How Rocks Form - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
How Rocks Form
Description:
How Rocks Form Geologists classify ... and mineral composition. Mineral Mixture Granite is a mixture of light-colored minerals, ... Graphic Organizer Exit Quiz ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:248
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: How Rocks Form
1
How Rocks Form
- Classifying Rocks
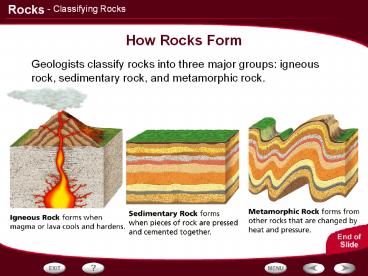
- Geologists classify rocks into three major
groups igneous rock, sedimentary rock, and
metamorphic rock.
2
Classifying Igneous Rocks
- Igneous Rocks
- Igneous rocks are classified according to their
origin, texture, and mineral composition.
3
Mineral Mixture
- Igneous Rocks
- Granite is a mixture of light-colored minerals,
such as feldspar and quartz, and dark-colored
minerals, including hornblende and different
types of mica. But granite can vary in mineral
composition. This affects its color and texture. - Study the circle graph and then answer the
questions.
4
Mineral Mixture
- Igneous Rocks
- Reading Graphs
- What mineral is most abundant in granite?
- Feldspar
5
Mineral Mixture
- Igneous Rocks
- Reading Graphs
- About what percentage of granite is made up of
dark minerals?
- 10
6
Mineral Mixture
- Igneous Rocks
- Calculating
- If the amount of quartz increases to 35 percent
and the amount of dark-colored minerals stays the
same, what percentage of the granite will be made
up of feldspar?
- 100 - (35 10) 55
7
Mineral Mixture
- Igneous Rocks
- Predicting
- How would the color of the granite change if it
contained less feldspar and more mica and
hornblende?
- The overall color would be darker.
8
- Igneous Rocks
Main Idea
Igneous rocks are classified by origin, texture,
and composition.
Detail
Detail
Detail
Extrusive rock forms from lava on the surface
intrusive rock forms from magma from beneath the
surface.
Intrusive rocks have larger crystals than
extrusive rocks because they cool more slowly.
High-silica rocks are light colored low-silica
rocks are dark colored.
9
End of SectionIgneous Rocks
10
From Sediment to Rock
- Sedimentary Rocks
- Most sedimentary rocks are formed through a
series of processes erosion, deposition,
compaction, and cementation.
11
Sedimentary Rocks
- Sedimentary Rocks
- From Sediment to Rock
- Erosion
- Deposition
- Compaction
- Cementation
- Uses of Sedimentary Rocks
- Building Materials
- Tools
12
End of SectionSedimentary Rocks
13
Do you know..
- Metamorphic Rocks
Q. Why do the crystals in gneiss line up in bands?
A. Gneiss is a type of metamorphic rock that is
foliatedthe crystals are flattened to form
parallel lines.
Q. How does quartzite form from sandstone?
A. High temperature and pressure on the minerals
in sandstone cause them to be changed into
minerals that make up quartzite.
14
End of SectionMetamorphic Rocks
15
A Cycle of Many Pathways
- The Rock Cycle
- Forces deep inside Earth and at the surface
produce a slow cycle that builds, destroys, and
changes the rocks in the crust.
16
Graphic Organizer
Metamorphic
Igneous
Organic
Foliated
Extrusive
Chemical
17
Exit Quiz Sequencing
- The Rock Cycle
- Before you leave, and without using your notes
from today, draw the rock cycle, using the three
types of rock below with arrows.
Igneous
Metamorphic
Sedimentary