Hydroprocessing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Hydroprocessing
Description:
stabilizing distillate fuels like gasoline, jet fuel by preventing ... steric hindrance by methyl groups. Other isomers of this compound are more. reactive: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1397
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Hydroprocessing
1
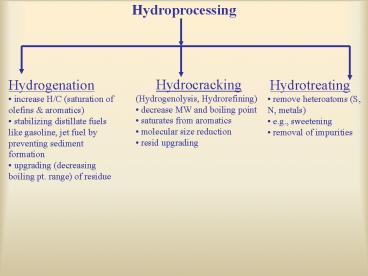
Hydroprocessing
- Hydrocracking
- (Hydrogenolysis, Hydrorefining)
- decrease MW and boiling point
- saturates from aromatics
- molecular size reduction
- resid upgrading
- Hydrogenation
- increase H/C (saturation of olefins aromatics)
- stabilizing distillate fuels like gasoline, jet
fuel by preventing sediment formation - upgrading (decreasing boiling pt. range) of
residue
- Hydrotreating
- remove heteroatoms (S, N, metals)
- e.g., sweetening
- removal of impurities
2
Hydrogenation
Catalysts Pt, Pd, Ni on supports (SiO2,
Al2O3) (hydrogen addition)
3
Hydrocracking
2H2
H2
2H2
2H2
4
Hydrocracking
- Hydrocracking has a dual function
(bi-functional) catalysts - metals acid supports
- to perform two functions
Hydrocracking Catalysts
Cracking (acid support) SiO2 Al2O3 Al2O3 Low
zeolite SiO2 Al2O3 High zeolite SiO2 Al2O3
Hydrogenation Noble Pt, Pd Non-noble Ni, Mo,
Co, W
- susceptible to S poisoning
- Sulfided forms (MxSy) for high sulfur feeds
5
Hydrotreatment
Hydrodesulfurization (HDS)
6
Hydrotreatment
Hydrodesulfurization (contd)
Catalysts Sulfided Mo/AlO3 Co is used as a
promoter MxMo6S8
7
Hydrotreatment
This compound is very stable and it is very
difficult to remove the S atom because of steric
hindrance by methyl groups . Other isomers of
this compound are more reactive
Reactivity in HDS (k methylated DBT/
k DBT) 1) 4,6 DBT 0.1 2) 3,7
DBT 1.5 3) 2,8 DBT 2.6 4) 6-methyl-
dibenzothiophene 0.16
8
Hydrotreatment
- Hydrodenitrogenation (HDN)
- reduce fuel Nox upon combustion
- basic N poisons acidic catalysts
Catalysts Mo (or W) / Al2O3 / Ni
as promoter
9
Hydrotreatment
- Hydrodemetalation (HDM)
- metals poison catalysst
- metals are toxic, cause corrosion
- removes principally Ni, V
H - M - porphyrins
Catalysts used Mo/Al2O3
Co and Ni as promoters