Diffusion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Diffusion
Description:
Speeded up by increased surface area, increased concentration gradient and ... E.g. minerals pumped into root xylem to maintain ? gradient from root to xylem ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:62
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Diffusion
1
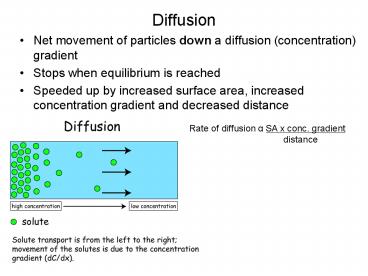
Diffusion
- Net movement of particles down a diffusion
(concentration) gradient - Stops when equilibrium is reached
- Speeded up by increased surface area, increased
concentration gradient and decreased distance
Rate of diffusion a SA x conc. gradient
distance
2
Simple diffusion across membranes
- Small, lipid soluble (non-polar) molecules will
diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer, e.g.
oxygen, steroid hormones - Large, polar (water soluble) molecules will not
cross membranes without the help of proteins - There are some exceptions (e.g. water)
- Normal diffusion rules apply
3
Facilitated Diffusion 1
- Large or polar molecules will not dissolve in
phospholipid membranes - They must diffuse through channels created by
proteins embedded in the membrane, e.g.
K-channel in neurone membrane - Rate of diffusion depends on number of channels
available
4
Facilitated Diffusion 2
- Many channels are always open
- However some can open and close in response to
chemicals or membrane potential (voltage) - These are called gated channels
- E.g. liver cells have glucose channels that open
when insulin binds to a receptor site beside the
channel - E.g. Na-channels in neurone membranes open when
membrane potential reaches -55mV (threshold)
5
Active transport
- Uses carrier proteins in membrane
- Moves substances against a concentration gradient
- Requires energy in the form of ATP
- Stops when respiration stops
- E.g. Na/K-pump
- E.g. minerals pumped into root xylem to maintain
? gradient from root to xylem
6
Water potential (?)
- ? is the tendency of a solution to lose water, it
is decreased by the addition of a solute, it is
increased by external pressure - ? is measured in kPa
- ? is always negative, i.e. ? of water is 0, ? of
sugar solution may be -2000 kPa - Water always moves to the lowest (most negative)
? - Hypotonic higher ? than cell
- Hypertonic lower ? than cell
- Isotonic same ? as cell
7
Osmosis
- Water molecules can diffuse easily across
membranes - Many solute molecules, e.g. Na, cannot diffuse
across membranes (without help) - Osmosis is the diffusion of water, down water
potential (?) gradient, across a selectively
permeable membrane
8
Bulk Transport
- Endocytosis takes substances into a cell
- Phagocytosis involves insoluble material (e.g.
bacteria) - Pinocytosis involves soluble material (liquid)
- Exocytosis removes substances (e.g. enzyme
secretion from pancreas cells)
- Transports large quantities of material
- Involves invagination of membrane to form
vesicles (vacuoles) - It is sometimes triggered by the substance
binding to a receptor on the cell surface