Homeostatic imbalances - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Homeostatic imbalances
Description:
Heart block any damage to the AV node results in irregular beating of ventricles Murmurs abnormal or unusual hearts sounds * * ECG: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:792
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Homeostatic imbalances
1
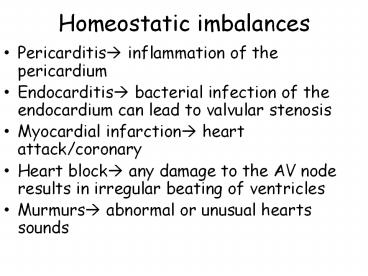
Homeostatic imbalances
- Pericarditis? inflammation of the pericardium
- Endocarditis? bacterial infection of the
endocardium can lead to valvular stenosis - Myocardial infarction? heart attack/coronary
- Heart block? any damage to the AV node results in
irregular beating of ventricles - Murmurs? abnormal or unusual hearts sounds
2
ECG normal and abnormal
3
Alterations in Electrocardiogram
Clinical Cardiology Concepts for Vets
4
Cardiac Output
- Cardiac Output - the amount of blood pumped by a
ventricle per minute. Units may be in milliliters
or Liters per minute. - Heart Rate - number of cardiac cycles per minute.
Average for males 64-72/min. Average for
females 72-80/min. - Stroke Volume - amount of blood pumped out of a
ventricle each beat. Average resting stroke
volume 70 ml.
5
Cardiac Output
- CO (mL/min) SV (70 mL/beat) X HR (75 beat/min)
- Cardiac output stroke volume X heart rate
5250ml/min - SV EDV - ESV
- Stroke volume end diastolic volume end
systolic volume - Cardiac reserve is the difference between a
persons maximum cardiac output and cardiac
output at rest.
6
Frank Starling Law of the Heart
- The more cardiac muscle is stretched within
physiological limits, the more forcibly it will
contract. - Rubber band analogy
- Increasing volumes of blood in ventricles
increase the stretch thus the force generated
by ventricular wall contraction. - Greater stretch means more blood volume is pumped
out, up to physical limits.
7
Regulation of stroke volume
- Preload is the degree of stretch on the heart.
- Contractility is the force of ventricular
contractions. - Afterload is the pressure that must be exceeded
to eject blood from the ventricles. - The Frank-Starling law of the heartpreload is
the critical factor controlling SV (stroke
volume).
8
Regulation of heart rate
- When blood volume drops or the heart is weakened,
SV drops and the HR increases. - Positive chronotropic factors increase HR.
- Negative chronotropic factors decrease HR.
- Extrinsic regulation by the ANS
- Sympathetic nervous system increases firing of
the pacemaker and enhances Ca2 entry into heart
cells. - Parasympathetic nervous system reduces heart rate
through ACh which opens K channels. - Under resting conditions the PNS is dominant
9
Chemical Regulation
- Hormones
- Epinephrine enhances HR and contractility
- Thyroxine enhances effects of Epi and NE and
leads to slower more sustained increase in HR - Ions
- Hypocalcemia (Ca2)depresses the heart
- Hypercalcemia prolongs the plateau phase and lead
to heart irritability - Hyperkalemia (K) may lead to heart block and
cardiac arrest hypokalemia leads to arrhythmia
and weakened contractions. - Excess Na blocks Ca2 inflow, decreasing
contractile strength
10
Other Factors
- Exercise leads to a reduced HR when at rest.
- Working large body muscles for at least 20
minutes elevates cardiac output and accelerates
metabolism. - Athletes have a larger heart and a resting HR of
40-60 beats per minute - Increased temperature increases heart rate
decreased temperatures reduce heart rate and
oxygen needs.
11
Homeostatic imbalances
- Congestive heart failure
- Caused by? Coronary artherosclerosis
- Caused by ? Persistent high blood pressure
- Caused by? Multiple myocardial infarcts
- Left side failure ?Pulmonary congestion
- Rights side failure? Peripheral congestion
12
Angina Pectoris
- Medical term for chest pain due to coronary heart
disease. - It occurs when the myocardium doesnt get as much
blood (Oxygen) as it needs. - Insufficient blood supply is called ischemia.
- May initially occur during physical exercise,
stress, or extreme temperatures. - It is a sign of increased risk of heart attack.
13
Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Arrhythmias? irregular heart rhythms that may
lead to fibrillation - Tachycardia Heart rate in excess of 100bpm
- Bradycardia Heart rate less than 60 bpm
- Sinus arrhythmia Heart rate varies 5 during
respiratory cycle and up to 30 during deep
respiration - Premature atrial contractions Occasional
shortened intervals between one contraction and
succeeding, frequently occurs in healthy people
14
Aneurysm
- Weakness of the wall of an artery causing an
abnormal enlargment or bulge. - The aorta or the arteries that supply the heart,
brain, legs or kindeys are most commonly affected.
15
Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis)
- Narrowing and hardening of arteries and
impairment of blood flow due to the deposition of
fatty materials and calcium in their walls. - Risk factors include
- smoking
- inactivity
- diabetes
- high blood cholesterol
- personal or family history of heart disease
- Atherosclerosis Animation
16
Resources
- Heart Sounds Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Live Cardiac Exam Video
- Anatomy Links
- Cardiac Cycle
- Cardiac Cycle Graphics
- Interactive Physiology Review
- AP II Notes Homepage
17
Conducting System of Heart