Efficiency gains - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Efficiency gains
Description:
Broadcast Radio. Cellular Radio. Microwaves. Communications Satellite. Infrared. 16. 17 ... Allows citizens to connect with servers. Access any number of web pages ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Efficiency gains
1
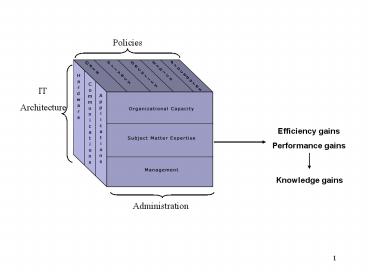
Policies
IT Architecture
Efficiency gains Performance gains
Knowledge gains
Administration
2
S Y N E R G Y
3
Input Process Output Storage
4
Computer Literacy hardware components communicatio
ns /networks programming languages software
applications Information Literacy how to find
information how to analyze information how to use
information
5
A Computer is. . .
- 1. An electronic device,
- 2. operating under the control of instructions
stored in its own memory unit, - 3. that can accept data (input),
- 4. process data arithmetically and logically,
- 5. produce results (output) from the processing,
and - 6. store results for future use.
6
Input is. . . ?
- Entering data, programs, commands, and user
responses into memory - Data - raw facts
- Programs - stored instructions that direct the
computer - Commands - keywords and phrases that direct the
computer - User responses - responses to questions or
messages from the software
7
Process is. . . ?
the computer manipulates data (numbers, words,
images, sounds) . . .and organizes the data to
create information that has meaning and is
useful. system behavior is determined by
arithmetic and logical rules
8
Output is. . . ?
Audio output Graphics Reports Video Output
Hard copy Soft copy Other types
9
Storage is. . .?
Area for storing instructions and data when they
are not in use. . . Often function as an input
source
10
Categories of Computers personal
computers servers minicomputers mainframe
computers supercomputers
11
Physical Transmission Media Wireless Transmission
Media Networks
12
How Communications are Used
- Electronic mail (e-mail)
- Voice mail
- Facsimile (fax)
- Telecommuting
- Videoconferencing
- Electronic data interchange
- Global Positioning Systems
- Online Services
- Groupware
- Bulletin Board Systems
General Concepts - Communications
13
Physical Transmission Media Twisted-pair
Cable Coaxial Cable Fiber-Optic Cable
14
Physical Transmission Media
15
Wireless Transmission Media Broadcast
Radio Cellular Radio Microwaves Communications
Satellite Infrared
16
(No Transcript)
17
temporary connection
3 to 24 signals
asymmetric
Up to 24 signals
Up to 672 signals
dedicated (leased) connection
18
Networks Local Area Networks Wide Area
Networks Intranets Internet
19
Client Server
file server database server web server print
server e-mail server firewall server
20
Internet
21
application software programs are designed to
perform a specific task
Productivity/business Graphic design/multimedia Ho
me/personal/education Communications
22
(No Transcript)
23
Enterprise Systems Workflow Systems Document
Management Systems Data Warehouse
Systems Geographic Information Systems Electronic
Government
24
Enterprise Systems
25
Workflow Systems
26
Document Management Systems
- Version tracking see how a document evolves over
time - Document sharing see in what business processes
the document is used and re-used - Electronic review enable users to add their
comments to a document without actually changing
the document itself - Document security refine the different types of
access that different users need to the document - Publishing management control the delivery of
documents to different publishing process queues - Workflow integration associate the different
stages of a document's life-cycle with people and
projects with schedules
27
Data Warehouse Systems
Extremely large database that stores and manages
the data required to analyze historical and
current business information
28
Geographic Information Systems
Portray data in a graphical / spatial context
29
E-Government Defined
- Governments use of technology, particularly
web-based Internet applications, to enhance
access to and delivery of, government services to
citizens, business partners, employees, and other
governmental agencies. - G2G, G2B, G2C, G2E
30
Software Applications
- Web browser software
- Web server software
- Firewall
- Transaction server software
- Electronic payment systems
- Commerce server software
31
Web Browser Software
- Allows citizens to connect with servers
- Access any number of web pages
- Follow links from document to document or page to
page
32
Web Server Software
- Allows citizens to request information
- Serves up the web pages as requested
33
Firewall Server Software
- Controls the flow of traffic between two or more
networks - Can protect against viruses, intrusions,
unauthorized system access
34
Transaction Server Software
- On-line transaction processing (OLTP) software
- Processes data according to the rules established
by an organization - Programs that tell the database server how to
handle the data
35
Electronic Payment Systems
- Collect fees and levy taxes for services
- Must be safe, secure, and confidential
36
Commerce Server Software
- Allows citizens to easily conduct one or more
transactions in one visit - Features include
- Shopping carts
- Shipping charges
- Taxes
- Payments receipts
37
Metrics. . .
Scalability - the system should be
capable of handling an increasing numbers of
users without any disruption to service.
Flexibility the system must provide a broadly
configurable array of hardware and software
devices that do not require major
re-installations as enterprise requirements
change. Compatibility - the system must
meet expandable configuration requirements as
well as standard industry specifications to
protect future application investment.
Manageability the system should not demand
excessive management time and effort for
maintaining on-line operations.
Availability - the system must be capable of
sustaining tens to hundreds of thousands of
processing transactions with minimal wait time or
downtime.
38
Computers - Male or Female? A language
instructor was explaining to her class that
French nouns, unlike their English counterparts,
are grammatically designated as masculine or
feminine. Things like 'chalk' or 'pencil,' she
described, would have a gender association
although in English these words were neutral.
Puzzled, one student raised his hand and asked,
"What gender is a computer?" The teacher wasn't
certain which it was, and so divided the class
into two groups and asked them to decide if a
computer should be masculine or feminine. One
group was comprised of the women in the class,
and the other, of men. Both groups were asked to
give four reasons for their recommendation.