Centrioles - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Centrioles
1
Centrioles
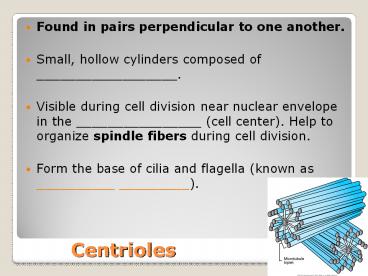
- Found in pairs perpendicular to one another.
- Small, hollow cylinders composed of
__________________. - Visible during cell division near nuclear
envelope in the ________________ (cell center).
Help to organize spindle fibers during cell
division. - Form the base of cilia and flagella (known as
__________ _________).
2
Nucleus
- Control center of the cell.
- Contains the DNA of the cell
- Cell may have one nucleus, be multi-nucleated, or
anucleated. - Anatomy is divided into four parts
- Nuclear Envelope/Membrane
- Nucleoplasm
- Chromatin
- Nucleoli
3
Nuclear Envelope and Nucleoplasm
- Nucleus is separated from cytosol by a nuclear
________________ composed of two lipid bilayers - Outer layer is continuous with the ER.
- Covered in ___________________.
- Contains nuclear __________ - channels through
envelope. - Pores are large enough to allow protein in and
RNA out of nucleus, but DNA cannot fit through. - _________________ - gelatinous substance that
fills the nucleus and is similar to cytosol.
4
Nucleoli
- Small, dark, spherical patches contained within
the nucleus. - Not bound by a membrane.
- Where _____________ _____________ are made
(before they are sent to the cytoplasm and become
functional). - Contain DNA that governs synthesis of __RNA.
5
DNA, RNA and Chromatin
- _____________ - made up of DNA and globular
proteins called histones. - DNA winds around 8 histone molecules to form a
________________. - Nucleosomes are joined together by linker DNA.
- The chromatin condenses into super-coiled
x-shaped structures called ________________
during cell division. - Two chromatids held together by a protein called
a centromere.
6
Life Cycle of the Cell
- Two major periods
- _______________
- Begins immediately after a cell has divided into
two new cells. - New cell is growing, maturing, and
differentiating. - DNA replication occurs here.
- Cells spend majority of time in this phase.
- ________________ phase
- When cell is actively dividing into two equal
daughter cells.
7
Interphase
- Three subphases
- ___________ 1 (G1)- intense metabolic activity
and cell growth cell size and number of
organelles doubles - _____________ (S)- DNA replication
- ___________ 2 (G2)- very brief synthesis of
proteins needed for mitosis
8
DNA Replication
- DNA must be replicated before the cell can divide
into two identical copies. - During S phase of Interphase
- Chromatin uncoils, histones separate from DNA,
and a helicase enzyme separates the helix into 2
nucleotide chains - DNA polymerase III matches free floating
nucleotides with the exposed nucleotides on the
unwrapped DNA chain - Histones wrap around each new strand. The strands
supercoil into a chromosome held together by a
centromere.
9
Mitosis Prophase
- Spindle apparatus appears
- Centrioles have just finished replicating and
each pair moves from being near the nucleus
(centrosome) to being at opposite poles of the
cell. - Microtubules called spindle fibers extend from
centrioles to the center of the cell - Nuclear envelope disintegrates
10
MitosisMetaphase
- Chromosomes are lined up in center of cell
(equator) to form the metaphase plate. - Centromere of each chromosome is attached to a
spindle fiber.
11
MitosisAnaphase
- Centomeres split apart and sister chromatids
separate as the spindle fiber pulls them away
from each other toward the centrioles. - Cell elongates and cytoplasm begins to constrict
along metaphase plate.
12
MitosisTelophase
- Final stage of mitosis
- Begins when chromosomal movement stops and
chromatin unraveling begins - New nuclear envelope appears as well nucleoli.
- Spindle fibers disassemble
- ------------------------------------------------
- CYTOKINESIS (division of cytoplasm) occurs after
Telophase. - New daughter cells enter interphase.
13
TRANSCRIPTION
- Process of making mRNA
- Occurs in the nucleus
- Helicase separates the double helix into single
strands of DNA - RNA polymerase connects free floating RNA
nucleotides to their coordinating DNA
nucleotides. - Once transcription ends, RNA polymerase detaches,
mRNA is released, and the DNA forms a double
helix again.
14
Translation
- Process of building protein. Occurs in the
cytoplasm. - Information on mRNA is translated from
nucleotides to amino acids. - A ribosome wraps around the strain of mRNA.
- rRNA on the ribosome has an active site where
tRNA can attach. - As each codon of mRNA is read, tRNA with a
corresponding anticodon brings the appropriate
amino acid to the mRNA. - A peptide chain is formed as amino acids link
together and is eventually released.
15
Membrane Processes
- In order to maintain homeostasis, a cell must
select what it needs from the ________cellular
fluid and bring it into ________cellular
environment. - Electrolytes, fatty acids, vitamins, amino acids,
hormones, gases - Must excrete waste products or transport
resources needed in other parts of the body to
the extra cellular environment. - Processes may be _______________ (do not require
ATP) OR _____________ (do use ATP).
16
Passive Membrane Processes
- Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Filtration
- NO ENERGY REQUIRED
17
Diffusion
- Movement of molecules from an area of _________
concentration to _____________concentration - Driven by a ____________ ____________- the
difference between the concentration of one area
and the concentration of another. - Will continue until the molecule is evenly
dispersed throughout the solution
18
Facilitated Diffusion
- Proteins assist in movement of molecules from an
area of high to low concentration - Speed of facilitated diffusion is limited by the
______________ of carrier molecules.
19
Osmosis
- Passive movement of ___________ through a
semi-permeable membrane from a dilute solution to
a concentrated solution. - Similar to diffusion, but here, we are referring
to the movement of water molecules rather than
solute.
20
Osmosis/TonicityTerminology
- ___________________ Cytoplasm (inside) of cell
is more concentrated than extracellular (outside)
fluid - __________________ Extracellular fluid is more
concentrated than cytoplasm - __________________ Extracellular fluid has same
concentration of dissolved substances as
intracellular fluid
21
Filtration
- The passage of a fluid/small molecules through a
semipermeable membrane that does not allow cells/
large molecules to pass through. - Fluid/small molecules are pushed through the
membrane when the pressure on one side of the
filter is greater than on the other side. - The force that pushes the liquid is the
_______________ pressure.
22
Active Membrane Processes
- Active Transport
- Cytosis
- Endocytosis, Exocytosis
- REQUIRE ATP
- Some molecules are unable to enter the cell via
passive routes because - Molecules are not lipid soluble, too large for
protein pores, or are on the wrong side of the
concentration gradient - Do not require a concentration gradient
23
Active Transport
- Active movement of molecules by a specific
carrier protein with a binding site for ATP
molecules may move against concentration
gradient. - __________ system substances are moved in the
same direction - __________ system substances are moved in
opposite directions
24
Endocytosis
- Importing substances from the extracellular space
to the intracellular environment. - ____________________
- Cell engulfs
- ____________________
- Cells invaginates
- ___________-___________ endocytosis
- Specialized protein receptors bind to ligands.
- Ligand-small molecules that bind to receptors or
larger molecules.
25
Exocytosis
- Exporting substances from the intracellular to
the extracellular environment - Excretion of waste products and secretion of
manufactured substances. - Packaged in secretory vesicles which fuse with
cell membrane and are ejected to extracellular
space. - _____________- exocytosis of wastes
- _____________- exocytosis of manufactured
molecules