Magnetic Domains - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Magnetic Domains
Description:
Fe synthesized using air free solution chemistry methods ... Dr. Jess P. Wilcoxon, Sandia National Laboratories. Oxide Shell Thickness ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:78
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Magnetic Domains
1
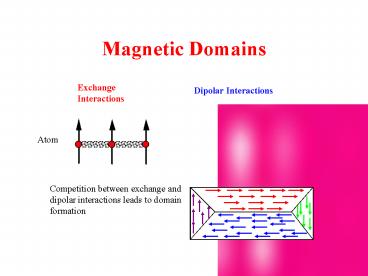
Magnetic Domains
Exchange Interactions
Dipolar Interactions
Atom
Competition between exchange and dipolar
interactions leads to domain formation
2
Magnetic Nanoparticle Arrays
Vary Size
Vary Spacing
Vary Ordering
3
Nanoparticle Synthesis
- Fe synthesized using air free solution chemistry
methods - Thermal decomposition of Fe(CO)5 in octyl ether
- Particles coated with surfactant
- Washed with ethanol and dispersed in hexane
D. F. Farrell, S. A. Majetich, and J. P.
Wilcoxon, J. Phys. Chem. 107, 11022-11030 (2003).
4
Heterogeneously Nucleated Fe
7.0 0.8 nm 9.2 0.7 nm
Seeded with Pt (FePt 10001)
5
Homogeneously Nucleated Fe
9.1 0.9 nm 11.2 1.0 nm
19 nm
No Pt salt, larger amount of oleic acid surfactant
6
Electron Diffraction
Heterogeneous Homogeneous
Fe oxide rings dominate
7
Blocking Temperatures
Field-cooled, Zero field-cooled Magnetization
7.0 0.8 nm
11.2 1.0 nm
H 200 Oe
0.01vol.
Heterogeneously Nucleated Homogeneously
Nucleated 2 Blocking Ts Fe, Fe oxide
8
Particle Concentration
Found from calibrated x-ray fluorescence of
solutions Use to determine total mass of Fe ??ss
Nucleation Method Fe conc. Particle Diameter Particles per mL
Heterogen. 0.051 M 5.8 0.5 nm 3.6 ???????
Heterogen. 0.0957 M 7.2 0.5 nm 3.5 ???????
Heterogen. 0.614 M 8.6 1.6 nm 1.3 ???????
Heterogen. 0.81 M 8.4 1.0 nm 1.9 ???????
Homogen. 0.0284 M 11.2 1.0 nm -----
Dr. Jess P. Wilcoxon, Sandia National
Laboratories
9
Oxide Shell Thickness
- Relate ss of particles to weighted average of ss
of Fe core and Ms of oxide shell - ss,partmpart ss,coremcore ss,shellmshell
Diameter ?s Fe core Oxide shell
7.0 0.7 nm heterogeneous 175 emu/g 5.8 nm 0.6 nm
9.2 0.7 nm heterogeneous 175 emu/g 8.4 nm 0.4 nm
11.2 1.0 nm homogeneous 110 emu/g 7.0 nm 2.1 nm
10
Return to Home Page