Resonance condition - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
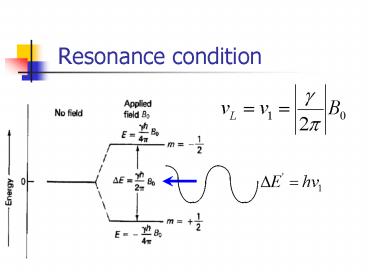
Resonance condition
Description:
When the alternating current through the coil is turned on and ... http://www.cis.rit.edu ... of a radio-frequency pertubation which excites the spin ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Resonance condition
1
Resonance condition
2
Pulse
- A coil of wire placed around the X axis will
provide a magnetic field along the X axis when a
direct current is passed through the coil. - An alternating current will produce a magnetic
field which alternates in direction.
In magnetic resonance, the magnetic field created
by the coil passing an alternating current at the
Larmor frequency is called the B1 magnetic field.
When the alternating current through the coil is
turned on and off, it creates a pulsed B1
magnetic field along the X' axis.
http//www.cis.rit.edu/htbooks/nmr/inside.htm
3
The spins respond to this pulse in such a way as
to cause the net magnetization vector to rotate
about the direction of the applied B1 field. The
rotation angle depends on the length of time the
field is on, , and its magnitude B1. a 2 p g
t B1. In our examples, will be assumed to be
much smaller than T1 and T2.
http//www.chem.queensu.ca/FACILITIES/NMR/nmr/webc
ourse/index.htm
4
Pulse
- Application for a specified period of time of a
radio-frequency pertubation which excites the
spin system non-selectively over a given
bandwidth - t time period bandwidth1/t
- Flip-angle of a pulse a 2p g t B1
- B1strength of r.f. field
- For proton 90? pulse is about 10 W and t ms
t
5
Flip Angle of the pulse
http//www.chem.queensu.ca/FACILITIES/NMR/nmr/webc
ourse/index.htm
a 2pgt B1
6
Perturbation by RF Pulse
7
Pulse Sequence
8
The Pulse FT NMR Experiment
90º pulse
Experiment
(t)
equilibration
detection of signals























![A Thumb rule to work out Electron Spin Resonance Frequency [and the corresponding Proton NMR frequency] is as follows: PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/A1257278165YQMfv.th0.jpg?_=202011170811)






