Fundus camera - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Fundus camera
Description:
Slit-lamp imaging systems are also offered which consist of the digital camera back, slit-lamp adapters, computer and database software and networking solutions. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:121
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Fundus camera
1
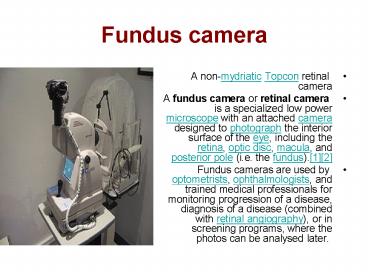
Fundus camera
- A non-mydriatic Topcon retinal camera
- A fundus camera or retinal camera is a
specialized low power microscope with an attached
camera designed to photograph the interior
surface of the eye, including the retina, optic
disc, macula, and posterior pole (i.e. the
fundus).12 - Fundus cameras are used by optometrists,
ophthalmologists, and trained medical
professionals for monitoring progression of a
disease, diagnosis of a disease (combined with
retinal angiography), or in screening programs,
where the photos can be analysed later.
2
Optical principles
- The optical design of fundus cameras is based on
the principle of monocular indirect
ophthalmoscopy.12 A fundus camera provides an
upright, magnified view of the fundus. A typical
camera views 30 to 50 degrees of retinal area,
with a magnification of 2.5x, and allows some
modification of this relationship through zoom or
auxiliary lenses from 15 degrees which provides
5x magnification to 140 degrees with a wide angle
lens which minifies the image by half.2 The
optics of a fundus camera are similar to those of
an indirect ophthalmoscope in that the
observation and illumination systems follow
dissimilar paths. The observation light is
focused via a series of lenses through a doughnut
shaped aperture, which then passes through a
central aperture to form an annulus, before
passing through the camera objective lens and
through the cornea onto the retina.3 The light
reflected from the retina passes through the
un-illuminated hole in the doughnut formed by the
illumination system. As the light paths of the
two systems are independent, there are minimal
reflections of the light source captured in the
formed image. The image forming rays continue
towards the low powered telescopic eyepiece. When
the button is pressed to take a picture, a mirror
interrupts the path of the illumination system
allow the light from the flash bulb to pass into
the eye. Simultaneously, a mirror falls in front
of the observation telescope, which redirects the
light onto the capturing medium, whether it is
film or a digital CCD. Because of the eyes
tendency to accommodate while looking though a
telescope, it is imperative that the exiting
vergence is parallel in order for an in focus
image to be formed on the capturing medium. - Since the instruments are complex in design and
difficult to manufacture to clinical standards,
only a few manufacturers exist Topcon, Zeiss,
Canon, Nidek, and Kowa
3
Applications
- Practical instruments for fundus photography
perform the following modes of examination - Color, where the retina is illuminated by white
light and examined in full color. - Red-free, where the imaging light is filtered to
remove red colors, improving contrast of vessels
and other structures. - Angiography, where the vessels are brought into
high contrast by intravenous injection of a
fluorescent dye. The retina is illuminated with
an excitation color which fluoresces light of
another color where the dye is present. By
filtering to exclude the excitation color and
pass the fluorescent color, a very high-contrast
image of the vessels is produced. Shooting a
timed sequence of photographs of the progression
of the dye into the vessels reveals the flow
dynamics and related pathologies. Specific
methods include sodium fluorescein angiography
(abbreviated FA or FAG) and indocyanine green
(abbreviated ICG) angiography.
4
Gallery
- A close-up of the controls of a Topcon retinal
camera
5
Canon CX-1 Myd/NonMyd 15.1 MP Digital Retinal
Imaging System for Color, Red-Free, Cobalt,
FA and Auto Fluorescent Retinal Photography
- Canon CR-1 Mark II Non-Mydriatic 45-degree (with
2X) , Canon CF-1 Mydriatic 50-degree (with 2X)
and Canon CX-1 Myd-NonMyd 50/45 degree Digital
Retinal Imaging Systems can be customized to
include an instrument table, computer, database
software, networking and printing capability.
System components can be customized to fit your
pre-test or exam lane area. Slit-lamp imaging
systems are also offered which consist of the
digital camera back, slit-lamp adapters, computer
and database software and networking solutions.
Ask about the 3 year warranty limited time
offer on Canon Retinal cameras!Ask about our
ADA (Section 44) Wheelchair Accessible Motorized
Instrument Tables!Ask about the Canon Financial
6 month 0 Same as Cash Lease program limited
time offer! Section 179 of Federal Tax Code
could allow up to 135,000 of capital
expenditures to be deducted in 2010. Check with
your Accountant. Image AMD, Glaucoma, Diabetic
Retinopathy, Nevus and other retinal pathologies
for annual comparative analysis! Change patient
fixation to image fields - nasal, temporal,
superior and inferior.Stereo imaging technique
is easily learned to obtain 3-D images of Optic
Disc or Macula!Anterior Segment Imaging is
easily obtained using Retinal camera!Call to
request an on-site demonstration - serious buyers
call now!
6
Slit Lamp Imaging
7
(No Transcript)
8
Testimonials Superior design and quality
- "Image transfer time from camera to computer is a
split second using the new EOS Series cameras
with USB 2.0 output". - "There are two equally important skills needed to
interpret retinal images accurately. The first is
to see what is there. The second is to not see
what is not there. Our patients trust us to care
for them correctly and Canon makes it possible." - "The Canon design was so intuitive that training
screeners could be done with a minimum of
effort." - "For patients that are young and have no retinal
pathology, the camera can image the concave
surface that surrounds the foveola known as the
"umbo", the central pit of the fovea. It is the
internal limiting membrane that appears as a
"very" small halo right at the center of the
fovea." This is "not" artifact!
9
Canon Non-Mydriatic Camera Development
- Canon's optical technology capability led to the
development of the World's First Non-Mydriatic
Retinal camera for mass screening of adult
diseases such as Diabetic Retinopathy, Glaucoma
and Macular Degeneration. Today, Canon offers
it's 10th generation camera system - the Canon
45-degree Non-Mydriatic Digital Retinal Camera
system using Canon's EOS Series Digital Cameras.
10
Advanced Digital Imaging, Quick access to images
and Upgradable
- Once images have been captured, they are
transferred to a connected PC for observation.
Using the imaging software, youll be able to
check ocular conditions right away, or take
another shot when necessary (for example if the
examinee blinked). The Canon Retinal
camera produces images that are ideal for diverse
applications, including telemedicine, PC-based
video conferencing, electronic filing, and remote
storage. A Canon digital camera can be easily
attached/detached without an adapter. Owners of
previous film based model cameras (Canon CR-6)
can upgrade to a digital system by contacting us
for more details.
11
Superior Image quality
- Canon technology provides the level of image
quality thats essential for diagnostic
needs. Canon retinal cameras use a combination of
Canon optics designed specifically for retinal
imaging and Canons renowned SLR digital (EOS)
camera technology. The EOS series incorporates
the Canon DIGIC imaging engine, creating images
that are well defined with color reproduction
that is completely natural. The large CMOS sensor
has a 32 aspect ratio, traditional to 35mm film,
providing images that are luminescent, life-like
and incredibly rich in detail. As a result, you
can capture extremely refined images of the
retina for detecting or monitoring Diabetes,
Glaucoma and other serious conditions
12
Digital Speed, Digital Versatility, Software
- From easy alignment to digital capture, the
Canon Retinal camera has all the features needed
to boost eye exam efficiency. Images can be
checked just moments after capture. Image quality
is outstanding! The software features an
easy-to-use windows format with drop-down menus
allowing access to many functions including
side-by-side and multi-image comparison, zooming,
2X cursor image magnifier, red/green/blue color
image, stereo, e-mail, export, printing,
archiving, networkable platform, export to EMR
software and many more diagnostic tools
13
User-Friendly Operation, Easy Alignment
Focusing
- Preparing for image capture is remarkably simple,
thanks to a two-step procedure. First, you align
the split pupil image with the operation lever.
Then you switch to the retinal display to adjust
the split lines and working distance dots. This
system makes it easy to obtain the correct
distance to the retina, ensuring sharp images
with practically every shot! Shifting the
joystick to perform sequential imaging for stereo
photography is attainable
14
Fixation target Reduced illumination
- Eye fixation is simplified by a user-friendly
internal fixation target. The target is
controlled with a button on the operation panel,
allowing you to induce movement with one hand
while adjusting focus with the other. The Canon
Retinal camera needs only a small amount of light
to capture clear images, so examinees wont be
discomforted by brightness. Required illumination
is 90 less than instant photography and 75 less
than with film photography.
15
- Edge-to-edge detail Confidence in detecting
pathology - With an entire image thats sharp and
clear, you get improved diagnostic insights. - Magnification without pixelation Superior image
quality - Because our cameras create images using
individual pixels versus clumps of pixels, they
retain high resolution even as the image is
magnified. As a result, Canon technology lets you
see what cant be seen with other cameras. - Alignment and focusing tools Reduced training
costs Our powerful but easy-to-use technology
lets even inexperienced technicians take perfect
pictures every time.
16
- Reduced illumination Increased patient comfort
Only a small amount of light is needed for
image capture, so your patient isnt discomforted
by brightness. - The Total solution Efficient servicing As the
only company to offer both the fundus and camera
back, Canon covers the whole picture. And the
camera back can be upgraded anytime.
17
Image Anywhere
- Canon is continually advancing imaging science.
Building on a long legacy of advanced
breakthroughs and industry leadership, we provide
innovative technologies expressly designed to
help you improve patient outcomes throughout
their healing process. Thats our commitment.
Thats Canon inSight. And youll see it in
everything we do.
18
Intraretinal Hemorrhage
HTN retinopathy with AV nicking and mild vascular
tortuosity
Mild NPDR
Picture artifact. Large optic cup Prominent
foveal reflex
19
Myopic degeneration with PPA and macular
Chorioretinal atrophy
Hypertensive retinopathy with Arteriolar
attenuation. Increased arterial reflex. AV
nicking.
Tigroid Fundus. Large optic cup
Proliferative retionpathy with regressed NVD.
Previous PRP
20
Diabetic retinopathy with microaneurysms with
macular exudates
Proliferative retinopathy with previous PRP
Nonexudative AMD with Drusen and RPE dropout
Subfoveal CNVM with surrounding subretinal
hemorrhage and exudates
21
Vitreous haze. Fleck Retinopathy
chorioretinal scar with fibrovascular stalk
secondary to focal chorioretinitis
AMD with Mild intermediate drusen
Advanced AMD with Geographic Atrophy involving
fovea
22
POHS with regressed macular CNVM, PPA, and
punched out CR scar
AMD with severe large drusen
Myopic Degeneration
Flat choroidal Nevus adjacent to optic nerve
23
Diabetic retinopathy with Macular exudates at
foveal edge, with possible CSME
Diabetic retinopathy with Macular exudates
POHS regressed macular CNVM with, PPA, and
punched out CR scar
Conjunctival nevus