DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Description:
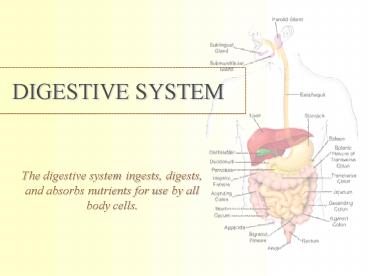
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. The digestive system ingests, digests, and absorbs nutrients ... the passage way intersection for both the digestive and respiratory system. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:954
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
1
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- The digestive system ingests, digests, and
absorbs nutrients for use by all body cells.
2
The Key Processes
- Digestion process of food break down
- enzymatic hydrolysis
- intracellular breakdown within cells (sponges)
- extracellular breakdown outside cells (most
animals) - alimentary canals (digestive tract)
- Absorption cells take up small molecules
- Elimination removal of undigested material
3
(No Transcript)
4
The Mouth
- Receives food and begins digestion. Made up of
- Cheeks and Lips
- -contains muscles associated with chewing
- Tongue
- -handles food and contains taste buds
- Palate
- - closes the opening to the nasal cavity during
swallowing - Teeth
- - mechanically break food into smaller pieces,
increasing the surface area exposed to digestive
actions
5
Salivary Glands
- Secrete saliva
- Moistens food
- Helps bind food particles
- Begins chemical digestions of carbohydrates
- Makes taste possible
- Helps cleanse the mouth
- Include serous cells that secrete digestive
enzymes including amylase and mucus cells that
secrete mucus.
6
Pharynx and Esophagus
- Pharynx the passage way intersection for both
the digestive and respiratory system. - - involuntary reflex actions move food from
pharynx to esophagus - - includes epiglottis flap like structure at
back of tongue near entrance to trachea - Esophagus muscular tube that conducts food from
the pharynx to the stomach. - - circular muscle fibers at the distal end of the
esophagus help prevent regurgitation of food from
the stomach
7
(No Transcript)
8
Stomach
- The stomach stores food and performs preliminary
digestion (moves food into small intestine). - Cells Mucous cells chief cells that secrete
Pepsinogen and Zymogen Parietal cells which
secrete HCl. - Gastric Secretion
- gastric juice contains
- Pepsin a protein splitting enzyme that digests
almost all types of protein - Hydrochloric acid regulates the pH of stomach
needed for the creation and function of pepsin - Intrinsic factor aids in Vitamin B-12 absorption
- Mucus provides protective layer on inside
stomach wall - Regulation of Gastric Secretions
- - controlled by nerve impulses and the hormone
gastrin
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Accessory Organs
- Include
- Pancreas secretes a digestive juice called
pancreatic juice - -Pancreatic Juice
- - pancreatic amylase breaks down carbohydrates
- - pancreatic lipase breaks down fats
- - nucleases break nucleic acid into nucleotides
- Liver
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Lipid metabolism
- Protein metabolism
- Blood filtering
- Detoxifies blood
- Stores glycogen, iron, and vitamins
- Secretes Bile
- Bile- a yellowish-green liquid that contains bile
salts - Helps with the digestion of fat molecules
- Gall Bladder secretes and stores bile (accessory
organ of the liver).
12
(No Transcript)
13
Small Intestine
- The small intestine receives secretions form the
pancreas and liver, completes nutrient digestion,
absorbs the products of digestion, and transports
the residues to the large intestine. - Parts of the small intestine Duodenum, Jejunum,
and Ileum. - Structure of intestine wall
- lined with villi which increase surface area
aid with absorption - Secretion
- Mucus and digestive enzymes enzymes split
molecules of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. - Regulation of small intestine secretion
- Gastric juice, chyme, and reflexes stimulated by
distension of small intestine wall stimulate
secretion
14
Small Intestine
- Absorption
- Enzymes on microvilli
- Villi absorb monosaccharides, amino acids,
fatty acids, and glycerol - fat molecules enter the lacteal of the villi
- fatty acids enter blood capillaries of villi
- Movements
- - ileocecal vavle controls movement of the
intestinal contents from small into large
intestine
15
Large Intestine
- Parts
- Cecum Rectum
- Anal Canal
- Colon
- divided into ascendin, transverse, descending,
and sigmoid portions - Major function is water reabsorbtion
- Functions
- secretes mucus
- absorbs water and electrolytes
- forms and stores feces
- Feces
- consist mostly of water, undigested material,
electrolytes, mucus, and bacteria - stored in rectum and pass through the two
sphincters (one voluntary and one involuntary) to
the anus
16
(No Transcript)
17
Hormones that Regulate Digestion
18
(No Transcript)
19
References
- Campbell, N.A., J.B. Reece, L.G. Mitchell.
1999. Biology. 5th Edition. Menlo Park, CA
Pearson-Benjamin/Cummings. - Shier, David, Butler Jackie, Ricki Lewis. 1998.
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology. 6th
Edition. Boston, MA McGraw-Hill. - AP Biology Glenbrook South High School. 26
October 2006. 29 October 2006 k.k12.il.us/Academics/gbssci/bio/apbio/Lecture/lec
ture.htm. - Massengales Biology Place. 29 October 2006.
h.htm. - Massengales Biology Place. 29 October 2006.
m.