SYNAPSES - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title: SYNAPSES
1
SYNAPSES
- A. INTRODUCTION
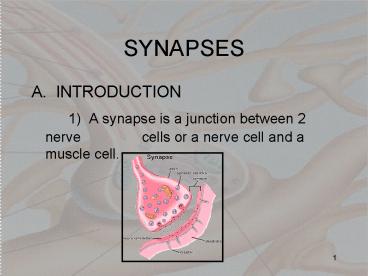
- 1) A synapse is a junction between 2 nerve
cells or a nerve cell and a muscle cell.
2
- B) ANATOMY OF A SYNAPSE
- 1) Synaptic knob with transmitter vesicles
and presynaptic membrane. - 2) Synaptic cleft.
- 3) Postsynaptic membrane with receptors for
transmitters.
3
- C) FUNCTION OF THE SYNAPSE
- 1) Electrical impulse in knob causes influx of
Ca, vesicles rupture, release transmitters. - 2) Transmitters diffuse across,cleft attach to
receptors.
4
- 3) Receptors open gates for ions.
- a) Can be direct
- b) May be indirect via G-proteins (which
diffuse from receptor to ion channel.) - 4) Transmitters can be broken down, taken
up by presynaptic membrane or diffuse
away.
5
- D) TRANSMITTERS
- 1) Acetylcholine was first discovered,
there are many others. - 2) Monoamines
- a) The catacholamines dopamine,
norepinephrine, epinephrine? - b) Serotonin
6
- 3) Amino acids
- a) glutamate
- b) GABA and glycine - inhibitory
- 4) Amines such as acetylcholine and
histamine. - 5) Polypeptides such as enkephalins and
endorphins. - 6) Gases such as nitric oxide and CO.
7
- E) ONE-WAY CONDUCTION
- 1) Synapses make nervous system a one- way
system - dendrites do not have neurotransmitter
vesicles. - 2) Synaptic delay
8
- F) TYPES OF SYNAPSES
- 1) Synapses can be excitatory or inhibitory.
a) If an excitatory transmitter is released,
then an excitatory postsynaptic potential
(EPSP)will be created. - b) If an inhibitory transmitter is released,
then an inhibitory postsynaptic potential
(IPSP)will be created.
9
- G) SYNAPTIC INTEGRATION
- 1) Most synapses involve many neurons.
- 2) Whether or not postsynaptic membrane has
an action potential is dependent upon algebraic
sum of EPSPs and IPSPs.
10
- 3) Spatial summation occurs when numerous
synaptic knobs release their transmitters. - 4) Temporal summation can occur if neuron
releases transmitter rapidly.
11
- H) CHEMICALS WHICH AFFECT THE SYNAPSE
- 1) Many chemicals that affect nervous system
do so by affecting synapse. - a) Clostridium botulinum toxin.
- b) Clostridium tetanii toxin.
- c) Caffeine
- d) Anesthetics
- e) Strychnine
- f) Psychotropic drugs
12
END
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)