System Life Cycle - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
System Life Cycle
Description:
Be able to prepare an operational need statement ... Evaluations consist of reviews and audits ... Ergonomic Design of an In-Car E-mail system. Functionality? ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:25
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: System Life Cycle
1
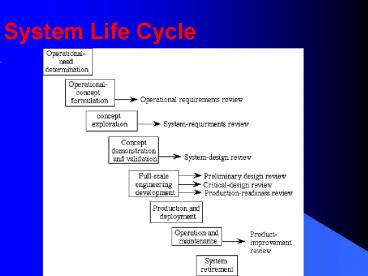
System Life Cycle
09/10/99
2
Goals
- Understand the major phases of the system life
cycle - Be able to prepare an operational need statement
- Be able to create an operational concept statement
3
Operational Need Determination
- Example of an Operational-Need Document
- The Fourth National Bank and Trust co.
- existing and Planned Operational Capabilities
- additional Operation Capability Required
- exploitable Technology
- constraints
- user Classes
09/10/99
4
Operational Concept Formulation
- Example of an Operational Concept that satisfies
the Operational Need for Automated Bank Tellers - bank Customer Transaction Concept
- allowable Bank Customer Transactions
- allowable Number of Transactions
- logistics and Maintenance Concept
- management Concept
- training Concept
09/10/99
5
Concept Exploration
- Major HF activities during concept exploration
- assist in allocation of functions
- conduct trade studies to evaluate costs and
benefits of alternatives - develop user-system interface requirements
- prototype and evaluate user interfaces
09/10/99
6
Universal Access to ATM
- http//www.sun.com/access/wp-aatm/
- Japanese Tourist Visiting Canada
- Spanish Businessman with Low Vision
- Blind Student Making a Deposit
7
(No Transcript)
8
Smart Card with User Profile
9
Concept Demonstration
- Design concept is mocked up, simulated and
tested. - Does it meet
- requirements for staffing, operating,
maintaining, and supporting the system? - dimensional requirements for workspace, etc.,
- safety, personnel and training requirements
09/10/99
10
Full Scale Engineering Development
- Full prototype is developed and tested.
- Prototype includes all necessary hardware and
software - Major HF tasks
- Usability testing with product and documentation
- Reference of testing results to performance
requirements
09/10/99
11
Production and Deployment
- Multiple copies of system are produced and
distributed - Major HF tasks
- training operators and users on system
- evaluating usability or operability of system
- identifying changes to be made for later versions
09/10/99
12
Operation and Maintenance
- Systems delivered and in use
- Major HF tasks
- conduct follow-on tests of operator satisfaction
with use and maintenance of system - results of tests serve as guides to engineering
changes for subsequent versions
09/10/99
13
System Retirement
- In this phase the system is retired from use,
scrapped or replaced - Concerns about environmental conversation and
recycling of materials - Ease and expense of disposal should be considered
during system design
09/10/99
14
Life Cycle Control Points
- There are control points throughout the system
lifecycle - Control points are milestones times at which
evaluations are made - Evaluations consist of reviews and audits
- System engineer describes what has been done and
defends activities
09/10/99
15
Questions asked at Control Points
- Is the work - to date- satisfactory?
- Do any changes need to be made in the
development? - Are the budgets and timetables for completion
realistic?
16
Exam
- Exams will be Closed book, closed notes
- Because, dont want people copying from the text
book and their notes to give the answers and then
telling me the answer must be right because it
was in the book! - You will be expected to study the material and
know it.
17
Project
- Ergonomic Design of an In-Car E-mail system.
- Functionality?
- Evaluative criteria (safety, performance, etc.)
- How will you prototype/test your design?
- Start by checking out relevant literature and the
state of the art.
18
Hands Free Computer Interfaces
- In many situations where keyboard input is
impractical and visual displays are restricted or
unavailable, speech provides the only way of
interacting with a computer.
- surgeons and other medical staff can use speech
dictation to enter reports when their hands are
busy and where touching a keyboard represents a
hygiene risk. - In vehicle and airline maintenance, warehousing
and many other hands-busy tasks