Environmental Attitudes, Appraisal - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Environmental Attitudes, Appraisal
Description:
Measures physical properties. Used for public policy. Uses experts ... Physical & spatial properties of setting. height of ceiling, amount of illumination, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1074
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Environmental Attitudes, Appraisal
1
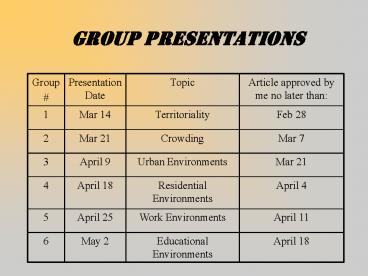
Group Presentations
2
Environmental Attitudes, Appraisal Assessment
This week . . .
3
Q What are attitudes?
- A Attitudes are lasting evaluations (positive
or - negative) of people, objects, actions,
ideas, etc.
Q What do we mean by environmental attitudes?
A An individuals concern (or lack thereof) for
the physical environment as something worthy
of protection, understanding and
enhancement.
4
(No Transcript)
5
Environmental (and other) Attitudesconsist of 3
components
1. Cognitive component --
What the person knows about the environment
(facts, etc.) People should know that littering
can pollute the environment
2. Affective component--
Emotional responses (feelings) toward toward the
environment I get angry when I see people
litter!
6
Components of Attitudes (contd)
3. Behavioral (conative) component --
A persons behavioral intentions toward the
environment
- When people throw candy wrappers on the ground I
try to pick them up and put them in the trash
can.
7
Example of Attitude ComponentsScoring the
Maloney-Ward Ecological Inventory
- Using the answer key Im handing out, score the
- Maloney Ward Scale I handed out last
Thursday. - I have extra copies of the scale available.
8
Scales of the Maloney-Ward Inventory
- Verbal Commitment what a person says he is
willing to do (behavioral component) - Actual Commitment what a person has actually
done (behavioral component) - Affect the degree of emotionality connected to
the issue (affective component) - Knowledge specific factual knowledge of
ecological issues (cognitive component)
9
Questions for Reflection
- How did you score on the various parts of the
- inventory? Which areas were highest? lowest?
- Which of the components do you think is most
- important? Why?
- What factors do you think have been important
- in shaping your attitudes toward the
environment?
10
Judeo-Christian influences . . .
And God blessed them and God said to them Be
fruitful and multiply and fill the earth and
subdue it and have domination over the fish of
the sea and the birds of the air and over every
living thing that moves upon the earth.
Genesis 128
11
Three world views on the role of humans in nature
- 1. Resourcism
- Natural environments are stockpiles of raw
materials to be transformed into the wants and
needs of humans.
12
Three world views (continued)
- Preservationism
- Emphasizes a wholistic view of nature.
- Assumes interactions among ecosystems are
complex and changes in one system can have
negative impacts on other systems. - Primary concern is on consequences for
humans.
13
Three world views (contd)
3. Ecocentrism
- natural ecosystems possess value in
- their own right, independent of their
- value to humans.
- Humans have no special standing and
- ethical human actions are those that
- promote all life on earth.
14
Where do you fall?
Resourcism Preservationism
Ecocentrism
__________________________________________
____ 1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8 9
Homocentric
Ecocentric
15
Research on environmental attitudes suggests . . .
- Most Americans say they are concerned
- about the environment, but fewer want to
- change their lifestyle (drive less, etc).
- Women report more concern and say they
- will do more, but they report doing less
- knowing less than men.
16
Research on environmental attitudes suggests . .
.(contd)
- Younger individuals appear to have more
- concern than older individuals.
- People with greater concern are more
- people-oriented, less authoritarian, and
- have higher levels of moral development.
17
What is the Weakest Link?
Linking concern with action (what we say vs what
we do)
blah blah blah
?
18
Linking Attitudes to ActionThe search for
mediating variables
- A mediator is a variable that, in a causal
sequence, fits between the attitude and the
behavior. - Attitude Mediating
Behavior - Variable
100 people say theyre concerned
But only 10 take action!!
. . . . . . . . . . .
19
Meta-analysis of 315 studies found the best
predictors were
- specific knowledge of environmental issues
- knowledge of action strategies
- internal locus of control
- verbal commitment
- environmental concern
- a sense of personal responsibility
20
Another environmental attitudeNIMBY Not In My
Backyard
- People agree that a particular resource (waste
disposal plant, nuclear power plant, group homes
for special populations, expressway, etc) is
needed in their community, but dont want it near
them! - One consequence of this environmental racism
- Residents of poor communities and communities
of color in the United States bear a
disproportionate burden of toxic contamination,
both through the generation and release of
hazardous chemicals in their neighborhoods, and
via the location of waste management facilities
(Michael K. Heiman, 1996)
21
What type of group home would you like next to
your house?
3
Alcoholics Ex-criminal offenders Drug
users Emotionally disturbed Children Mentally
ill adults Mentally retarded adults
6
5
2
4
1
22
Two Ways of Examining the EnvironmentEnvironment
al Appraisal vs Environmental Assessment
- Environmental Appraisal
- Person-Centered
- Measures psychological constructs
- Used for psychological research
- Uses non-specialists
- Environmental Assessment
- Place-Centered
- Measures physical properties
- Used for public policy
- Uses experts
23
Six Types of Environmental Appraisals
- Description What is there?
- Evaluation Is it good?
- Aesthetic Is it beautiful?
- Emotional How does it make you feel?
- Meaning What is its significance?
- Risk Is it safe?
24
- Description Its a waterfall with a mountain
behind it - Evaluation I like it
- Aesthetic I think its beautiful
- Emotional I feel so calm and peaceful when I
look at this - Meaning This place is important to me. My
family always came here each summer. - Risk I always feel safe when Im in a natural
settings like this
25
Four categories of environmental assessment
- Physical spatial properties of setting
- height of ceiling, amount of illumination,
- ambient sound level, etc.
- 2) Number and variety of artifacts
- number of chairs, types of artwork, etc.
26
Four categories of environmental assessment
(contd)
- (3) Typical behavior patterns
- kinds of behaviors occurring in the
- setting
27
Four categories of environmental assessment
(contd)
(4) Social Climate the personality of
the setting
28
How do we describe the Social Climate of a
setting? According to Rudolf Moos, 3 major
dimensions
- 1. Relationship Dimensions measure the nature
and intensity of personal relationships in the
environment.
- Examples from Work Environment Scale (WES)
- Involvement - 1, 11, 21, 31, etc.
- Peer Cohesion - 2, 12, 22, 32, etc.
- Staff Support - 3, 13, 23, 33, etc.
29
3 Dimensions of Social Climate (contd)
- 2. Personal Development Dimensions
- measure opportunities in the environment
- for personal growth development.
Examples from WES Autonomy- 4, 14, 24, 34,
etc. Task Orientation - 5, 15, 25,
35, etc.
30
3 dimensions of Social Climate (contd)
- 3. System Maintenance Change Dimensions
- measure the extent to which the environment is
- orderly and clear in its expectations, maintains
- control, and is responsive to change.
- Examples from WES
- Work Pressure - 6, 16, 26, 36, etc.
- Clarity 7, 17, 27, 37, etc.
- Control - 8, 18, 28, 38, etc.
- Innovation - 9, 19, 29, 39, etc.
- Physical comfort - 10, 20, 30, 40, etc.
31
The next 4 slides describe Activity Sheet 2
32
Environmental Appraisal Activity(Activity Sheet
1)
- ? Assess your emotional response to 5 campus
- settings
- ? Examine the effect of one personality
- variable on your ratings
33
Environmental Appraisal Activity(Activity Sheet
2)
- ? Please complete and self-score the Short
- Sensation-Seeking Scale (SSS)
34
Sensation Seeking
- A complex personality trait with a number of
components. High sensation seekers - Enjoy physical risk-taking activities
- Pursue new sensory and mental experiences
- Enjoy the disinhibited pursuit of pleasure
- Have higher susceptibility to boredom
35
Environmental Appraisal
- ?Circle the words the members of your group chose
on the Affective Pattern sheets. Use a separate
sheet for each setting. - ?Visually distinguish the words chosen by high
sensation-seeking (above gender mean) members
from low sensation-seeking members of your group,
e.g., use dotted vs. solid lines, different color
inks, etc.