TCP handshake - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
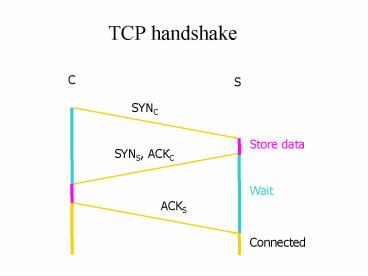
Title:
TCP handshake
Description:
Handshake is a negotiation of parameters between two end-points ... If ACK is to an unopened socket, server validates returned sequence number as SYN-cookie ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:794
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: TCP handshake
1
TCP handshake
2
TCP handshake
- What is stored at the server in the handshake?
- Handshake is a negotiation of parameters between
two end-points - TCP Control Block (TCB) keeps track of what the
server agreed to - gt 280 bytes
- FlowID, timer info, Sequence number, flow control
status, out-of-band data, MSS, other options
agreed to - Half-open TCB entries exist until timeout
- Fixed bound on half-open connections
- Resources exhausted ? requests rejected
3
SYN Flooding
4
TCP SYN flooding
- Attacker sends many connection requests
- Spoofed source addresses
- RSTs quickly generated if source address exists
- No reply for non-existent sources
- Attacker exhausts TCP buffer to w/ half-open
connections - Basic problem
- No client authentication of packets before
resources allocated
5
TCP SYN flooding
TCP Buffers
169.237.5.23
168.150.241.155
169.237.7.114
6
SYN-flood
TCP Buffers
128.120.254.1
128.120.254.2
128.120.254.3
128.120.254.4
128.120.254.5
128.120.254.6
128.120.254.7
128.120.254.8
128.120.254.9
128.120.254.10
128.120.254.11
128.120.254.12
128.120.254.13
128.120.254.14
169.237.7.114
128.120.254.15
7
TCP SYN flooding counter-measures
- End host
- Reduce half-open timeout value
- May deny legitimate access
- Increase backlog queue
- Degradation of service
- Disable non-essential services
- Router
- Ingress filtering to prevent spoofing
8
TCP SYN flooding counter-measures
- Firewall
- Full connection proxy
- Terminates handshake, re-establishes connection
on valid 3-way handshake - Must translate each subsequent packet
- Semi-transparent
- Spoofs ACKs optimistically when receiving SYN/ACK
- Subsequent (duplicate) ACK let through or RST
generated if ACK not received
9
TCP SYN flooding counter-measures
- Active monitoring (synkill)
- synkill
- keep track of source IP addresses
- null (never seen), good (seen to be OK before)
- new (seen, but not sure yet if spoofed)
- bad (non-existent, 0.0.0.0, 127.0.0.0, 10.0.0.0,
192.168.0.0, etc.) - Send RST packets for bad source IP addresses
- Send ACK packets for new, potentially spoofed IP
addresses - degrade service if you can't tell for sure
- if ACK or RST received, place in good
- if ACK or RST not observed, reclassify IP as bad
- Reclassify periodically
- ACK/RST spoofing is a problem (see state machine)
10
Cookies
- Network cookies
- Karn, Dec. 1994, Photuris session-key protocol
- TCP SYN cookies
- Bernstein, Schenk Sept. 1996
- Mostly backwards-compatible
- See http//cr.yp.to/syncookies.html
11
TCP SYN cookies
- General idea
- Client sends SYN
- Server responds to Client with SYN-ACK cookie
- sqn f(src addr, src port, dest addr, dest port,
rand) - Server does not save state
- Honest client responds with ACK(sqn)
- Server checks response
- If matches SYN-ACK, establishes connection
12
TCP SYN cookie
- Server's TCP SYN/ACK seqno encodes a cookie
- seqno 32-bits
- t mod 32 gt counter to ensure seqno's increase
every 64sec - MSS gt encoding of server MSS (can only have 8
settings) - Cookie gt easy to create and validate, hard to
forge blindly
32
0
t mod 32
MSS
CookieHMAC(t, Ns, SIP, SPort, DIP, DPort)
5 bits
3 bits
13
SYN-Cookies
SYN ack-number
- Modified TCP Handshake
- Example of stateless handshake
- client
- sends SYN packet and ACK number to server
- waits for SYN-ACK from server w/ matching ACK
number - server
- responds w/ SYN-ACK packet w/ initial SYN-cookie
sequence number - Sequence number is cryptographically generated
value based on client address, port, and time. - No TCP buffers are allocated
- client
- sends ACK to server w/ matching sequence number
- server
- If ACK is to an unopened socket, server validates
returned sequence number as SYN-cookie - If value is reasonable, a buffer is allocated and
socket is opened. - .
- Spoofed packets will not consume TCP buffers
SYN-ACK seq-number as SYN-cookie, ack-number NO
BUFFER ALLOCATED
ACK seq_number ack-numberdata
SYN-ACK seq-number, ack-number TCP BUFFER
ALLOCATED
14
Status?
- Support exists in all modern operating systems
- Not turned on by default....Why?
- Not sure, but it...
- May break some options such as large windows
- Assumes TCP parameters that are negotiated do not
change
15
Cookies for the bad guy
- TCP SYN cookies
- Used by good guy to securely keep track of valid
half-open connections using constant-state at the
server - Encode information in destination seqno
- Inverse TCP SYN cookies
- Kaminsky 2002
- Used by bad guy to securely keep track of valid
half-open connections using constant-state at the
client - Encode information in the source port/seqno
- Allows for high-speed scanning