MEMS design and Microfabrication Lab - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
MEMS design and Microfabrication Lab
Description:
MEMS design and Micro-fabrication Lab. MML. 2-Dimensional SPR ... Simplified fabrication process of the SPR/MIP microfluidic chip. ... Fabrication. Abstract ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:237
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: MEMS design and Microfabrication Lab
1
2-Dimensional SPR Detection System Integrated
with Molecular Imprinting Polymer Microarrays
Using Microfluidic Technology
Kuo-Hoong Lee, Yuan-Deng Su, Shean-Jen Chen and
Gwo-Bin Lee Department of Engineering Science,
National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan 701
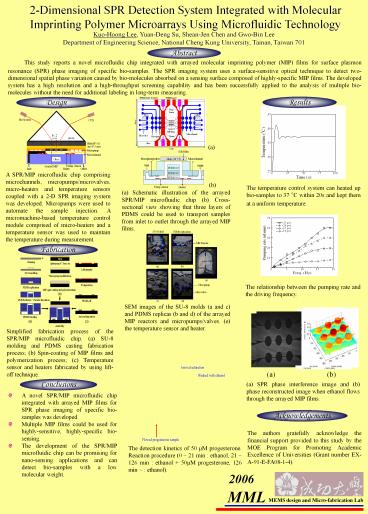
Abstract
This study reports a novel microfluidic chip
integrated with arrayed molecular imprinting
polymer (MIP) films for surface plasmon resonance
(SPR) phase imaging of specific bio-samples. The
SPR imaging system uses a surface-sensitive
optical technique to detect two-dimensional
spatial phase variation caused by bio-molecules
absorbed on a sensing surface composed of
highly-specific MIP films. The developed system
has a high resolution and a high-throughput
screening capability and has been successfully
applied to the analysis of multiple bio-molecules
without the need for additional labeling in
long-term measuring.
Results
Design
(a)
A SPR/MIP microfluidic chip comprising
microchannels, micropumps/microvalves,
micro-heaters and temperature sensors coupled
with a 2-D SPR imaging system was developed.
Micropumps were used to automate the sample
injection. A micromachine-based temperature
control module comprised of micro-heaters and a
temperature sensor was used to maintain the
temperature during measurement.
(b)
The temperature control system can heated up
bio-samples to 37 C within 20s and kept them at
a uniform temperature.
(a) Schematic illustration of the arrayed SPR/MIP
microfluidic chip (b) Cross-sectional view
showing that three layers of PDMS could be used
to transport samples from inlet to outlet through
the arrayed MIP films.
Fabrication
The relationship between the pumping rate and the
driving frequency.
SEM images of the SU-8 molds (a and c) and PDMS
replicas (b and d) of the arrayed MIP reactors
and micropumps/valves. (e) the temperature sensor
and heater.
Simplified fabrication process of the SPR/MIP
microfluidic chip. (a) SU-8 molding and PDMS
casting fabrication process (b) Spin-coating of
MIP films and polymerization process (c)
Temperature sensor and heaters fabricated by
using lift-off technique.
(a)
(b)
(a) SPR phase interference image and (b) phase
reconstructed image when ethanol flows through
the arrayed MIP films.
Conclusions
- A novel SPR/MIP microfluidic chip integrated with
arrayed MIP films for SPR phase imaging of
specific bio-samples was developed. - Multiple MIP films could be used for
highly-sensitive, highly-specific bio-sensing. - The development of the SPR/MIP microfluidic chip
can be promising for nano-sensing applications
and can detect bio-samples with a low molecular
weight.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial
support provided to this study by the MOE Program
for Promoting Academic Excellence of Universities
(Grant number EX- A-91-E-FA08-1-4).
The detection kinetics of 50 µM progesterone.
Reaction procedure (0 21 min ethanol, 21
126 min ethanol 50µM progesterone, 126 min
ethanol).
2006
MML
MEMS design and Micro-fabrication Lab