Electrophilic Reaction on Nitrogen - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Electrophilic Reaction on Nitrogen
Description:
6-membered rings - electron deficient - reactive in Nu-fil. Ar subst. 2 / 4 Pos. ... Metal - Halogen Exchange. R-Li: Alkyllithium, NOT LDA etc. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:141
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Electrophilic Reaction on Nitrogen
1
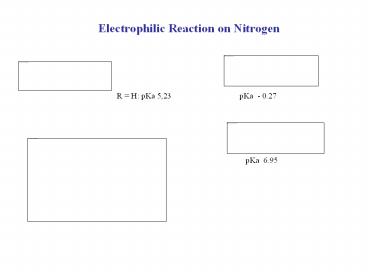
Electrophilic Reaction on Nitrogen
R H pKa 5,23
pKa - 0.27
pKa 6.95
2
Electrophilic Reaction on Carbon Electrophilic
Aromatic Substitution
6-membered rings - electron deficient - ?
reactivity
- Both C and N may react
- 3/5 pos. most reactive C
- Diazines less reactive
Benzo ring most reactive Much slower react. than
naphthalene
3
5-membered rings - electron rich - reactive i
E-fil. Ar subst.
React. in a-position generally preferred Selectivi
ty not always good React. Pyrrole gt thiophene gt
furan
4
Nucleophilic Reaction on Carbon Nucleophilic
Aromatic Substitution
- SNAr
- SN1 Via diazonuim salts and arylic cation
- Benzyne
- SRN1 Involves radicals
- VNS Vicarious nucl. Subst.
5
6-membered rings - electron deficient - reactive
in Nu-fil. Ar subst.
2 / 4 Pos. reactive electron def. C, neg. charge
partly on N in intermed 3 / 5-Pos. much less
reactive (benzenoid pos.)
5-membered rings - electron rich - not reactive
in Nu-fil. Ar subst.
6
Radical Reactions
6-membered rings
Electron rich radical
Electron deficient heterocycle
5-membered rings
Electron rich heterocycle
Electron def. radical
7
Deprotonation NH
C-metallation
C-Litiation a) Direct litiation (C-H ?C-Met)
(Metal-Hydrogen exchange) b) Metal-Halogen
exchange (C-X ?C-Met) C-Met a)
Transmetallation (C-Li?C-Met) (Met?Li) b)
Insertion (C-X ?C-Met-X)
8
Direct Litiation
- Reactivity / Acidity / Anion Stability
- Other subst - Directed ortho metallation
- R-Li Alkyllithium and lithium amides
9
Metal - Halogen Exchange
R-Li Alkyllithium, NOT LDA etc. Metall - halogen
exchange favored over direct litiation, low
temp. Formation of R-X may be avoided 2 equivs.
t-BuLi
10
5-Membered rings - examples
11
6-Membered rings
12
Magnesium Derivatives
Zinc Derivatives
Boron / Silicon / Tin Derivatives
Transmetallaton
13
Reactions on Metallated Heterocycles
Pd-Catalyzed coupling reactions (C-C bond) Zn,
Sn, B
Ipso Substitution (react with E) Si, Sn
14
Metallation in Alkyl Side Chains