Metamorphic Reactions PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title: Metamorphic Reactions
1
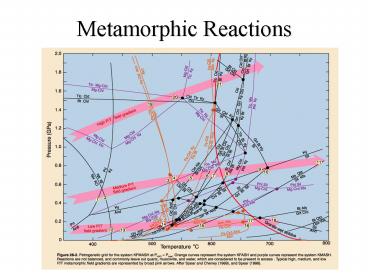
Metamorphic Reactions
2
Today
- Updates
- Review on Wednesday
- Final next Monday, 10.00 am
- Lecture outline
- Finish up
- Reaction types
- Example for metapelites
3
Chemical Equilibrium in Metamorphism
http//www.earth.ox.ac.uk/sem/SEMProbe_pics/fras
_gt_mini.gif
4
Types of Metamorphic Reactions
- Types
- Phase transformations
- Exsolution
- Solid-solid net transfer
- Devolitalization
- Ion-exchange
- In the field recognized as isograd
- First occurrence of new mineral
- P-T-X dependent
- Given X, estimate P-T
5
Phase Transformations Al2SiO5
- Isochemical
- Only f(P,T)
- Common in Al rich rocks (metapelites)
- Rough P-T indicator
- Andalusite suggests low P
- Kyanite high P
- Sillimanite high P and T
6
Exsolution
7
Solid-Solid Net-Transfer Reactions
8
Net-Transfer Reactions and Volatiles
9
Devolatilization Reactions
- Other volatiles besides H2O-CO2 systems
- Example
- KAl2Si3AlO10(OH)2 SiO2 KAlSi3O8 Al2SiO5
H2O - Ms Qtz Kfs Sill W
- Dependence
- P, T
- Partial pressure
- Not all pores filled
- gt Pfluid lt Plithostatic
- Other volatiles in fluid
- Plith PH2O PCO2
10
Devolatilization Reactions
11
Ion Exchange
Mg2 Fe2
12
Pseudomorphs and (Dis)ContinuousReactions
Discontinuous reaction geotherm crosses reaction
curve at 1 P T, reaction takes place at those
constant P T Continuous reaction reaction
occurs over range in P T similar to melting in
solid solution Pseudomorphs small change in
entropy need fair bit of energy from heat
(T) reaction over small T range
13
(No Transcript)
14
- The ACF Diagram
- Mafic rocks
- Concentrate only on minerals that appeared /
disappeared - from 8 to 3 pseudo
- -components
- A Al2O3 Fe2O3
- - Na2O - K2O
- C CaO - 3.3 P2O5
- F FeO MgO
- MnO
15
- The AKF Diagram
Pelitic sediments high in Al2O3, K2O
- In the AKF diagram, the pseudo-components are
- A Al2O3 Fe2O3
- - Na2O - K2O CaO
- K K2O
- F FeO MgO
- MnO
16
- A(K)FM Diagram
Project from a phase that is present in the
mineral assemblages to be studied to make a
triangular plot (AFM)
Figure 24-18. AKFM Projection from Mu. After
Thompson (1957). Am. Min. 22, 842-858.
17
- Projections
- Why we ignored SiO2 in the ACF and AKF diagrams
assumed present in all rocks - AFM A Al2O3 - (3)K2O
- Subtraction for pseudo-components
- A Al2O3 Fe2O3 - Na2O - K2O (AKF)
- Na, K typically combined with Al in Fsp
- In the ACF diagram only interested in Al2O3
outside Fsp - Since the ratio of Al2O3 to Na2O or K2O in
feldspars is 11, we subtract from Al2O3 an
amount equivalent to Na2O and K2O in the same 11
ratio
18
- Plotting in A(K)FM Diagram
- Biotite (from Ms)
- KMg2FeSi3AlO10(OH)2
- A Al2O3-3K2O
- 0.5 - 3 (0.5) - 1
- F FeO 1
- M MgO 2
- To normalize we multiply each by
1.0/(2 1 - 1) 1.0/2 0.5 - Thus A -0.5
- F 0.5
- M 1
- MgO/FeOMgO.67
19
Medium P-T path for Metapelites
20
Upper Biotite zone
21
Garnet zone
22
Kyanite zone
23
Sillimanite zone
24
Granulite facies