Normal Distribution PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title: Normal Distribution
1
- Normal Distribution
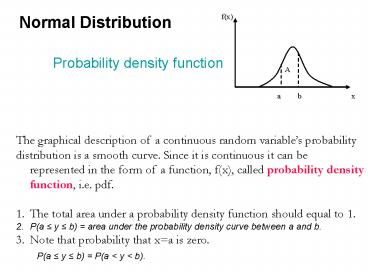
Probability density function
- The graphical description of a continuous random
variables probability - distribution is a smooth curve. Since it is
continuous it can be represented in the form of a
function, f(x), called probability density
function, i.e. pdf. - The total area under a probability density
function should equal to 1. - P(a y b) area under the probability density
curve between a and b. - Note that probability that xa is zero.
P(a y b) P(a lt y lt b).
2
Note
- Histogram and relative polygons can approximate
the probability density curve. - From the shape of the probability density curve,
we can know the shape of the distribution such
as skew to the right, skew to the left, bell
shaped, multimodal or bimodal.
3
normal random variable
- Key Properties
- It is characterized by its mean ? and its
standard deviation ?. - The probability density function is symmetric
about ?. - The maximum value occurs at ?.
- The area to the left of ? is .5.
- The Standard Normal density has ? 0 and ? 1.
4
Standard Normal Probability Distribution
- A random variable that has a normal distribution
with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of
one is said to have a standard normal probability
distribution.
5
Computing Probabilities
- Let X be a continuous random variable with Normal
density (normal random variable) with parameters
? and ?. - where Z is a normal random variable ? 0, ? 1.
- We sometimes write X N (?, ?) when X is normal
random variable with parameters ? and ?.
6
How to compute probabilities
- Determine ? and ? and expression for desired
probability, e.g. P(Xlt20), P(Xgt12), etc. - Convert to Z, e.g. (z-score)
- Sketch a Standard normal density and shade the
desired region. - Use Standard Normal Table (out -gtinside) to find
probabilities needed. - Adjust to compute the probability of the shaded
region
7
Examples
- 1. Let X be N (20, 5) random variable, ie ? 20
and ? 5. Find the following probabilities - a) P(X 23 ) (area directly above point x 23
) - b) P(X 23 ) (area to the left of x 23 )
- c) P(X gt 17.2 ) (area to the right of x 17.2
) - d)P(17.2 X 26.7 )
8
Normal Percentiles
- Definition For any continuous random variable,
X, the p-th percentile is a number a such that
- P(X a) p
- Useful Formula Convert Z to X
- X ? ? Z
9
How to compute percentiles for Normal random
variables
- Sketch a Standard normal density and shade the
given region. - Adjust to compute the probability of the region
that agrees with the table. - Use Standard Normal Table (inside -gt out) to find
the desired percentile (z-value). - Convert z-value to X with X ? ? Z.
10
Example of Percentile Problems
- Let X be a N(20 , 5 ) random variable. Find a
value of x such that - P(X x ) 0.38
- P(X x ) 0.33
- P(X x ) 0.63
- P(X x ) 0.72
11
Normal Probabilities in Context
- 3. The heights of adult males in Neverland are
normally distributed with mean 69 inches and
variance 25 inches squared (i.e. standard
deviation of 5 inches). - a) Find the probability that a randomly selected
adult male is taller than 6 feet (72 inches). - b) Find the probability that a randomly selected
adult male is between 5 and 6 feet tall. - c) How tall must a male be to be among the
tallest 10 of the population.
12
- 4. The lifetime of a certain type of television
tube is normally distributed with mean 3.8 years
and standard deviation of 1.2 years. - a) Suppose that the tube is guaranteed for two
years. What proportion of TVs will require a new
tube before the guarantee expires? - b) If the company wishes to set the warranty
period so that only 10 of the tubes would need
replacement while under warranty, how long a
warranty must be set?
13
5.At Upton-Webber, the salaries of the employees
are normally distributed with mean 27,000 and
standard deviation 2,500.a) Mr. Smith is paid
32,000. What proportion of the employees of
Upton-Webber are paid less that Mr. Smith?b)
What proportion of the employees have their
salaries between 22,000 and 32,000?c) What
proportion of the employees have their salaries
between 30,000 and 32,000?d) Mrs. Jones claims
that her salary is high enough to just put her
among the highest paid 15 of all employees
working at Upton-Webber. Find her salary.e) Ms.
Green claims that her salary is so low that 90
of the employees make more than she does. Find
her salary.
14
End of Chapter 4
15
- Introduce the formula for calculating the Exp and
Var - End