failure as the
normal load is varied.
Mild steel 35o
Normal load
Measure wall friction
Shear force
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
Shear cell
Normal load
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
Draw the yield locus to define the powder
friction.
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
Shear force
5
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
Yield locus defined under different loads.
Measure shear stress required for failure with
the material to be used for construction. .
Mild steel 35o
Normal load
Measure wall friction
How?
Shear force
Construction Material
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
Normal load
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
Use tables to calculate wall friction.. .
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
Shear force
6
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
Yield locus defined under different loads.
Use Jenike graphs to determine design - minimum
hopper angle - minimum hopper outlet . .
Mild steel 35o
Measure wall friction
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
How?
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
angle.
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
Outlet size.
7
Hopper Design Process
Example
Measure powder Bulk Density.
B D 500 kg/m3
Calculate the height and diameter required to
incorporate the total volume required. . .
Volume Weight/BD100 000kg /500kg/m3
200 m3
Define volume of storage required
Measure powder flow properties with shear cell
under worst conditions.
Yield locus defined under different loads.
Diameter.
E.g.200 m3
Mild steel 35o
Measure wall friction
height.
Select hopper angle and shape.
Circular outlet at 30o to vertical (from Jenike
Tables)
How?
Select outlet size
Minimum is 0.5m (from Jenike tables)
Design overall shape and size
Overall cylinder diameter x m Overall
cylinder height y m
8
Note powders can become more cohesive with time,
e.g. Indiciser Test Data
12
Powder O
10
- Note the huge increase of arch strength with
time. - Design for the worst case.
8
Arching
6
Index
Powder M
4
2
0
0
100
200
Time (hours)