River PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title: River
1
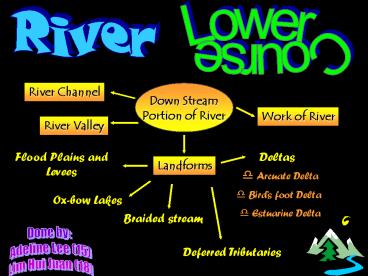
River
Lower Course
River Channel
Down Stream Portion of River
Work of River
River Valley
Flood Plains and Levees
Deltas
Landforms
- Arcuate Delta
- Birds foot Delta
- Estuarine Delta
Ox-bow Lakes
Braided stream
Done by Adeline Lee (15) Lim Hui Juan (18)
Deferred Tributaries
2
River Channel
- widest and deepest
- Largest volume of water and load
- flows over land with a gentle gradient
River Valley
- broad and flat
- valley sides are bounded by bluffs
Work of River
- Vertical erosion has almost stopped
- lateral erosion still occurs
- main work or river is deposition of the load it
is transporting
3
- wide and low lying plain found on both sides of
the river - covered with alluvium deposited by the river
- outermost edge is the bluffs.
- Levees are natural embankments found along banks
of river and are made up of coarser alluvial
materials than flood plain - heavy rain causes floods
- overflows water encounter more friction due to a
larger wetted perimeter formed by by the large
flat lowland. Increased friction reduces the
energy of the water and slows down its speed,
resulting in deposition. - The larger and coarser materials are deposited
at the river bank first - forming raised embarkments levees
- The smaller and lighter materials are carried
further away the river - forming flood plain
Flood Plain and Levees Pg 100
4
A floodplain is a wide and flat plain. It is
built up by alluvium laid down on the river banks
during repeated flooding. When there is a flood,
the river overflows its banks. When the flood
subsides, there is a decrease in the volume of
water and the river starts to deposit its load.
Most of the alluvium is deposited on the banks
close to the river. With repeated flooding, the
materials that are deposited on the river banks
accumulate to form floodplains. The path of the
middle river is always changing as it cuts
sideways into the land and starts to deposit its
load. Loops, called meanders, and oxbow lakes are
typical features of this part of the river.
During a storm, meanders stop river water flowing
easily. This causes water to build up in places,
and may lead to flooding. Most rivers end their
journey when they flow into a sea. The river
slows down and deposits then sediment it is
carrying. Heavy grains of sand and gravel drop to
the bottom while lighter particles of fine silt
and clay are carried further out to sea.
Eventually, the sediment spreads out to form a
new piece of land with gently sloping sides. This
is called a delta.
5
Ox-bow lakes(Pg101)
- An ox-bow lake is a horseshoe-shaped or
crescent-shaped lake. - River in the lower course meanders widely across
the low-lying plain. Lateral erosion and
undercutting occur on the concave bank where the
stream flows the fastest. - Deposition occurs on the convex bank due to lack
of water. - Continuous erosion of concave bank and
decomposition on convex bank cause the formation
of very pronounced meander with two concave banks
getting closer. - Narrow neck of land between the two concave
banks is eventually cuts through by either
lateral erosion of two concave banks or the
strong current during flood. A straighter river
channel is created and an abandoned meander
loop,a cut-off, is formed. When deposition
finally seals off the cut-off from the river
channel, an ox-bow lake is formed.
6
Braided Stream
- A river becomes braided when its volume of water
is insufficient to carry its entire load. - river splits into two or more twisted and turned
channels to avoid the deposited materials. - These channels join again as one river when
there is no obstruction of flow of water by the
deposits. - Braided stream is best developed between wet and
dry season when water fluctuates.
Deferred Tributries
- Tributaries in the flood plain may not be able
to enter the main river due to the raised levees
on either side bank of the river. - Deferred tributaries flow parallel to main river
for some distance before being able to enter it.
7
- Deltas at river mouth are formed only when load
deposited in the coast exceeds the amount
transported away. - Favourable conditions for formation of delta
- An active erosion along the course of the river
- the river flows through less resistant rocks so
that weathered and eroded rocks can add to load. - The tributaries help to increase the load.
- No/ few large lakes along the river to trap the
load. - A gentle offshore gradient with shallow water.
- The coastal water is quiet and has few or no
strong currents and waves to remove the deposited
sediments. - The climate favours fast growth of vegetation
which binds and stabilizes the sediments. - Delta can form even if there are strong coastal
currents and waves as long as the load deposited
exceeds the amount swept away.
Deltas
8
Formation of delta
When river enters the sea, it is mixed with the
surrounding water.The gravel and sand are
deposited first before the silt. The fine clay is
transported in suspension quite far out in the
sea. When salt water causes the clay to
flocculate, it becomes heavier and sinks to the
sea bed. As layers of alluvial materials are
deposited, a platform of alluvium is built up and
it finally rises above the water. This flat
alluvial platform is the delta. As the main
river channel in a characteristic
triangular-shaped delta gets silted up and its
bed rises, the water overflows the banks into
different channels called distributaries. These
distributaries build up their own levees. The
vegetation that later grows on the alluvium helps
to bind and stabilize the delta. A delta can
also form when a river enters a lake which causes
it to lose speed and deposit its load.
9
Types of delta
- Arcuate delta
- triangular- or fan-shaped
- water enters the sea through many distributaries
- Formed when the deposits are evenly spread out
- Longshore currents help to form spits and
lagoons at the mouths of the distributaries and
smoothen the seaward edge of the delta - Nile delta in Egypt.
- Birds foot delta
- has distributaries that extend far out to sea
- have currents strong enough to carry the
sediments for quite a distance before depositing
them far out to sea. - sediments deposited are more than what the tides
and currents can remove - Mississippi Delta in the USA.
10
- Estuarine delta
- materials are deposited in a long narrow
submerged estuary - delta does not grow beyond the general coastline
- because the deposits are being washed away by
the waves and currents - Seine Delta in France.
Thank you!!!
11
ARCUATE DELTA
12
BIRD'S FOOT DELTA
13
NILE DELTA
14
FLOOD PLAIN
15
AMAZON
16
Ganges River