KAL 007 PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 58
Title: KAL 007
1
KAL 007
2
KAL 007
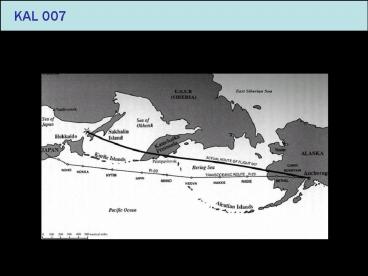
- Korea Air Lines 007
- 31 August 1983
- 400 a.m.
- Anchorage Airport, Alaska
- To Seoul, Korea
3
KAL 007
4
KAL 007
5
Command and Control
6
Command and Control
7
Command and Control
8
Machine
- Mechanical Interaction
- Physical artifacts
- Knob, handle, switch, etc.
- Ergonometric
- Operation governed by the physical constraints
of the machines.
9
Control and Display
10
Control and Display
11
Force and Precision
12
Force and Precision
13
Mission Impossible
14
Mission Impossible
15
Homer Simpson Springfield Nuclear Plant
16
Control Centre
17
Control Centre
18
Control Centre
19
Control Centre
- Characteristics
- Multiple users
- Shared display screen
- Physical operation control
- Check and balance among operators
- Use of physical distance
20
Car Steering
21
Car Steeling
22
Cybernetics
- Negative Feedback System
- In General System Theory
- Imagine you need to drive in a straight line in
a rough road. - What will be the movement of your steering wheel?
23
Cybernetics
- Automatic System
- Negative feedback loop will maintain the state
of the system. - Positive deviation will trigger a negative
action. - Negative deviation will trigger a positive
action.
24
Thermostat
25
The System
- The System includes
- Environment
- Active agent
- Control artifacts
- The mechanism
26
Ecology
- Ecological Approach
- Environment
- Perception
- Interaction with the environment
- Making use of the artifacts
- Opposed to the Information Processing approach
of cognition
27
Information Processing
Mental model
Information Processing
Input - stimulus
Output - behaviour
28
Information Processing
- Try to design an Information Processing model for
driving a car - What are the input stimuli?
- What is the mental model?
- What are the output behaviors?
29
Real World Driving
- Actual driving session
- Is there any clear mental model of the route
from starting point to destination? - Numerous inputs at any moment.
- Complexity of situation cannot be explained by
rules. - No concrete plan before sitting on the driver
seat.
30
Real World Driving
- What does it mean?
- The actual situation provides information cues.
- The physical artifacts suggest methods of usage.
- Affordance
31
Affordance
- The classic example
- Door knobs can be either PUSH or PULL.
- Design two door knobs such that the first one
can only be pushed and the second one can only be
pulled.
What is it about this object that makes people
want to use it this way?
32
Door Knob
33
Door Knob
34
Door Knob
35
Door Knob
36
Door Knob
37
Affordance
- The mechanism
- Visual information may not be adequate to
perceive the affordance. - May need to start interacting with the artifact
to perceive the affordance.
38
Affordance
39
Affordance
- Embedded Information
- Information on the usage of the hammer is
embedded in the world, i.e. the hammer and its
environment. - Information does not need to reside in the
memory of the user.
40
The Usage
- How the hammer is used?
- As a tool to drive nail into wood.
- Continued interaction among the body of the
carpenter, the hammer, the nail and the piece of
wood. - What the carpenter concerns is to drive the nail
into wood. - The hammer extends the body of the carpenter.
41
The Key Moment
- How the hammer is used?
- The carpenter will not be aware of the existing
of the hammer when working. - Until something wrong happens, like hitting the
finger, breaking the nail, etc.
42
Look familiar
43
Look familiar
- Remember the moments
- When you concentrate on tracing an image in
Illustrator. - When the mouse reaches the edge of your desk.
44
Hammer Again
45
Interacting with This
- The mechanism
- One does not interact with the hammer by its
internal representation. - But through the physical body and the actual
object.
46
Virtual Interaction
- Remember Virtual Reality last week
- You are one single point with no volume, no
weight in the 3D Cartesian space. - Interaction is through immersive head mounted
display, CAVE, data glove, etc. - The world is the numeric representation of
something.
47
Virtual Interaction
48
Virtual Interaction
49
Virtual Interaction Trip
How to describe it?
Timothy Leary (1920 1996)
50
Virtual Interaction Trip
Osmose Char Davis
51
Alternatives
- What else?
- Embodied interaction
- Pervasive computing
- Tangible interaction
- Social interaction
- Augmented reality
52
Embodied Interaction
- What is it?
- Everyday life in everyday world.
- Leverage on the usual practice of bodily
interaction. - Interaction occurs in real situations with
context.
53
Pervasive Computing
- Anywhere
- Computing environment with information and
communication technology everywhere, for everyone
at any time. - Context awareness
- Location awareness
54
Social Interaction
- You are not alone
- Interaction can be social.
- Not only human machine dialog.
- Platform for interaction among human subjects.
- Creation of situations.
- Creation of communication methods.
55
Social Interaction
56
Augmented Reality
57
Augmented Reality
58
Case Studies
IDEO Prada Dressing Room