FACIES MODELS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
FACIES MODELS
Description:
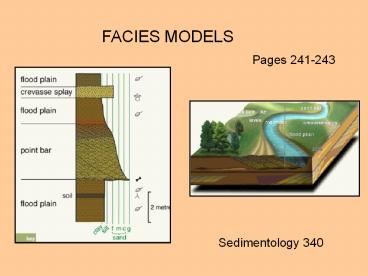
FACIES MODELS Pages 241-243 Sedimentology 340 Previous Work Majority of the semester has been largely descriptive, identifying; Lithology & mineralogy Sedimentary ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1055
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: FACIES MODELS
1
FACIES MODELS
Pages 241-243
Sedimentology 340
2
Previous Work
- Majority of the semester has been largely
descriptive, identifying - Lithology mineralogy
- Sedimentary fabric and texture
- Sedimentary structures
- Scales of observation
- Now a Story to tell and puzzles to solve
- Sediments are products of sedimentary processes
- Snapshot of the environment of deposition
3
Sedimentary Facies
- Facies analysis
- The interpretation of rocks and sediments for the
purpose of reconstructing the processes that were
responsible for the original deposition - Multi-pronged approach
- Physical
- Chemical
- Biological
- Lithofacies and Biofacies
Example of sedimentary facies modal Delta
distributary channel
4
Pardon me, what are facies?
- In the field of geology, facies is often misused
and misunderstood - AGI (1984) Definition
- The aspect, appearance, and characteristics of a
rock unit, usually reflecting the conditions of
its origin especially as differentiating it from
adjacent or associated units
Facies! Refers to the lithologic and biologic
characteristics of a sedimentary deposit imparted
by the processes collectively operating in the
depositional environment
5
Facies defined
- Deposits that evolve in a specific depositional
environment are considered to be sedimentary
facies - Ex. Arid desert lakes/salt flats
Bonneville Salt Flats, Utah
6
Facies defined
- For this class and facies will be defined as
- A description of physical, chemical and
biological properties of a sedimentary unit - Main criteria in facies definition are
- Lithology, sedimentary structures, paleontology,
and sediment body geometry
7
Sediment body geometry is the 3-D shape of deposit
barrier island
8
Question?
What are you looking at? How can you describe it
in the framework of its depositional environment?
This is a delta
How do we know?
?
9
Delta
Delta is at the end of a river and is the
sedimentary record of deposition into deeper water
10
Nile Delta Example
Modern examples are used to gather data on
processes and deposits (cores)
Facies model - a 3-D block diagram
11
Facies model 2-D vertical succession diagram
Delta depositional environment?
12
So question was.how do we know ? Answer facies
associations
- Depositional environments are generally composed
of multiple subenvironments - Ex. Delta
- Thus, we can expect that facies will vary
throughout the environment to reflect the
transition between subenvironments - We must assume that adjacent facies represent
adjacent environments
13
Delta components and facies
14
So how are they related?
- The association of certain facies near or
adjacent to each other are characteristic of
distinct depositional environments
Based on observations from modern environments of
deposition and parallels to past environments
By understanding these associations, we can
generate facies models
15
4-D models add understanding of processes
3-D Block daigram facies associations in a delta
distributary channel environment
16
Facies Models
- General summary given to a depositional system
- 2-D Vertical successions of sediment that
represent facies relationships expected in the
geologic record - 3-D Block Diagrams
- 4-D Models detailing sedimentary processes
17
Walthers Law of Correlation of Facies
- Facies that occur in comformable vertical
successions of strata also occur in laterally
adjacent environments - Thus, facies boundaries may shift so that the
deposits of an adjacent environment may lie
directly atop those of a laterally related
environment
18
Takeaway Message For any sedimentary package
you can examine the facies and their
relationships to each other, apply a facies model
and assign a depositional environment
So, what is this?
19
Catskill Delta (Devonian)
Catskill Delta builds westward through time with
sediment delivered by rivers
fluvial
delta
marine
Regressive- sediments coarsen upwards
20
3-D Barrier Island Facies Model
barrier island
21
Environments are dependent on sediment supply,
subsidence and changing sea level
Conditions (tectonics or climate) usually change
with time
With rise in sea level ..
The shoreline shifts landward and fine grained
marine sediments will overly coarser beach
sediments
Transgressive sediments fine upwards,
22
Facies Changes
- Transgressive and Regressive systems can be
identified by observing facies and lithological
changes in rock/sediment - Transgressive sediments fine upwards, represent
deeper water environments - Regressive- sediments coarsen upwards, represents
shallowing effect
23
Facies Distribution
- What factors control the nature and distribution
of facies? - 1. Sedimentary Processes
- 2. Sediment Supply
- 3. Climate
- 4. Tectonics (subsidence or uplift)
- 5. Sea level change
24
Summary using an example
- What facies would you expect to find from this
depositional environment?
- Fluvial Environment
- Meandering River
- Cross bedded sandstones
- Coarse gravel deposits
- Broad sheets of silty shale with root casts and
plant debris - Isolated Shale bodies
- Beds of peat and coal
- Facies models help solve the puzzle of
depositional environment