Business vs. Consumer Marketing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
Business vs. Consumer Marketing
Description:
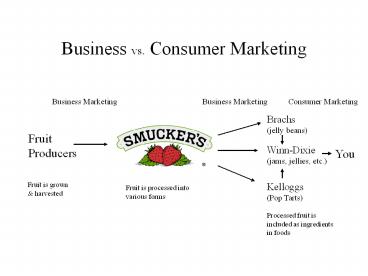
Business vs. Consumer Marketing Business Marketing Business Marketing Consumer Marketing Brachs (jelly beans) Fruit Producers Winn-Dixie (jams, jellies, etc.) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:160
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Business vs. Consumer Marketing
1
Business vs. Consumer Marketing
Business Marketing
Business Marketing
Consumer Marketing
Brachs (jelly beans)
Fruit Producers
Winn-Dixie (jams, jellies, etc.)
You
Fruit is grown harvested
Kelloggs (Pop Tarts)
Fruit is processed into various forms
Processed fruit is included as ingredients in
foods
2
From Industrial Product toCommercial Consumer
Electrical Equipment Manufacturer (Producer
of Electrical Motors)
Business Marketer
Type of Commercial User
Appliance Manufacturer (OEM)
Electrical Supply Dealer (Industrial Distributor)
Food-Processor Firm (User)
OEMs
Users
Electrical motors are purchased and resold to
users and OEMs
Electrical motor used in high-speed mfg system of
food proc.
Electrical motor incor- porated directly
into product (e.g., washer)
Purpose Product Serves
3
Classifying Goods Servicesfor the Business
Market
Entering Goods
Foundation Goods
Installations - Buildings Land Rights - Fixed
Equipment Accessory Equipment - Light Factory
Equipment (e.g., lift trucks) - Office
Equipment
Raw Materials - Farm Products - Natural
Products (e.g., iron ore, lumber) Manufactured
Materials/Parts - Component Materials -
Component Parts (e.g., tires, microchips)
Facilitating Goods
Supplies - Operating Supplies (e.g.,
lubricants, paper) - Maintenance Repair Items
(e.g., paint) Business Services - Maintenance
Repair Services - Business Advisory Services
4
The Supply Chain(the entire system for
lawnmowers)
Transportation, a facilitating service
Finished Lawnmower
Manufactured Materials
Raw Materials
Component Parts
Assembly
Purchase Order Copied, a facilitating product
Number, type, style of mowers determined
by research, a facilitating service
5
The Realm of Buyer-Seller Relationships
Sellers Motivation to Relate
High
Joint relationship maintenance
Seller-maintained relation
Buyers market
Buyers Motivation to Relate
Low
High
Buyer-maintained relation
Discrete exchange (spot contracts)
Sellers market
No Exchange
Low
6
The Relationship Development Process
Relationship Phase
Phase Characteristics
1. Awareness 2. Exploration 3.
Expansion 4. Commitment
1. No interaction 2. Interaction occurs
testing, gradual increase in dependence 3.
One party makes a successful request for
adjustment more benefits sought from current
partner rather than from others 4. Means of
sustaining the relationship develop social
ties, shared ownership, etc. Disputes
resolved internally
Enabling Subprocesses for Deepening Dependence
Communication Bargaining
Attraction
Power Justice
Expectations Development
Norm Development
Shared values and decision- making structures
support joint investment in relationship.
0 Sellers dependence Buyers
dependence 0 on buyer
on seller
7
Market Segmentation
Substantiality
Identifiability and Measurability
Criteria for Successful Segmentation
Accessibility
Responsiveness
8
Segmenting Consumer Markets
Geographic
Demographic
Bases for Segmenting Consumer Markets
Psychographic
Benefits
Usage Rate
9
The Family Life Cycle
Middle-aged divorced without children
Young divorced without children
Middle-aged married without children
Middle-aged married without dependent children
Middle-aged married with children
Young married with children
Young married without children
Young single
Older married
Older unmarried
Usual flow Recycled flow Traditional flow
Middle-aged divorced without dependent children
Middle-aged divorced with children
Young divorced with children
10
The VALS 2 Categories
Abundant resources
Principle- oriented
Status- oriented
Action- oriented
Actualizers
Experiencers
Achievers
Fulfillers
Makers
Believers
Strivers
Strugglers
Source The VALS 2 Categories. Reprinted by
permission of SRI International, Menlo Park,
California.
Minimal resources
11
Segmenting Business Markets
Geographic
Customer Type
Macro- segmentation
Customer Size
Business to Business
Product Use
Purchasing Criteria
Purchasing Strategy
Micro- segmentation
Importance
Personal Characteristics
12
Steps in Segmenting a Market
Select Market or Product Category
Choose Segmentation Bases
Steps in Segmenting a Market
Select Segmentation Descriptors
Profile/Analyze Segments
Select Target Markets
Subsequent Marketing Activities
Design, Implement, Maintain Marketing Mix
13
Strategies for Selecting Target Markets
Concentrated Strategy
Undifferentiated Strategy
Multisegment Strategy
14
Multisegment Targeting
Benefits Potentially greater sales volume
Higher profits Larger market share Economies
of scale in manufacturing marketing
Costs Production design costs Production
costs Promotion costs Inventory costs
Market research costs Management costs
Cannibalization
15
Positioning Bases
Attribute
Price and Quality
Use or Application
Positioning Bases
Product User
Product Class
Competitor
16
Marketing Research
Descriptive Diagnostic Predictive
17
The Marketing Research Process
Define Problem
Plan Design/ Primary Data
Specify Sampling Procedure
Collect Data
Analyze Data
Prepare/ Present Report
Follow Up
18
Advantages/Disadvantages of Secondary Data
Advantages Rapid availability Inexpensive May
shed light on the problem Disadvantages Often
doesnt provide a sufficient answer Quality of
data sometimes difficult to determine
19
Sources of Secondary Data
Source
Description
Internal Information
Sales Invoices, Accounting Records, Previous
Market Research
Market Research Firms
Companies Such As A.C. Nielsen, Arbitron, IMS
International
Trade Associations
Associations Such As National Industrial
Conference Board, National Retail Merchants
Association
University Research Bureaus, Professional
Associations, Foundations
Variety of Nonprofit Organizations
Commercial Publications
Advertising Age, Sales Management, Product
Marketing, Selling Power
Government Data
Federal Government publications such as Census of
Housing, Census of Manufacturers, Economic
Indicators
20
Advantages/Disadvantages of Primary Data
Advantages Answer specific questions Current Kn
own source Secrecy can be maintained Disadvant
ages Time-consuming Expensive
21
Forms of Survey Research
In-Home
Common Forms of Survey Research
Mall Intercept
Telephone (Interviewer)
Telephone (Central)
Focus Group
One-Time Mail Survey
Mail Panel Surveys
22
Consumer Products
23
Product Lines
Advertising Economies
Package Uniformity
Benefits of Product Lines
Standardized Components
Efficient Sales and Distribution
Equivalent Quality
24
Gillettes Product Lines Mixes
Width of the product mix
Blades and Writing razors Toiletries instru
ments Lighters Depth of Sensor Series Paper
Mate Cricket the product Trac II Adorn Flair S.
T. Dupont lines Atra Toni Swivel Right
Guard Double-Edge Silkience Super
Adjustment Soft and Dri Lady Gillette Foamy Su
per Speed Dry Look Twin Injector Dry
Idea Techmatic Brush Plus Three-Piece Knack
Blades
25
Abbreviated Product MixKraft
Width of Product Mix
Breakfast Cereals
Baked Goods
Beverages
Alpha-Bits Fruit Fiber Grape-Nuts Honeycomb
Pebbles Post 40 Bran Flakes Post Raisin
Bran Post Toasties Smurf-Berry Crunch
Entenmanns Hostess Snacks Krema Candy Orowheat
Country Time Lemonade Crystal Light Kool-Aid Su
gar-Free Kool-Aid Tang
Depth of Product Lines
26
Changing Product LinesKraft
Width of Product Mix
Breakfast Cereals
Baked Goods
Beverages
Alpha-Bits Fruit Fiber Grape-Nuts Honeycomb
Pebbles Flintstones Post 40 Bran Flakes Post
Raisin Bran Post Toasties Smurf-BerryCrunch
Entenmanns Hostess Snacks Krema Candy Orowheat
Country Time Lemonade Crystal Light Kool-Aid Su
gar-Free Kool-Aid Tang Sweet Stuff
Depth of Product Lines
27
Adjustments to Items, Lines, Mixes
Product Modifications
Strategies for Changing Product Lines
Repositioning
Product Line Extensions
Product Line Contractions
28
Branding
Individual
Types of Manufacturers Brands
Family
Co-Branding
Combination
29
Major Branding Decisions
Brand
No Brand
Private Brand
Manufacturers Brand
Combination (family and individual)
Combination (family and individual)
Individual Brand
Family Brand
Family Brand
Individual Brand
30
Packaging
31
MKTG 501 Marketing Rocks!