THINK PAIR SHARE - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
THINK PAIR SHARE
Description:
Since we cannot cover all areas, the largest ring represents knowledge that the ... 'linchpin idea' Is this worth an adult's knowing it? IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:805
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: THINK PAIR SHARE
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
THINK PAIR SHARE
- Think about what large ring means. Examples?
Exchange thoughts with a partner. - Share in large group.
- Repeat with rings 2 and then 3.
4
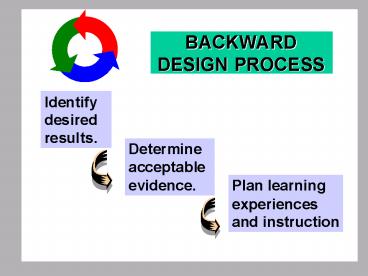
STAGE 1. IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS
- WORTH BEING FAMILIAR WITH
- Since we cannot cover all areas, the largest ring
represents knowledge that the students will hear,
read, view, research or encounter.
5
STAGE 1. IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS
- IMPORTANT KNOWLEDGE/ SKILLS
- These are the facts, concepts and
principals,processes, strategies and methods that
are essential for mastery of the course.
6
IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS
- ENDURING UNDERSTANDING
- big ideas that anchor a course.
- -what they will remember when many details are
forgotten
7
IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS
- FOUR CRITERIA FOR SELECTION
- To what extent does the idea, topic, process
represent a big idea having enduring value
beyond the classroom? linchpin idea - Is this worth an adults knowing it?
8
IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS
- 2. To what extent does the idea, topic or process
reside at the heart of the discipline? - Will this involve an authentic learning
situation? - 3. To what extent does the idea, topic or process
require uncoverage? - What concepts do students have trouble grasping?
9
IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS
- 4.To what extent does the idea, topic or process
offer potential for engaging students? - Can we frame this in ways that provoke and
connect to students interests (as questions,
issues or problems) so that they will become
engaged in sustained learning?
10
STAGE 2. DETERMINE ACCEPTABLE EVIDENCE
- When planning to collect evidence of
understanding, teachers should consider a range
of assessment methods. (1.3, 1.4 1.5) - Assessment of understanding involves a range of
evidence over time rather than a single event.
(test, project) - Our unit or course will be anchored by
performance tasks or projects.
11
STAGE 3 PLAN LEARNING EXPERIENCES
- KEY QUESTIONS
- What enabling knowledge and skills will students
need to perform effectively and achieve desired
results? - What activities will equip students with the
needed knowledge and skills? - What will need to be taught and how to achieve
performance goals? - What materials and resources are best suited?
- Is the design coherent and effective? (1.6)
12
WHAT SHOULD BE UNCOVERED?
- Complex, abstract and counterintuitive ideas
- Examples?
- students are involved in active questioning and
practice to try out ideas and rethink what they
thought they already knew - Examples?
13
WHAT SHOULD BE UNCOVERED?
- HOW?
- Educators need to know what will need to be
uncovered from the students point of view. - We will need to go beyond most textbooks to bring
important issues to life. Students must believe
topic is worth uncovering.
14
FOCUSING ON PRIORITIES
- What knowledge is worth understanding - worth
spending time on to uncover? - What kind of achievement target is understanding
and how does it differ from other targets or
standards? - What are matters of understanding in any
achievement target? How does an educator
identify or select the understanding element
embedded or contained in any complex achievement
target, such as ministry documents?
15
What knowledge is worth understanding?
- Enduring
- At the heart of the discipline
- Needing uncoverage
- Potentially engaging
- 3 degrees of specificity in program guidelines
- topical statements
- general understandings
- specific understandings
16
What kind of achievement target is understanding
and how does it differ from other targets or
standards?
- Students are able to use knowledge and/or skills
in sophisticated , flexible ways. - Students need to make conscious sense and apt use
of the knowledge they are learning and the
principles underlying it. - Students have made links between facts/skill and
can apply it in context. - Students can apply this knowledge in authentic
situations.
17
What are matters of understanding in any
achievement target?
- What conceptual or theoretical elements might lie
within any objective? - Example persuasive writing?
- Other examples?
18
What curricular elements are best suited for
enduring understanding?
- Principles, laws, theories or concepts that are
meaningful to students - counterintuitive, nuanced, subtle or easily
misunderstood ideas - Conceptual or strategic element of any skill-
what works, what doesnt and why?
19
QUESTIONS
- GROUP WORK Half of the group answer question 1
other half answer question 2 and be prepared to
share major points of discussion. - What is the role of questions in traditional
curriculum? - How is this role different in backwards design?
20
ESSENTIAL AND UNIT QUESTIONS
- UNIT QUESTIONS
- provide subject and topic doorways to essential
questions - have no obvious right answer
- are deliberately framed to provoke and sustain
student interest
- ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- go to the heart of a discipline
- recur naturally throughout ones learning and in
the history of the field - raise other important questions
21
ENTRY POINT QUESTIONS
- Four Criteria
- framed for maximum simplicity
- worded in student friendly language
- provoke discussions and questions
- point towards larger essential and unit questions
22
WHAT CAN PEOPLE DO WHEN THEY REALLY UNDERSTAND?
- Can explain
- Can interpret
- Can apply
- Have perspective
- Can empathize
- Have self-knowledge
23
SIX FACETS OF UNDERSTANDING
- PERSPECTIVE
- EMPATHY
- SELF-KNOWLEDGE
- EXPLANATION
- INTERPRETATION
- APPLICATION
24
EXPLANATION
- definition
- sophisticated and apt explanations and theories,
which provide knowledgeable and justified
accounts of events, actions and ideas - includes knowledge of why and how and warranted
opinions
- Examples
- Questions
- Why is that so?
- What explains these events?
- How can we prove it?
- How does this work?
- What is implied?
- To what is this connected? How?
25
WHAT ARE THE INSTRUCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?
- 5 W questions
- use unit and essential questions that demand
student theories and explanations - explain not just recall
- link facts to big ideas
- justify connections
- show their work, multiple solutions
- support conclusions
26
INTERPRETATION
- Examples?
- Questions
- What does it mean?
- Why does it matter?
- What does it illustrate or illuminate about human
experience? - How does it relate to me?
- What makes sense?
- definition
- interpretations, narratives and translations that
provide meaning - interpret, translate, make sense of, show the
significance of, decode or make a story
meaningful.
27
WHAT ARE THE INSTRUCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?
- Teach children to build stories not just
passively take them in. - Give out 2 or 3 versions of same event and have
students create the real event. - Peacemakers students each give their version of
the story of what happened. Then they are
encouraged to come up with a common version.
28
APPLICATION
- Definition
- the ability to use knowledge effectively in new
situations and diverse contexts - You need to walk the walk, not just talk the
talk.
- Examples?
- Questions
- How and where can we use this knowledge, skill or
process? - How should my thinking and action be modified to
meet the demands of this particular situation?
29
WHAT ARE THE INSTRUCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?
- Matching an idea to a context
- We show our understanding of something by using
it, adapting it and customizing it. - Real world problems
- Make the situation as close as possible to the
situation face by a scholar, artist, engineer or
other professionals.
30
PERSPECTIVE
- Definition
- critical and insightful points of view.
- making tacit assumptions explicit.
- By shifting perspective one can create new
theories, stories or applications. - Any answer to a complex question involves a
point of view.
- Examples?
- Questions
- From whos point of view?
- From which vantage point?
- What is assumed?
- What is justified or warranted?
- Is there adequate evidence?
- Is it reasonable? plausible?
- What are the strengths and weakness of the idea?
31
WHAT ARE THE INSTRUCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?
- Teach perspective in advertising, newspaper
writing and editorials, television programming,
text book writing and novels being studied. - Provide explicit opportunities for students to
confront alternative theories and diverse points
of view involving the big ideas. - Examples?
32
EMPATHY
- Definition
- The ability to get inside another persons
feelings of worldview. - The ability to walk in anothers shoes, to escape
ones own emotional reaction and grasp anothers. - gt change of heart
- Examples?
- Questions
- How does it seem to you?
- What do they see that I dont?
- What is the artist, songwriter, performer
feeling, seeing and trying to make me feel or see
too?
33
WHAT ARE THE INSTRUCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?
- Offer multiple perspectives on things such as
- human rights issues
- environmental issues
- accounts of history
- topics in the news
- issues debated for an election
- controversial laws such as gun legislation.
- Have students experience things from anothers
point of view. Examples?
34
SELF-KNOWLEDGE
- Examples?
- Questions
- How does who I am shape my views?
- What are the limits of my understanding?
- What are my blind spots?
- What am I prone to misunderstand because of
prejudice, habit or style?
- Definition
- the wisdom to know ones ignorance and how ones
patterns of thought and action inform as well as
prejudice understanding.
35
WHAT ARE THE INSTRUCTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?
- We need to continue teaching self reflection and
assessing in the broadest terms. - Increase time spent on metacognition.
- Uncover prejudices and thinking in either/or
terms.
36
GROUP WORK
- Read the example about the nutrition unit. (p.35)
37
GROUP WORK
- What are the essential questions in the unit plan
you have chosen? - What are the unit plan questions?