Constraints - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: Constraints
1
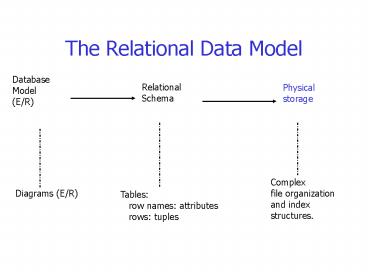
The Relational Data Model
Database Model (E/R)
Relational Schema
Physical storage
Complex file organization and index structures.
Diagrams (E/R)
Tables row names attributes rows tuples
2
Terminology
Attribute names
Title Year Length
FilmType Star Wars 1997
124 color Mighty Ducks
1991 104
color Waynes World 1992 95
color . . . .
. . . . . . . .
components of tuples
tuples
3
More Terminology
Every attribute has an atomic type.
Relation Schema relation name attribute names
attribute types Relation instance a set of
tuples. Only one copy of any tuple! Database
Schema a set of relation schemas. Database
instance a relation instance for every relation
in the schema.
4
From E/R Diagrams to Relations
- Entity sets become relations with the same set of
attributes. - Relationships become relations whose attributes
are only - The keys of the connected entity sets.
- Attributes of the relationship itself.
5
Entity Sets to Relations
Relation schema Movies(title, year, length,
filmtype )
A relation instance
6
E/R Relationships to Relations
- Relationships in the E/R model are also
represented by relations. - The relation for a given relationship R has the
following attributes - For each entity set involved in relationship, we
take its key attribute(s) as part of the schema
of the relation for R. - If the relationship has attributes, these are
also attributes of relation R. - When one entity set is involved several times in
a relationship - - or -
- the same attribute name appears in the keys of
different ES participating in the relationship R,
- - or -
- even when we like to avoid confusion and to be
clearer in meaning - we should rename the attributes.
7
Example (with Renaming)
- The relationship Owns between entity sets Movies
and Studios is represented by a relation with
schema Owns(title,year,studioName). - A sample instance is
- title year studioName
- Star Wars 1977 Fox
- Mighty Ducks 1991 Disney
8
Example (with Renaming)
- The relationship Stars-In between entity sets
Movies and Stars is represented by a relation
with schema Stars-In(title, year, starName) - A sample instance is
- title year starName
- Star Wars 1977 Carrie Fisher
- Star Wars 1977 Mark Hamill
- Star Wars 1977 Harrison Ford
- Mighty Ducks 1991 Emilio Estevez
- Waynes World 1992 Dana
Carvey - Waynes World 1992 Mike
Meyers
9
Example (with Renaming)
10
Combining Relations
- It is OK to combine the relation for an
entity-set E with the relation R for a many-one
relationship from E to another entity set. - Example Drinkers(name, addr) and
Favorite(drinker, beer) combine to make
Drinker1(name, addr, favBeer).
11
Risk with Many-Many Relationships
- Combining Drinkers with Likes would be a mistake.
Why? - It leads to redundancy, as
12
Handling Weak Entity Sets
- Relation for a weak entity set must include
attributes for its complete key (including those
belonging to other entity sets), as well as its
own, nonkey attributes. - A supporting (double-diamond) relationship is
redundant and yields no relation.
13
Example
name
name
Logins
Hosts
At
location
billTo
Hosts(hostName, location) Logins(loginName,
hostName, billTo) At(loginName, hostName,
hostName2)