Pavement Base - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
Pavement Base
Description:
Title: Flexible Pavements Subject: Flexible Pavement Introduction Author: Stephen T. Muench Last modified by: mohd Created Date: 10/3/2000 4:02:09 AM – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:116
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Pavement Base
1
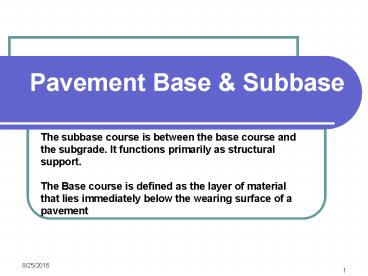
Pavement Base Subbase
The subbase course is between the base course and
the subgrade. It functions primarily as
structural support. The Base course is defined
as the layer of material that lies immediately
below the wearing surface of a pavement
CEE 320Steve Muench
2
Subbase Material
- Subbase
- May consist of selected materials, such as
natural gravels, that are stable but have
characteristics which make them not completely
suitable as base course (less CBR, MR) - They may also be of stabilized soil or simply
select borrow. - The quality of subbase can vary within wide
limits as long as the thickness design criteria
(SN) are fulfilled.
3
Base Material
- Base
- Consist of selected good quality Aggregate. In
the case of asphalt pavement, the base course
lies close to the surface and therefore, it must
possess high resistance to deformation in order
to withstand the high pressure imposed upon it. - Base material should be of the same quality as
that used in the Surface layer. The aggregate
should me hard, sound and durable, resistant to
abrasion, and angular.
4
Purpose Importance of Subbase
- The purpose of a subbase is to permit the
building of relatively thick pavement at low
cost. - It functions primarily as structural support but
it can also - Minimize the intrusion of fines from the
subgrade into the pavement structure. - Improve drainage.
- Minimize frost action damage.
- Provide a working platform for construction
5
Purpose Importance of Base
- The purpose and function of the base varies
according to type of pavement. - Base course is used under rigid pavements for
- 1- Prevention of pumping,
- 2- Protection against frost action,
- 3- Drainage,
- 4- Prevention of volume change of the subgrade,
- 5- Increase structural capacity, and
- 6- Expedition of construction
- Base course is used under flexible pavement to
- 1- increase the structural capacity by
providing added stiffness and resistance to
fatigue, - 2- Additionally, it distribute the traffic load
on larger area of the subbase and therefore,
prevent failure, - 3- It also provide drainage,
- 4- prevent frost and volume change in the base,
and - 5- Expedition of construction
6
Some Representative Aggregate Gradation for
pavement layers.
Percent Passing Percent Passing Percent Passing
Sieve Size Sieve Size Subbase Course Base Course Surface Course
63 mm 2.5-inch - 100 -
50 mm 2-inch 100 97 100 -
37.5 mm 1.5-inch 97 100 - -
25.0 mm 1-inch - - 100
19.0 mm 0.75-inch - - 97 100
12.5 mm 0.5-inch - 40 60 (8) -
4.75 mm No. 4 40 60 (8) - 41 71 (7)
0.425 mm No. 40 - 9 17 (4) 12 28 (5)
0.075 mm No. 200 0 12 (4) 4 8 (3) 5 16 (4)
Notes Number in parentheses indicates the allowable deviations ( ) from the target value. These are only representative gradations and do not represent a comprehensive list of FHWA specified gradations. Notes Number in parentheses indicates the allowable deviations ( ) from the target value. These are only representative gradations and do not represent a comprehensive list of FHWA specified gradations. Notes Number in parentheses indicates the allowable deviations ( ) from the target value. These are only representative gradations and do not represent a comprehensive list of FHWA specified gradations. Notes Number in parentheses indicates the allowable deviations ( ) from the target value. These are only representative gradations and do not represent a comprehensive list of FHWA specified gradations. Notes Number in parentheses indicates the allowable deviations ( ) from the target value. These are only representative gradations and do not represent a comprehensive list of FHWA specified gradations.
7
Some Representative Gradation Specifications for
Aggregate Courses from the 1996 FHWA