HutchinsonGuilford Progeria - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
HutchinsonGuilford Progeria
Description:
high salt concentration (hybrids melt in water) low temperatures (hybrids melt with heat) ... to simultaneously detect low and high. abundance genes accurately ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:560
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: HutchinsonGuilford Progeria
1
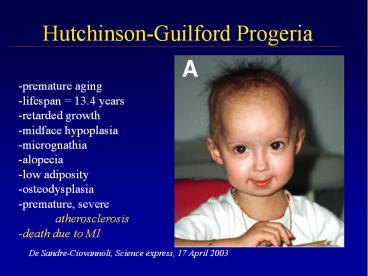
Hutchinson-Guilford Progeria
- premature aging
- lifespan 13.4 years
- retarded growth
- midface hypoplasia
- micrognathia
- alopecia
- low adiposity
- osteodysplasia
- premature, severe
- atherosclerosis
- -death due to MI
De Sandre-Ciovannoli, Science express, 17 April
2003
2
Lamin A mutations in HGS
Exons 11 and 12 code the Lamin A tail (not lamin
c) Red is coiled-coil and blue is globular
domains 1824CgtT is aa conservative (G608G) but -
in 300 con. 1824CgtT creates a cryptic donor site
at 1819, -50 aa del
3
Best guess
Most diseases are probably interactions
between polygenic heritable events, and
environmental pressures leading to somatic
epigenetic changes. Translation diseases are
complicated.
4
Gene by Environment Interaction
Predisposition
Event
Disease
DNA
FAP MSH BRCA LDLr
hydrocarbons radiation estrogens low fiber
colon CA colon CA breast CA atherosclerosis
5
Microarrays-the big net.
Ideal disease-hunter genomic scale protein
quantitation and sequencing. Imperfect solution
A genomic scale detection of mRNA
level. Problem little information on protein
level Imperfect solution B genome-wide
SNP/haplotype. Problem statistical limits on
patient populations Common compromise
microarray profiling mRNA transcripts (transcript
profiling) to identity target areas. Target
genes are then followed by proteomics and SNPs.
6
Array flavors
DNA detection (SNP, genotyping, etc.) short
oligonucleotides to detect mismatches RNA
detection (transcript profiling) Plasmid
Inserts Long oligonucleotides (60 mers)
Short oligonucleotides (20 mers)
7
Hybridization-basic elements
- Hybridization Annealing - Melting
- CRUCIAL non-covalent, hydrogen bonds
- --gtequilibrium rules, binding is statistical
- Best hybridization occurs with
- long sequences (no hyb when ntlt4)
- high salt concentration (hybrids melt in water)
- low temperatures (hybrids melt with heat)
- G and C (3 H) bind better than A and T (2 H)
- self-complementarity is low (high GC is bad)
8
Base-pairing (the stuff of life)
A
T
G
C
T
A
C
G
Lewin. Genes VII page 8.
9
Tm-a good thing.
Tm is a measure of the stability of DS-DNA under
a given set of conditions. Stability, and
therefore Tm, is affected by Strand length -
the longer the strand, the higher the Tm Base
Composition - higher the GC content, the higher
the Tm. Ionic Strength - as the ionic strength
increases, so does Tm. Double helical DNA is
stabilised by cations. Divalent cations (eg
Mg2) are more effective than monovalent
cations ( or K). Organic Solvents - formamide
for instance lowers the Tm by weakening the
hydrophobic interactions.
10
Melting Curves-Tm measured
Tm
Tm
11
PCR Primer design
www.oligo.net
12
Array Choice Factors
Expression profiling Sequence known? Not
known? Oligo arrays cDNA arrays High
confidence Clone drift/cross hyb Immediate
ID sequence clones
13
Sample selection
- isolate the purest phenotypic examples of test
and control - laser capture microdissection (LCM)
- always control for treatment and manipulation
- people are the most meaningful, but least
controllable - animals are highly controllable, but less
meaningful - cell systems (in vitro) are controlled, but
meaningful? - small amounts of RNA can be amplified
- while purifying cells is good, the processing is
bad. - The quality of the results are directly
proportional to the samples that are chosen.
14
Laser Capture Microdissection
15
The importance of purity
Human colon cancer Blue are normal cells Red
are tumor cells
16
Assessing sample quality
Amount gt 5 ug total RNA or 500 ng of poly
A Basic O.D. 260/280 ratio gt2.1, nucleic
acids absorb at 260, protein at 280 nm thus,
increasing impurity reduces ratio Better
agarose gel electrophoresis, EtBR stained if
total RNA, 28s 2 x 18s ribosomal
(Lab-on-chip) or Q-PCR of a low and high gene,
against standard Best test chip
17
GeneChip Probe Arrays
GeneChip Probe Array
11 µm
1.28cm
gt1 million probes
Image of Hybridized Probe Array
18
Synthesis of Ordered Oligonucleotide Arrays
19
GeneChip Expression Array Design
Gene Sequence
Probes designed to be Perfect Match
Probes designed to be Mismatch
20
Procedures for Target Preparation
Cells
Labeled transcript
AAAA
IVT (Biotin-UTP Biotin-CTP)
L
L
L
L
Poly (A) RNA
cDNA
Fragment (heat, Mg2)
L
L
Wash Stain
Hybridize (16 hours)
L
L
Scan
Labeled fragments
Streptavidin-Phycoerythrin (SAPE) Fluorescent
stain-laser stimulated
21
Analysis of expression level from probe sets
A single, contiguous gene set for the rat B-actin
gene.
Each pixel is quantitated and integrated for each
oligo feature (range 0-25,000)
Perfect Match (PM)
Mis Match (MM) Control
PM - MM difference score All significant
difference scores are averaged to create average
difference expression level of the gene.
22
Affymetrix Instrument System
Platform for GeneChip Probe Arrays
- Integrated
- Exportable
- Easy to use
- Versatile
23
GeneChip analysis of human atherosclerosis
Dissect normal media from atherosclerotic lesion
Prepare highly purified RNA O.D. 260/280 2.0
Reverse transcribe w/poly dT T7
cDNA Transcribe with T7 biotin dUTP cRNA
Purify probe/hybridize to chip
Wash and detect with avidin/PE ab amplification
Read fluorescent label And deconvolve genes
24
Basic Bioinformatics-Scatterplot
25
Transcript profiling of aged rat aorta.
- Affymetrix GeneChip analysis of 10 aortas _at_ 20
mo. vs. 3 mo.
26
FAQs How many replicates?
27
Simple fold changes
- Crude, insensitive--but effective
Criteria Present 1.5-fold up/down
28
Hierachical clustering
29
Statistical testing and ontology
30
Pathways of genetic information
31
Expression of Egr-1 mRNA in human lesions.
32
Egr-1 mRNA and protein in lesions vs normal cells.
Western blot
B)
A)
Media
E240
E221
E197
E243
20
Lesion
M
L
M
L
M
L
M
L
15
Egr-1
Egr-1 mRNA
x
x
10
5
Actin
0
E197
E196
33
Expression screening by GeneChip
each oligo sequence (20 mer) is synthesized
as a 11 µ square (feature) each feature
contains gt 1 million copies of the oligo
scanner resolution is about 2 µ (pixel) each
gene is quantitated by 11 oligos and compared to
equal of mismatched controls 44,000 genes
are evaluated with 11 matching oligos and 11
mismatched oligos 4 x 106 features/chip
features are photolithographically
synthesized onto a 2 x 2 cm glass substrate
34
GeneChip Array Advantages Specificity
Oligo arrays
cDNA arrays
Gene on
150 µm
24 µm
Gene off
Detection Pattern
Single Spot
35
Limitations to all microarrays.
- dynamic range of gene expression
- very difficult to simultaneously detect low and
high - abundance genes accurately
- - each gene has multiple splice variants
- 2 splice variants may have opposite effects
(i.e. trk) - arrays can be designed for splicing, but
complexity 5X - - translational efficiency is a regulated
process - mRNA level does not correlate with protein level
- - proteins are modified post-translationally
- glycosylation, phosphorylation, etc.
- - pathogens might have little genomic effect
36
CardioChip
- in silico workup