A cholinergic synapse - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 50
Title:
A cholinergic synapse
Description:
16 different alleles; the gene products can combine into heteromers ( 2 2 1 and ... Miosis; eye accommodation, eased outflow of humor. Nicotinic agonists. Nicotine ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:818
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: A cholinergic synapse
1
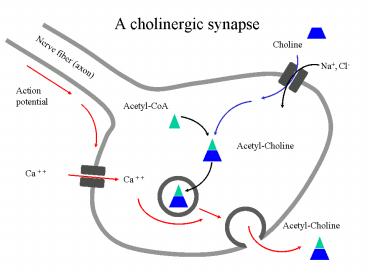
A cholinergic synapse
Choline
Nerve fiber (axon)
Na, Cl-
Action potential
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-Choline
Ca
Ca
Acetyl-Choline
2
A cholinergic synapse (2) Rapid transmitter
inactivation by cholinesterase
Choline
Acetate
Acetyl-CoA
Action potential
Acetyl-Choline
Choline esterase
Ca
3
Types of cholinergic receptors
- The nicotinergic acetylcholine receptor
- Activated by nicotine
- A pentameric protein transmembrane channel
- Permeability for small cations
- 16 different alleles the gene products can
combine into heteromers (?2?2?1 and so on),
giving rise to an even greater number of variants
- Related to GABAA, glycine, and 5-HT3 receptors
- The muscarinergic acetylcholine receptor
- Activated by muscarine
- A single chain transmembrane protein, not a
channel - Relays signals through G-proteins (various types)
4
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor A
ligand-gated channel
- There are two important functional classes of ion
channels - Voltage-gated channels. With these, a change in
the transmembrane potential (voltage) effects a
transient opening. - Channels of this type are the basis of action
potential propagation along excitable membranes. - Ligand-gated channels. Here, the transient
opening is effected by the binding of specific
ligand molecules neurotransmitters, or, with
intracellular channels, second messengers (IP3,
cAMP). - Ligand-gated channels are important for rapid
intercellular transmission of action potentials.
5
NAR in / isolated from electric ray cell membranes
6
How fish electric organs work
a)
b)
NAR
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Nerve endings
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
7
Contour maps of the NAR receptor
8
NAR structure (electron density map)
9
ACh
ACh
Leucine residues
10
The bottleneck of NAR in the open state
11
The intracellular vestibule and its role in
conductance and ion selectivityKelley et al.,
Nature 424321-324 (2003)
12
Characterization of the NAR acetylcholine binding
site by photoaffinity labelling
acetylcholine
4-(3-Trifluoromethyl)-3H-diazirin-3-ylbenzoylcho
line
Biochemistry, 42 (2), 271 -283, 2003
13
Characterization of the NAR acetylcholine binding
site by photoaffinity labelling
Biochemistry, 42 (2), 271 -283, 2003
14
Narrowing down the site of labelling with
proteolytic fragmentation
Biochemistry, 42 (2), 271 -283, 2003
15
Excision of V8 fragment from gel
HPLC purification of radioactive fragment
Protein sequencing, identification of residue
Biochemistry, 42 (2), 271 -283, 2003
16
What forces are responsible for interaction of
acetylcholine with the NAR?
- Acetylcholine and all (?) related agonists and
antagonists have a positive charge - Ionic bond? Binding pocket has no complementary
negative charge - Cation-pi interaction? Binding pocket has
aromatic (tryptophan) residues
17
Experimental proof of a cation-pi
interactionbetween acetylcholine and the NAR
(1) Fluorination of Trp should weaken the
interaction
18
Experimental proof of a cation-pi
interactionbetween acetylcholine and the NAR
(2)Construction of NAR with single fluorinated
tryptophan residues
19
Fluorination of trp149 in the a-chain reduces
the agonist sensitivity of NAR
20
The NAR at work
21
NAR desensitization
22
NAR functional cycle
- Three interconvertible conformations
- Ligand binding favors the open and inactivated
states over the resting state - Open state is favored kinetically, but
inactivated state is favored thermodynamically
23
The bottleneck of NAR in open state ?The 0.50
(Canadian Tire) question
If desensitization occurs fast, how can we even
observe, let alone crystallize the open state?
24
An ingenious apparatus for trapping NAR in the
open state
NAR in lipid membranes, crystalline but alive
letting go forceps triggers gun
gun blows acetylcholine
25
Cholinergic agonists
- Direct agonists Bind to the receptor and
stimulate it
Acetylcholine
Carbamoylcholine
Metacholine
Betanechol
26
Cholinergic agonists
- Direct agonists bind to the receptor and
stimulate it
NAR MAR CE (-) -
Acetylcholine
Carbamoylcholine
Metacholine
27
Muscarinic agonists
Muscarine (Amanita muscaria toadstool)
Pilocarpine (Pilocarpus some South American
shrub)
28
Effects of muscarinic agonists
- Slowed heartbeat
- Stimulation of intestinal and urinary bladder
motility bronchial constriction - Secretion of exocrine glands (saliva, intestinal,
sweat, bronchial mucus) - Miosis eye accommodation, eased outflow of humor
29
Nicotinic agonists
Nicotine (Nicotiana tabacum)
Lobeline (Lobelia inflata American tobacco)
Dimethylpiperazinium (synthetic)
30
Effects of nicotine (and nicotinic agonists)
- Preganglionic stimulation of both sympathetic
and parasympathetic effectors in the autonomic
nervous system
- Increased heart rate / blood pressure
- Increased intestinal motility (boy runs for the
bathroom after purloining one of grandpas
cigars) - Effects on motor endplate negligible in normal
dose range (depolarizing blockade can be
experimentally observed at high dosages)
- Stimulation of nicotinic synapses in the brain
Increased vigilance, heightened mood, whatever
(ask smoker). Vomiting, tremor,
31
Muscarinic antagonists
Atropine
Ipratropium
Benztropine
32
Nicotinic antagonists (I) Ganglion blockers
Hexamethonium
Mecamylamine
H
33
Trimethaphan has a sulfonium ion instead of an
amino group
34
Nicotinic antagonists (II) Motor end-plate
blockers
d-Tubocurarine
Pancuronium
35
Depolarizing motor endplate blockers
36
Do d-tubocurarine and pancuronium actually occupy
both binding sites on the NAR?
37
Clinical use of neuromuscular blockade (muscle
relaxation)
- Supplementary to systemic narcosis
- Prevents reflex movements in e.g. abdominal
surgery - Permits narcosis to be less severe Just knock
out consciousness and arousal by pain, not the
brain stem / spinal chord
- Treatment of tetanus
- Tetanus Toxin-mediated permanent and maximal
activity of skeletal muscle - Life-threatening by interfering with respiration
- Treatment Muscle relaxation, artificial
respiration until toxin effect has abated
(usually weeks)
38
Cleavage and regeneration of acetylcholine
Choline acetyltransferase (intracellular)
CoA-SH
H2O
Acetylcholine esterase Choline esterase
(extracellular)
39
Acetylcholinesterase has a catalytic triad in
the active site
short, strong hydrogen bond
40
The catalytic mechanism of acetylcholinesterase
(I)
Enzyme
Enzyme
Acetylcholine
Tetrahedral transition state
Enzyme
Acetylated enzyme intermediate
Choline
41
The catalytic mechanism of acetylcholinesterase
(II)
42
Carbamoylation of acetylcholinesterase is slowly
reversible
Enzyme
Enzyme
fast
fast
Enzyme
Enzyme
Hydrolysis
slow
fast
43
Carbamoylation of acetylcholinesterase by
carbamoylcholine
Enzyme
Enzyme
Hydrolysis
slow
44
Covalent acetylcholinesterase blocking agents
Ser
Ser
Diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP)
45
Nerve gases such as soman and sarin are
cholinesterase blockers
Diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP)
Soman
Tabun
46
Cholinesterase blockers are widely used as
insecticides
Paraoxon
Parathion
Malathion
47
Reactivation of alkylphosphorylated
acetylcholinesterase
Hydroxylamine
Obidoxime
Pralidoxime
48
Indirect-acting cholinomimetics
cholinesterase-blocking agents
(Acetylcholine)
49
Medical applications of cholinesterase-blocking
agents
- Act on both muscarinic and nicotinic synapses
- Nicotinic Mysasthenia gravis pseudoparalytica
- Autoimmune disease Antibodies against NAR
diminish number of functional receptors in
neuromuscular junction - Compensate by increasing the lifetime of
endogenously released acetylcholine by inhibition
of cholinesterase
- Muscarinic
- Activate ciliary muscle to lower intra-ocular
pressure - Stimulate intestinal activity (sluggish e.g.
post-surgery)
50
The Ordeal Bean
The Calabar negroes call the seed eséré, and use
it as an ordeal for the purpose of deciding the
guilt or innocence of persons accused of crimes.
http//www.ibiblio.org/herbmed/eclectic/kings/phys
ostigma.html