the Balance Sheet PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title: the Balance Sheet
1
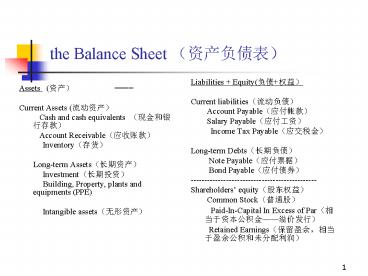
the Balance Sheet (?????)
- Liabilities Equity(????)
- Current liabilities(????)
- Account Payable(????)
- Salary Payable(????)
- Income Tax Payable(????)
- Long-term Debts(????)
- Note Payable(????)
- Bond Payable(????)
- ----------------------------------------------
- Shareholders equity(????)
- Common Stock(???)
- Paid-In-Capital In Excess of
Par(????????????) - Retained Earnings(????,?????????????)
- Assets (??)
- Current Assets (????)
- Cash and cash equivalents (???????)
- Account Receivable(????)
- Inventory(??)
- Long-term Assets(????)
- Investment(????)
- Building, Property, plants and equipments
(PPE) - Intangible assets(????)
2
Shareholders Equity (????)
- Equity Assets Liabilities
- It is financing by shareholders, i.e., owners of
the company - Two classes of shareholders common
shareholders(?????) and preferred
shareholders(?????)
Imagine yourself as an entrepreneur, with your
and your friends money, you are starting a
company. The money you put into the company is
your equity.
3
Liabilities (??)
- Another type of financing(??)
- Arises when 1) receive goods or services without
paying cash 2) borrow money - Represents obligation to pay cash to a third
party when liabilities become due - Usually quantifiable
- Liability financing is a good thing, unless
4
Assets (??)
- a) Assets are resources that may provide the firm
with future economic benefits through the
generation of cash flows (???). - b) To be recorded by accountants, an asset must
have been acquired the right of use, and the
value of the assets future benefit must, to a
reasonable extent, quantifiable(??). - c) If something that the company owns will
provide benefits in the future, but the benefits
are hard to identify and measure, then we do not
recognize this thing as asset.
5
Retained Earnings (????)
- Accumulated net income (?????)(profits/losses),
less dividends, since the inception (??)of the
firm - The third form of financing of the company--
shareholders direct investments, borrowing
money, and making money by the company itself - Every year, when we prepare financial statements,
we transfer net income, be it profit or loss,
into retained earnings, and dividends, if any,
are paid out of retained earnings. - Retained Earnings are a part of equity.
6
Valuation
- To evaluate who much an asset, or liability, or
equity is worth in terms of current money - Value depends on the future cash flows the object
will generate, and on the risk of receiving the
cash flows - Higher future cash flows, higher value higher
risk, lower value - Valuation is a homework of forming expectation
about future cash flows and risk - Distinguish value from price price is what you
pay, value is what you get.
7
Valuation of Assets
- An asset has different valuations depending on
what assumptions you make regarding the use of
the asset - Historical cost(????)
- Replacement cost (entry cost ????)
- Current net realizable value (exit value ?????)
- Net Present value of future cash flows (NPV, ???)
8
Valuation of Liabilities
- Most liabilities are monetary liabilities so
carried on balance sheet at net present value - Some non-monetary liabilities, such as
warranty(????), are carried at estimated costs to
fulfill the obligations
9
Undervalued Assets and Hidden Assets
- Accounting is based on historical cost. The value
of assets may change according to market
conditions, but accounting does not change the
value of assets on balance sheet undervalued - Accounting is conservative. Expenditures that
generate difficult-to-measure future benefits are
not recognized as assets. For example,
advertising cost hidden
10
Undervalued Assets and Hidden Assets cond
- The most difficult part of balance sheet analysis
is to figure out undervalued assets and hidden
assets - If not properly discovered, firm value tends to
be understated.
11
Undervalued Assets
- Inventories bought last year, the inventory price
gone up this year, then book value of inventory
understates the market value of inventory - A building acquired by GE 100 years ago in
downtown New York - A piece of land on which oil was discovered
- With some maintenance work, an equipment with
original useful life of 10 years can be used for
20 years
12
Hidden Assets
- Something that benefits a companys future cash
flows, but that is not recognized on balance
sheet - Managerial talents Jack Welch not on GEs
balance sheet Bill Gates not on Microsofts
balance sheet - Employee talents number of employees with MBAs
not shown up on balance sheet - Drug patents Mercks balance sheet does not
show its patent protection periods - Contracts Boeings balance sheet does not know
number of aircrafts being ordered - Connections Enrons balance sheet does not show
how much contribution it made to George Bush and
Dick Cheneys presidential election. - Reputation (brand name) Arthur Andersons
balance sheet did not show the reputation the
firm earned for 70 years honest work.
13
Hidden Liabilities
- Some obligation that a company has to fulfill in
the future but currently not recognized on
balance sheet - Environmental costs
- Pending legal obligations(????)
- Outstanding employee stock options
- Money losing derivative trades
- Enrons SPE
14
An example of hidden liability
Wyeth (????)produces diet drug. A woman died
after taking Wyeths drug. April 27, 2004, a
Texas court awarded her family 1 billion U.S.
dollars, 100 million for actual damage, the rest
for punitive purpose. Wyeths stock price dropped
4, market capitalization dropped 1.33 billion2
2.66 billion U.S. dollars, about 5 of its
market cap.
15
????
??
??????
16
?????
????
??????
17
Hidden liabilities, the Case of Enron
124.8
124.8
4.02
115.2
124.8
115.2
115.2 4th quarter of 2000, 53 1st quarter of
2001, 57.9 3rd quarter of 2001, reverse
5357.9 110.9 as losses
124.8
18
Understanding footnotes
- Summary of significant accounting policies
- Provide detailed analysis of aggregate numbers on
the three statements - Disclose information that is not recorded in
statements, but required to be disclosed.
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
Common size analysis of Balance Sheet
- Express every item on balance sheet as a
percentage of total assets (total liabilities and
equity) - Cross-time comparison of common-size balance
sheet reveals changes in the structure of
investing and financing (????????????) - Cross-section comparison of common-size balance
sheet reveals the efficiency of investing and
financing relative to comparable firms (?????)
24
Common size analysis of Balance Sheet
- Microsoft corporation 1999 balance sheet
Common-size analysis
25
Market-to-Book Ratio (P/B ratio)(?????/?????????
??,???)
- On Dec. 31, 2001, GE common shares were traded at
40.08 (from finance.yahoo.com) - Total Market Capitalization
- 40.089,925,938,000 397,931,595,040
- GEs Market-to-Book (P/B ratio)
- 397,931,595,040/54,824,000,000 7.26
26
Why GE stock was sold 6.26 times more than its
value on balance sheet on Dec. 31, 2001?
- Assets on balance sheet are undervalued, e.g., GE
building at downtown New York city. - Hidden assets not shown on balance sheet
- Balance sheet, i.e., accounting, is backward
looking, emphasizes historical cost stock price
is forward looking, reflects investors
expectations on future cash flows that GE will
generate - Market mispricing
27
P/B Anomaly (??)
- Stock return (Stock price t Stock price
t-1)/Stock price t should be explained by the
risk for holding this stock (CAPM beta). High
risk stock earns high return. - But researchers found stocks with high
price-to-book ratio earn low returns, while
stocks with low price-to-book ratio earn high
returns, controlling for stock beta. (e.g., Fama
and French Journal of Finance, 1992) - Potential risk factor or market mispricing?
- High Price-to-Book, P/B, stocks are called growth
(glamour) stocks, and low P/B stocks are called
value stocks.
28
High P/B
Low P/B
29
Investing motto
- "Today the only people who don't think markets
work are the North Koreans, the Cubans and the
stock pickers. - ---Rex Sinquefield of Dimentional Fund Advisor,
Fortune July 6, 1998, pp152 - Remember, we are the stock pickers!!!