Condensation Reactions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Condensation Reactions
Description:
Condensation Reactions Two molecules combine with the generation of a smaller molecule Condensation Reactions Reaction of Acetic Acid and Ethanol Looking at the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:99
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Condensation Reactions
1
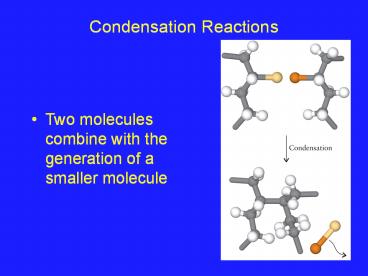
Condensation Reactions
- Two molecules combine with the generation of a
smaller molecule
2
Condensation Reactions
- Reaction of Acetic Acid and Ethanol
3
Looking at the Reaction Mechanism
- The carbonyl carbon is
- Electron deficient
- In a trigonal planar geometry
- 120º between substituents
- The carbonyl oxygen is pulling electrons towards
it - Resonance stabilization
- The Lone Pair of the alcohol oxygen can react
with the carbonyl carbon to set the whole thing
in motion - Remember your VSEPR Geometry
4
Condensation Reactions Making Lipids from
Sugars and Fatty Acids
- Your cells can synthesize lipids from glycerol
and fatty acids in a condensation reaction
?
5
Condensation Reactions Polymerizing
Carbohydrate Monomers
6
Condensation Reactions Forming a Peptide Bond
- What are the amino acids in the figure?
- What function group is formed?
Its not really this simple, but it illustrates a
point!
7
Hydrolysis The Opposite of Condensation
- In a hydrolytic reaction, we add the elements of
water (H and OH-) across a bond - Many enzymes use this kind of reaction to degrade
polymers - Lipases Hydrolyze lipid esters
- Glycosidases Hydrolyze carbohydrate polymers
- Peptidases Hydrolyze peptide bonds
- Compound Name ase Usually indicates a
hydrolase (but not always!) - If it isnt a compound name and ase, then it
usually does something else - Lyase
- Reductase
- Kinase
- Transferase
8
Hydrolysis of Sugar Polymers
- We add water across the Glycosidic Bond of
Maltose to break it and generate 2 monomers - Catalyzed by a glycosidase (Maltase perhaps?)
9
Hydrolysis of Peptides
- Dipeptide (What are the amino acids) is
hydrolyzed to ??? - Catalyzed by a peptidase or a protease
10
Amino Acids
- Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins
- They consist of an amino group bonded to an
?-carbon, a hydrogen bonded to the ?-carbon and a
carboxylic acid
11
Amino Acids and Stereochemistry
- The ?-carbon is all amino acids except for
glycine is chiral - Stereoisomers exist that is non-superimposable
- Any carbon with 4 different substituents can be
chiral - We describe the chirality of the ?-carbon as
being Levorotary or Dextrorotary - L- or D-
- Refers to how the molecule rotates polarized light
12
Amino Acids and Stereochemistry
13
Amino Acid Side Chains Where the Action is!
- The amino acids are classified according to the
chemical character of the R-grop attached to the
?-carbon - Important Criteria
- Polar or Nonpolar side chains
- Acidic or Basic
- Charged or uncharged Polar residues
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
Side Chain Classification
- Nonpolar (hydrophobic) Amino Acids
- G, A, V, L, I, P, F, W, M
- These amino acids have aliphatic side chains
- Phenylalanine and Tryptophan are aromatic
- Proline is cyclic
- Induces turns in proteins
21
Side Chain Classification
- Polar, Uncharged Amino Acids
- S, T, Y, C, N, Q
- S, T, Y have hydroxyl groups (-OH)
- C has a sulfhydryl (-SH)
- N and Q have amide side chains
- Uncharged at neutral pH
22
Side Chain Classification
- Acidic Amino Acids
- D and E have carboxylic acids on their side
chains - The side chains are negatively charged at neutral
pH - This means the pKas of the side chains are less
than 7
23
Side Chain Classification
- Basic Amino Acids
- H, K and R have side chains that are positively
charged at neutral pH - Because these side chains have basic groups, they
accept protons at pH values lower than the pKa of
the side chain
24
Titrating Amino Acids
- Free amino acids can have up to 3 pKa values
associated with them - Carboxylic acid
- Amino group
- R-group
- The carboxylic acid group has the lowest pKa
(2.0) - The pKa of the ?-amino is around 9-10
- D, E, H, C, Y, K and R have R-groups that can
ionize and their pKas range from 4 to 12
25
(No Transcript)
26
Titrating and Amino Acid Alanine
- Well start at a pH of 1
- The carboxylic acid and the amino group are
protonated - As we start adding base, more and more of the
carboxylic acids start losing protons until we
reach pH 2.34 (the pKa of COOH) - At this concentration, NH3CHCH3COOHNH3CHCH3C
OO- (same as we learned with regular titrations) - As we add more base, we deprotonate all the
carboxylic acids - Midway up the sharp slope increase
- For alanine, this is the isoelectric point
- As we add more base, well start deprotonating
the ?-amino group until we reach pH9.69 (the pKa
of the group) - NH3CHCH3COO-NH2CHCH3COO-
- Finally we can keep adding base until the only
species is NH2CHCH3COO-
27
Titrating and Amino Acid Histidine
- Well start at a pH of 1, the only species is the
fully protonated form. - pK1 (COOH) 1.82
- pK2 (Imidazole nitrogen) 6.0
- pK3 (Amino) 9.17
- As we start adding base, the pH increases as the
carboxylic acid converts to carboxylate - At pK1, the concentration of the carboxylate
specie equals the concentration of the carboxylic
acid species - As we add more base, we start deprotonating the
imidazole nitrogen - At pK2, the conc. of the deprotonated imidazole
group equals that of the protonated state - The pI is reached then the imidazole group is
completely deprotonated - As we add more base, well start deprotonating
the ?-amino group until we reach pH9.17 (the pKa
of the group)
28
Amino Acid Titrations
- At the isoelectric point, the molecule has zero
net charge - The pH where this occurs is called the pI
- We can calculate the pI of an amino acid using
the following equation - We average the pK values from the higher pKa that
lost a hydrogen and the lowest pKa that is still
protonated - For example Histidine
- pK1 1.82
- pK2 6.0
- pK3 9.17
- Wed use the last two values
- Usually it will be the alpha amino and the R
group pKs that are used
But we must take care to use the correct pK
values!
29
The Peptide Bond
- Amino acids are joined together in a condensation
reaction that forms an amide known as a peptide
bond
30
The Peptide Bond
- A peptide bond has planar character due to
resonance hybridization of the amide - This planarity is key to the three dimensional
structure of proteins