Kinetics Revision PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title: Kinetics Revision
1
Kinetics Revision
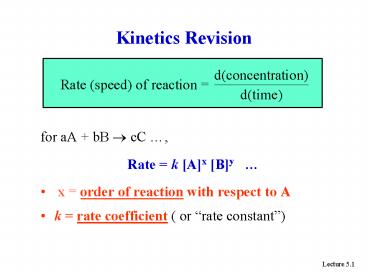
- for aA bB ? cC ,
- Rate k Ax By
- x order of reaction with respect to A
- k rate coefficient ( or rate constant)
2
Elementary Reactions
- Occur in a single collision
- have simple rate laws which follow stoichiometry
- A ? products unimolecular Rate k A
- Cl2 ? Cl Cl
- A A ? products bimolecular Rate kAA
- Cl Cl ? Cl2
- A B ? products bimolecular Rate kAB
- Cl H2 ? HCl Cl
3
Example
- For reaction A 3B ? product,
- initial A / M initial B / M
initial rate R / M s1 1 0.10
1.0 5.0 2 0.14 1.0 10.0 3
0.14 0.5 5.0 - Answer
- sets 2 3 A constant, halving B halves rate
- hence R µ B1 first order in B
- sets 1 and 2 B constant, look at order with
respect to A
- For B constant, R µ Ax
4
Hence second order with respect to A 2nd order in
A, 1st order in B, 3rd order overall
overall order sum of individual orders
- Find rate coefficient k where R k A2 B
- from set 1 5.0 M s1 k ? (0.10 M)2 ? 1.0 M
- hence k 5.0 ? 102 M2 s1
- Units found from rate law.
5
Rate LawsDependence On Time
- Reaction obeying 1st-order rate law A ? products
(negative sign because A disappears its
concentration is decreasing)
- Solve this differential equation by integrating
both sides
6
First Order lnA vs time
- Plot of lnA as function of time
- lnA -kt lnA0
7
Half Life
Integrated rate law
- Half Life is independent of initial concentration
- Solutions also exist for second-order reactions...
8
Half life for a First Order Reaction
A0
9
Reaction Mechanism andRate-determining Step
- Mechanisms can be complex, but sometimes all
steps are fast except onethen slow step
rate-determining step
10
Example
- H2(g) 2ICl(g) ? I2(g) 2HCl(g)
- Suggested mechanism
- (1) H2 ICl ? HI HCl slow Rate(1)
k1H2ICl - (2) HI ICl ? I2 HCl fast Rate(2)
k2HIICl
H2 2ICl ? I2 2HCl net reaction
(1) is slow rate determining step ?
Overall rate k1H2ICl Experimental rate
kH2ICl, supports mechanism HI is an
intermediate, it doesnt appear in the overall
reaction
11
- Often no simple solution to rate equations,
solved coupled differential equations
numerically.Example - oscillating reaction iodate, malonic acid
(CH2(CO2H)2), H2O2 - ozone layer destruction by CFCs
(chlorofluorocarbons) simplified mechanism is - CCl2F2 ? CClF2 Cl
- Cl O3 ? ClO O2
- ClO NO2 ? ClONO2
- ClONO2 HCl ? HNO3 Cl2
- Cl2 ? 2Cl
hn
hn
12
Example
- Fast reversible reaction followed by a slow step
- (1) 2NO(g) ? N2O2 (g) fast equilibrium, K
- (2) N2O2 (g) N2O2(g) ? 2NO slow (rate
coefficient k)
2NO(g) O2 (g) ? 2NO2 (g) net reaction
Rate rate of slow step k N2O2O2
So rate k N2O2 O2 k K NO2 O2 hence
rate constant ? NO2 O2 consistent with
observed rate law