Unit I: Lesson 1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Unit I: Lesson 1
Description:
Which era of Western Civilization began with the Italian Renaissance? Modern Times (present times) This economic system is the one practiced in the United States ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:190
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Unit I: Lesson 1
1
(No Transcript)
2
- Unit I Lesson 1
- Geography
- Pre-history
- History
- Revolution
- Civilization
3
- Identify 10 details you see in this scene.
- How would you describe the scene?
- Who are the people involved?
- What do you hear, smell, taste and feel in this
scene? - What action do you see in this scene?
4
GEOGRAPHY IS
- the study of
- people, their
- environment, and the
- resources available to them.
5
5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY
Place
Movement
Region
THE HUMAN
STORY
Human- Environment Interaction
Location
6
HISTORY IS
- humanitys past based on written records
(evidence) - recorded time beginning about
- 5,000 yrs. ago
- found in letters, tax records, diaries, film,
photographs, and on the - internet
7
- History is based on three factors, each one
affecting the other - two (ESP)
- E
conomics
- Society
- P
olitics
8
TRAITS OF PRE-HISTORIC PALEOLITHIC (OLD STONE)
AGE
- nomadic
- used a spoken language
- wore clothing
- were technical (could make use tools)
- caves / over-hangs as shelters
- built fires for
- light,
- warmth,
- protection,
- cooking
- belief in an afterlife
?
9
THE NEOLITHIC (NEW STONE) AGE INTRODUCED AN
AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION
- People B/4
- hunted
- gathered
- nomadic
- push factors
- People after
- learned to farm
- produced own food
- settled in villages
- domesticated animals
- pull factors
10
BASIC FEATURES OF CIVILIZATIONS
- Farmers cultivated lands along river valleys,
producing surplus food gt - Surpluses caused populations to expand gt
- As populations grew, villages swelled into
- cities.
11
EFFECTS OF THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION
- Changed the way humans lived
- Use of agriculture allowed humans to develop
permanent settlements, social classes, new
technologies - Some of these early groups settled in the
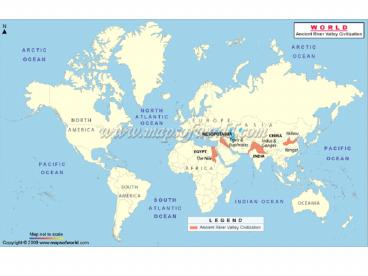
fertile valleys of - the Nile, Tigris-Euphrates, Yellow, and Indus
Rivers - This resulted in the rise of great
civilizations in - Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, and India
- In the Americas, groups of Asian hunters
crossed a land-bridge
connecting Asia and - Alaska along what is now known as the
- Bering Strait. By spreading southwards, they
settled
along lakes and rivers where they
experienced their
own - Neolithic Revolution in which they learned to
grow maize.
12
A CIVILIZATION
- is a complex, highly organized, social order
with the following 5 traits
13
1). cities (centers of trade for a larger area)
14
2). advanced technology
15
3). specialized (specifically trained)
workers
4). form of writing
16
5). Complex institutions
White House
Congress
a. form of government
b. organized religion
17
HOW DO CIVILIZATIONS SPREAD AND CHANGE?
- Ancient rulers often gained enough
- power to conquer territories beyond their cities
- these rulers, therefore, created
- city-states and
- even more powerful rulers often created
- empires
- Civilizations can also change when the natural
environment changes. - Interaction among people also causes
environments to change.
18
CULTURAL DIFFUSION IS
- the spread of ideas,
- customs, technologies from one people to
another through migration, trade, - warfare.
19
INDIVIDUAL YEARS OF DATING HISTORY
- B.C. b/4 the birth of
- Christ or B.C.E.
- (b/4 the Common Era)
- A.D.
- Anno Domini (since the birth of Christ) or C.
E. - (since the Common Era)
20
AGES OR ERAS OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION
- Ancient Times 4000 B.C. A.D. 500 (until the
fall of the Roman Empire) - Medieval Times (the Middle Ages) A.D. 500
(from the fall of Rome) A.D. 1400 (until the
Italian Renaissance)
21
- Modern Times A.D. 1400 (when Italian
Renaissance began) - to the present
22
Oink or Cackle?
LETS REVIEW WHAT WE KNOW SO FAR!
23
The five themes of geography are
human-environment interaction, location, place,
movement, and ___
region
24
Geography is the study of people, their ___, and
the resources made available to them.
environment
25
When people changed from hunting and gathering
their food to settling in villages and learning
to farm their own crops and raise their own
animals, this change became known as the ___ ___.
Neolithic Revolution
26
Humanitys past based on written records is
called ___.
history
27
A complex, highly organized social order is
called ____.
civilization
28
The three factors that always relate to and
affect one another are economics, society, and
___.
politics
29
The spreading of ideas, customs, and technologies
from one people to another through migration,
trade, or war is called ___ ___.
cultural diffusion
30
How did Asian groups during the Stone Age arrive
in the Americas?
They crossed a land bridge that is now known as
the Bering Strait.
31
The five characteristics or traits that
constitute any civilization are specialized
workers, advanced technology, form of writing,
complex institutions (government religion), and
___.
centers of trade (cities)
32
Which era of Western Civilization ended with the
fall of the Roman Empire in A.D. 476?
Ancient Times
33
Which era of Western Civilization began with the
fall of the Roman Empire?
Medieval Times (Middle Ages)
34
Which era of Western Civilization began with the
Italian Renaissance?
Modern Times (present times)
35
This economic system is the one practiced in the
United States.
capitalism
36
People in ancient civilizations practiced this
when they moved from their farming communities to
centers of trade to work as skilled artisans and
merchants
urbanization
37
- TERMS
- Latin term for A. D. meaning in the year of our
Lord or since the birth of Christ - Anno Domini
- a state that controls other lands and peoples
- empire
- kind of government headed by religious leaders
- theocracy
- dictatorial government controlling all aspects of
life - totalitarian
- a small, usually wealthy, group that holds
political power - oligarchy
- ruler with unlimited power
- autocrat