What is Sampling - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
What is Sampling
Description:
Sampling frame: a list of the population elements from which we select units to be sampled. ... requires a sampling frame, which is not always available ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: What is Sampling
1
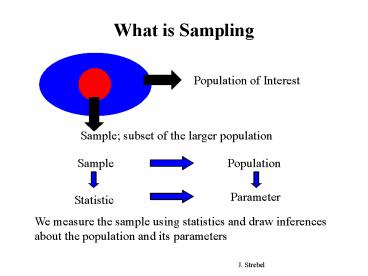
What is Sampling
Population
Sample
Parameter
Statistic
We measure the sample using statistics and draw
inferences about the population and its parameters
2
Definition of Sampling
Population
Sample
Population the total group of people from whom
information is needed Census data
obtained from every member of the
population Sample a subset of the population of
interest Sampling frame a list of the
population elements from which we select
units to be sampled.
3
Steps in developing a sampling plan
- Define the population of interest
- Choose the data collection method
- Choose the sampling frame
- Select a sampling method (discussed below)
- Determine sample size (next lecture)
- Develop and specify operational plan for
selecting sample elements
4
Probability and Nonprobability Sampling
Probability sampling
Non-probability sampling
- Subjective procedure
- Probability of selection of an element is unknown
- Cannot calculate sampling error
- Sample not always representative
- Objective procedure
- Probability of selection of an element is known
and non-zero - Can calculate sampling error
- Strict procedures to follow
- Yields a representative sample
5
Classification of Sampling Methods
Convenience
Systematic
Snowball
Stratified
Judgement
Quota
Cluster
Simple Random
6
Nonprobability Sampling Convenience
Sampling frame none used Sampling size selected
based on research goals, not on statistical
methods Operational plan find willing
participants based on researchers
convenience. Representativeness can be
representative if chosen carefully. Can
also be completely unrepresentative.
7
Nonprobability Sampling Judgment
Sampling frame none used Sampling size selected
based on research goals, not on statistical
methods Operational plan find willing
participants based on researchers
judgmental selection criteria. Representativeness
can be representative if the researcher
chooses carefully.
8
Nonprobability Sampling Quota
Sampling frame none used Sampling size selected
based on research goals, not on statistical
methods Operational plan find participants to
represent various characteristics important to
the research study, e.g.50 males and 50 females
who are marketing majors. Selection of men and
women is done using convenience or
judgment. Representativeness can be
representative if the researcher
chooses carefully.
9
Nonprobability Sampling Snowball
Sampling frame none used Sampling size selected
based on research goals, not on statistical
methods Operational plan find one
person(s) who fits the characteristics of
interest and ask that person (s) to generate
names of others with the same characteristics who
are then interviewed. Low incidence or rare
populations
Representativeness unlikely to be
representative
10
Nonprobability Sampling Summary
Advantages
Samples can be drawn quickly and easily No
sampling frame is necessary With care, can be
representative, or at the very least, can exclude
irrelevant units Excellent for exploratory
research
Disadvantages
Samples can include irrelevant units Cant
generalize to population of interest Cant
evaluate sampling error
11
What is Probability?
In statistics, probability is a number that
expresses the likelihood that a specific event
will occur, expressed as a ratio of the number
of actual occurrences to the number of possible
occurrences.
- Since its a ratio, it has to be between 0
and 1 - The sum of all probabilities must be 1
12
Probability and Nonprobability Samples
- Probability Samples must be selected in such a
way that every element of the population has a
known, nonzero probability of selection - Nonprobability samples include the selection of
specific elements from the population in a
nonrandom manner.
13
Probability Sampling Techniques
Simple Random Sampling
Enumerate the sampling frame
Assign numbers to each element
Select elements using random number tables
14
Probability Sampling Techniques
Systematic Sampling
Enumerate the sampling frame
Create a sampling interval k population size
/sample size
Choose every kth element in the sampling frame
15
Probability Sampling Techniques
Stratified Sampling
Undecided
IBM/Compatible enthusiasts
Relevant subsets in the population
Population is divided into two or more mutually
exclusive subsets
Technique Simple Random Sampling
16
Probability Sampling Techniques
Cluster Sampling
- Each cluster represents many elements, such as X
number of city blocks. - We select clusters using Simple Random Sampling.
- We next select elements within the clusters using
one of these probability techniques.
17
Probability Sampling - Summary
Advantages
- Generally will produce more representative
samples - Avoid conscious bias
- Disadvantages
- requires a sampling frame, which is not always
available - often takes longer and costs more to select